Heart failure is a complex clinical syndrome that is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality annually in Western industrialized countries. Nutraceuticals have already achieved good clinical results, especially in prevention, but also in the treatment of the early stages. Extracts from hawthorn are traditionally used in cardiovascular medicine. Now, cardiopoietic differentiation of stem cells has been detected.
More than 23 million people worldwide suffer from heart failure (HF). It is one of the main factors for hospitalization and disability in the elderly and significantly affects the quality of life. As mortality rates exceed 10% annually and can even rise to 50% in advanced stages, the need for effective therapies is high.
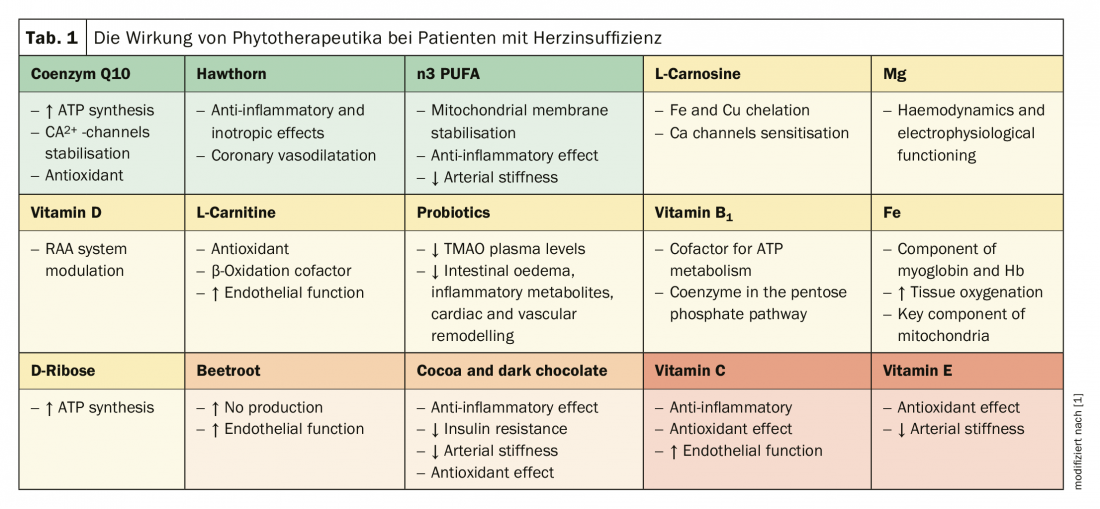
Natural agents have long been used in cardiovascular medicine with good results. A position paper from the International Lipid Expert Panel (ILEP) has now broken down the evidence regarding efficacy and safety. These include coenzyme Q10, magnesium, probiotics, vitamins, and also hawthorn (Table 1) [1]. According to the experts, coenzyme Q10 supplementation may be particularly beneficial in early stages, promoting a reduction in major adverse cardiac events and all-cause mortality. The role of magnesium deficiency in heart failure has not yet been adequately demonstrated. Therefore, the prognostic significance of serum concentration as well as the clinical relevance of supplementation needs further investigation. However, available data suggest that hypomagnesemia should be avoided. With regard to probiotics, the experts conclude that some strains (especially lactobacilli and bifidobacteria) can be used as adjuvants to conventional therapy. However, long-term data are still lacking to conclusively assess the effects on cardiovascular events. Among vitamins, vitamin D in particular seems to have a positive effect on heart health. Therefore, in vitamin D-deficient patients, the deficiency should be compensated. Routine administration is not currently recommended due to lack of clinical studies.
Crataegus extracts support HF patients
The experts in the position paper conclude that according to clinical evidence, Crataegus (hawthorn) extracts have been shown to have benefits in terms of functional capacity, symptom control, and health-related quality of life in both HFrEF and HF with preserved EF (HFpEF). This analysis is supported by results of an in vitro and in vivo study in humans and animals [2]. The aim was to elucidate the main mechanisms relevant to a regenerative potential of hawthorn extract WS® 1442 in patients with heart failure after myocardial infarction. WS® 1442 was shown to stimulate cardiomyogenesis from embryonic stem cells. This effect is induced by promoting the differentiation of cardiovascular progenitor cell populations. Proliferation, on the other hand, is not encouraged. In summary, the underlying mechanisms for a pro-differentiation profile of WS® 1442 on cardiovascular progenitor cells involve rather nonspecific stress-associated effects as well as disruption of different signaling pathways. It will be important to investigate the extent to which WS® 1442 and its bioactive fractions contribute to cardiogenic and/or angiogenic potential in vivo under physiological conditions as well as after ischemic injury, implying an unprecedented pharmacology of this traditional medicinal plant.
Literature:
- Cicero AFG, Colletti A, von Haehling S, et al: Nutraceutical support in heart failure: a position paper of the International Lipid Expert Panel (ILEP). Nutrition Research Reviews 2020. doi: 10.1017/S0954422420000049.
- Halver J, Wenzel K, Sendker J, et al: Crataegus Extract WS®1442Stimulates Cardiomyogenesis and Angiogenesis From Stem Cells: A Possible New Pharmacology for Hawthorn?
HAUSARZT PRAXIS 2020; 15(9): 52
CARDIOVASC 2020; 19(3): 34