In the secondary analysis published last year in the journal Advances in Clinical and Experimental Medicine , researchers compared the effects of St. John’s wort versus SSRIs or placebo in adults with depressive disorders. Controlled studies from large scientific databases, in which the Hamilton Depression Scale (HAM-D) was used in each case, were used as the data basis.
Depression is the most common mental disorder, with a prevalence of around 3.8% worldwide. The main symptom is anhedonia, but many other symptoms can also occur, such as mood swings and anxiety. In addition to psychotherapeutic methods, the use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) is one of the most widespread treatment methods. St. John’s wort preparations (Hypericum perforatum) are considered a low-side-effect alternative to SSRIs.
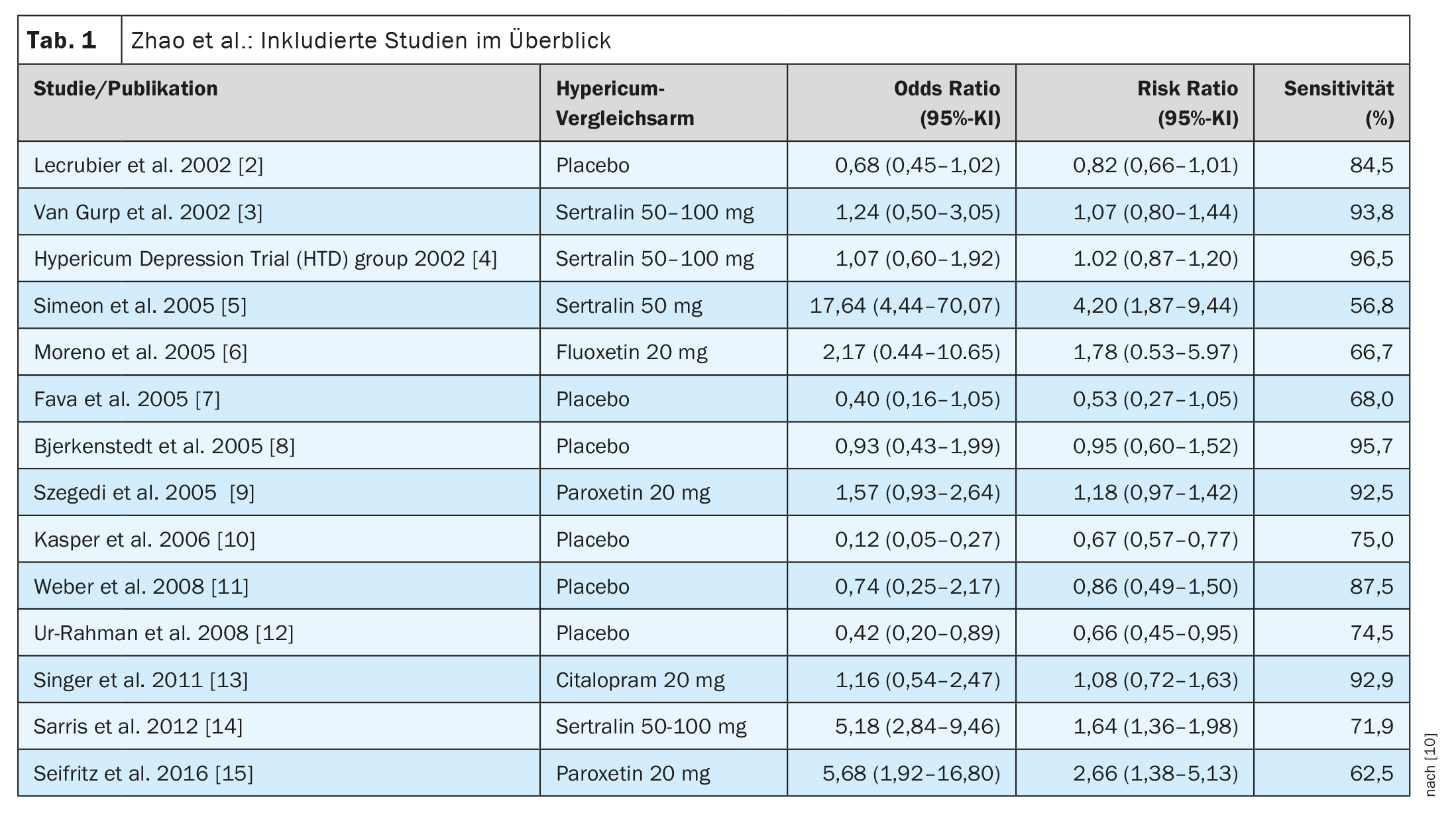
In order to objectively evaluate the efficacy of Hypericum preparations compared to SSRIs and placebo, Zhao et al. conducted a meta-analysis [1]. The researchers used the following databases to search for relevant articles: Medline via PubMed; Cinahl via EBSCO; Scopus; Web of Sciences databases. A total of 14 studies with 2270 depressed patients were identified that met the predefined inclusion criteria** [1–15] (Table 1). The duration of the included studies was 6 weeks (7 studies), 8 weeks (4 studies), 12 weeks (2 studies) and 26 weeks (1 study). In 8 studies the reference substance was an SSRI (sertraline 4 studies, paroxetine 2 studies, fluoxetine 1 study, citalopram 1 study) and in 6 studies St. John’s wort extract was compared with placebo.
** The predefined inclusion criteria concerned study population, intervention, comparator arms, endpoints and PICOS.
According to the meta-analysis, the overall effectiveness of the treatment was in favor of St. John’s wort. The HAM-D score improved more with SSRIs than with SSRIs (pooled odds ratio of 2.44; 95% confidence interval [KI] 1.33-4.45).
Literature:
- Zhao X, et al: The efficacy and safety of St. John’s wort extract in depression therapy compared to SSRIs in adults: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Adv Clin Exp Med 2023; 32(2): 151-161.
- Lecrubier Y, et al: Efficacy of St. John’s wort extract WS 5570 in major depression: A double-blind, placebo-con¬trolled trial. Am J Psychiatry 2002; 159(8): 1361-1366.
- Van Gurp G, et al: St John’s wort or sertraline? Randomized controlled trial in primary care. Can Fam Physician 2002; 48: 905-912.
- Hypericum Depression Trial Study Group. Effect of Hypericum perforatum (St John’s wort) in major depressive disorder: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2002; 287(14): 1807.
- Simeon J, et al: Open-label pilot study of St. John’s wort in adolescent depression. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 2005; 15(2): 293-301.
- Moreno RA, et al: Hypericum perforatum versus fluoxetine in the treatment of mild to moderate depression: A randomized double-blind trial in a Brazilian sample. Rev Bras Psiquiatr 2006; 28(1): 29-32.
- Fava M, et al: A double-blind, randomized trial of St John’s wort, fluoxetine, and placebo in major depressive disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol 2005; 25(5): 441-447.
- Bjerkenstedt L, et al: Hypericum extract LI 160 and fluoxetine in mild to moderate depression: A randomized, placebo- controlled multicenter study in outpatients. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2005; 255(1): 40-47.
- Szegedi A, et al: Acute treatment of moderate to severe depression with hypericum extract WS 5570 (St John’s wort): Randomized controlled double blind non-inferiority trial versus paroxetine. BMJ 2005; 330(7490): 503.
- Kasper S, et al: Superior efficacy of St John’s wort extract WS®5570 compared to placebo in patients with major depression: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center trial [ISRCTN77277298]. BMC Med 2006; 4(1): 14.
- 11. Weber W, et al: Hypericum perforatum (St John’s wort) for attentiondeficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2008; 299(22): 2633.
- Ur-Rahman R, et al: Double blind placebo controlled clinical trial examining the effectiveness of St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum) in mild to moderate depression. J Pakistan Psychiatric Soc 2008; 5(2): 106-111.
- Singer A, et al: Duration of response after treatment of mild to moderate depression with Hypericum extract STW 3-VI, citalopram and placebo: A reanalysis of data from a controlled clinical trial. Phytomedicine 2011; 18(8-9): 739-742.
- Sarris J, et al. St John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum) versus sertraline and placebo in major depressive disorder: Continuation data from a 26-week RCT. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2012; 45(07): 275-278.
- Seifritz E, Hatzinger M, Holsboer-Trachsler E: Efficacy of Hypericum extract WS®5570 compared with paroxetine in patients with a moderate major depressive episode: A subgroup analysis. Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract 2016; 20(3): 126-132.
FAMILY PHYSICIAN PRACTICE 2024; 19(4): 50