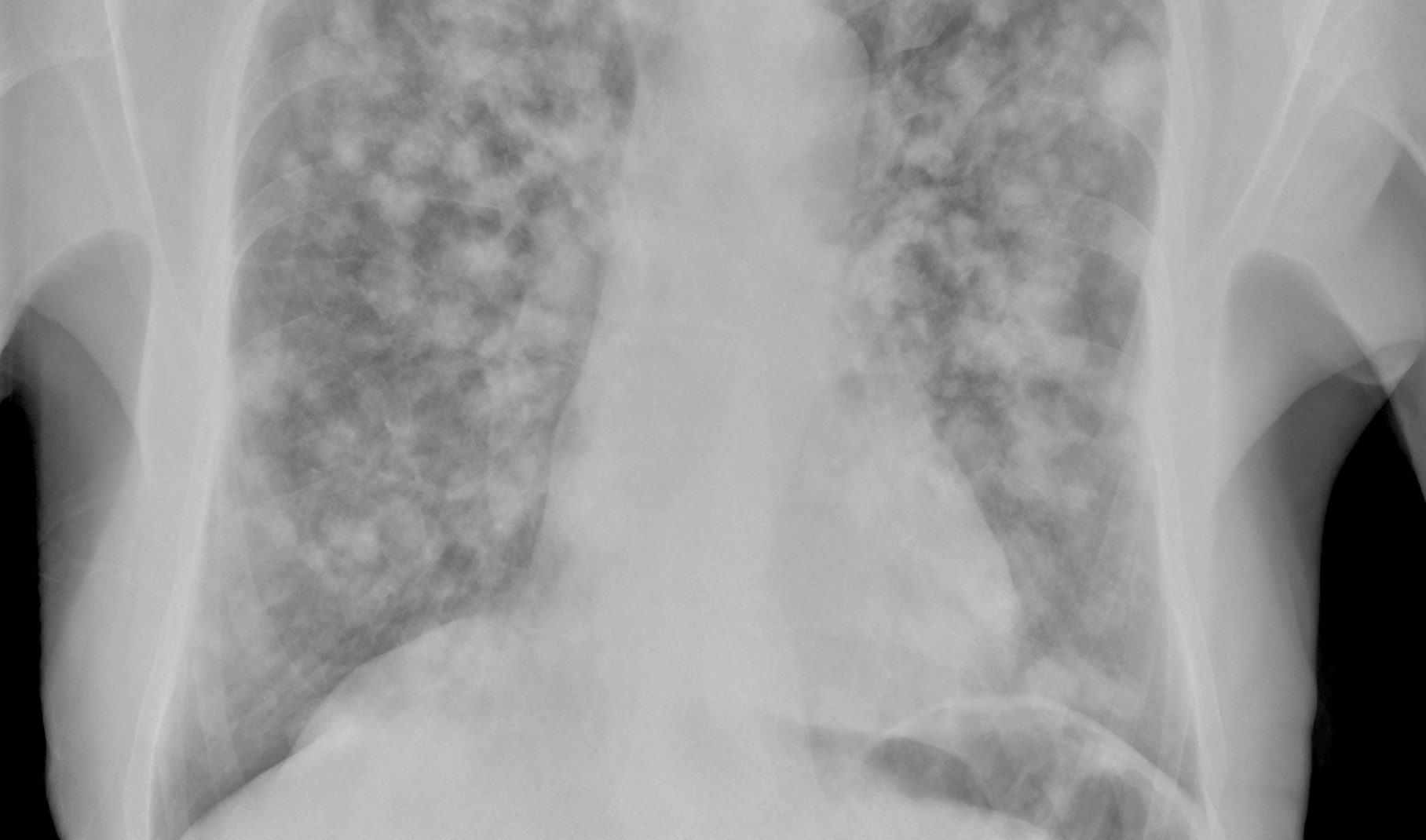
Tumor cells from lung metastases have the typical characteristics of the original type of cancer. Affected patients often have no symptoms at first. As the disease progresses, however, they may experience shortness of breath, a (bloody) cough and chest pain. Lung metastases can be detected using imaging examinations such as X-ray, CT, PET-CT and MRI. Which procedure is most suitable depends on various factors.
Autoren
- Dr. med. Hans-Joachim Thiel
Publikation
- InFo PNEUMOLOGIE & ALLERGOLOGIE
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- Pediatric epilepsy
Diazepam nasal spray for infants
- Findings from research on the generalization of exposure therapy
Treatment of comorbid anxiety
- Symptom-free despite asthma?
Asthma treatment requirements have increased
- Phytotherapy for rhinosinusitis
Evidence, active substances and clinical classification for medical practice
- Contact eczema
Causes and prevention at work
- Pulmonary hypertension
PH and lung diseases
- Respiratory infections: viral bronchitis or bacterial pneumonia?
Old crucial question in the light of current findings
- What biomarkers reveal about "biological youth" - and what not (yet)