Patients with mild cognitive function impairment – mostly affecting those over 60 years of age – may benefit from symptomatic therapy based on a standardized extract of ginkgo. This is also shown by a recent study in which the efficacy and safety of a corresponding phytotherapeutic agent was investigated over a period of two years. In addition to memory-enhancing effects, relief of accompanying depressive symptoms has also been demonstrated.
By definition, dementia is a clinical syndrome resulting from a usually chronic or progressive disease of the brain characterized by various neuropsychiatric symptoms [1]. In addition to cognitive functional impairments, these include changes in emotional well-being and social behavior. Mild cognitive impairment (“MCI”) is defined as a transitional state between normal aging processes and the early phase of dementia [2]. The risk for manifestation of AD is higher in MCI patients compared to the normal population of the same age, with an annual progression rate of 10-15% [3]. The amnestic subtype of MCI (“amnestic mild cognitive impairment”, aMCI) is considered the most common prodromal syndrome of AD-type dementia [4].
Professional societies recommend EGb 761® for symptom relief
The high-quality special extract EGb 761® is obtained from leaves of Ginkgo biloba in a patented manufacturing process. Based on empirical data, the use of EGb 761® in mild to moderate dementia is advocated in the corresponding S3 guideline [2]. And also with regard to MCI, there is ample evidence of efficacy for EGb 761® in placebo comparisons. In the treatment guidelines of the World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry, EGb 761® is included among the antidementia drugs [5]. A high level of empirical evidence demonstrates improvements in cognitive and behavioral symptoms and activities of daily living (ADL) in both Alzheimer’s disease and patients with vascular dementia. The safety data attest to good tolerability of EGb 761® even when taken over a longer period of time. Several randomized trials and two meta-analyses refute the concerns expressed here and there about a possible increased risk of bleeding, as can be read in a recent expert consensus report [6].
|
Abbreviations MMST: Mini Mental Status Test FAQ: Functional Activities Questionnaire CGI: Clinical Global Impression HAM-D: Hamilton Depression Scale |
Improvement of memory functions and reduction of depressive symptoms
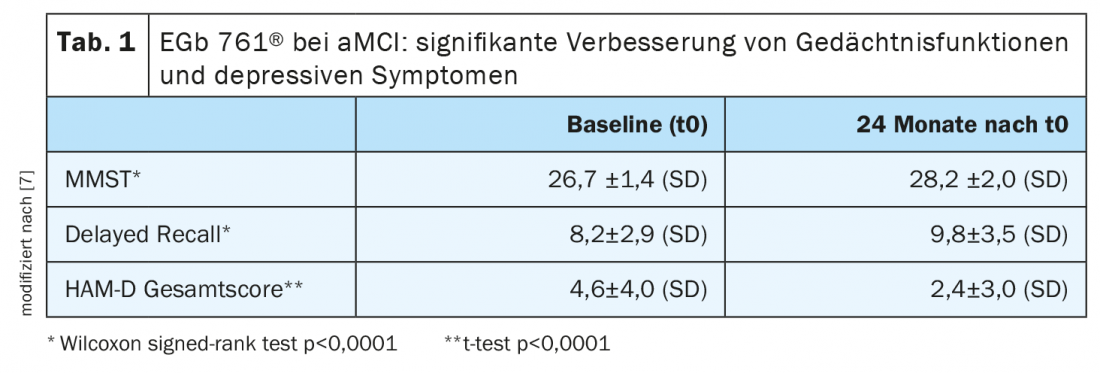
A longitudinal study published in 2021 evaluated the efficacy of EGb 761® in patients with an amnestic subtype of MCI (“amnestic mild cognitive impairment”, aMCI) over a 24-month period [7]. A total of 500 patients (mean age 66 years) with aMCI were included in the non-interventional multicenter study and assigned to treatment with the standardized Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761® . The dosage was 120 mg/d.
Various validated procedures for testing cognition, memory, activities of daily living, and depression were used for follow-up measurement (MMST, FAQ, CGI, HAM-D). Survey time points after baseline took place at 6-month intervals. The primary end point was the mean change in MMST at the follow-up measurement point 2 years after baseline. Data analyses show: EGb 761® resulted in significant improvements in memory performance and depressive symptoms after this treatment period. The corresponding changes in mean values (±SD) in the MMST, “Delayed Recall” and HAM-D test procedures in the measurement 24 months after baseline are shown in Table 1. MMST scores improved significantly from a baseline value of 26.7 ± 1.4 to 28.2 ± 2.0 (p<0.0001, Wilcoxon sign rank test). The delayed recall test showed a significant increase from 8.2±2.9 to 9.77±3.5 (p<0.0001, Wilcoxon sign rank test). An improvement from 4.6±4.0 at baseline to 2.4±3.0 was registered in the total HAM-D score, with the mean change of -2.0 points also proving statistically significant (p<0.0001, paired samples t-test). Finally, briefly on the FAQ total score: this was 2.3±2.3 at baseline and 1.7±2.7 at follow-up after 24 months (p<0.0001, Wilcoxon sign rank test).
Also effective at a daily dosage of 120 mg/d
In summary, treatment with the ginkgo specialty extract EGb 761® proved useful in both improving memory functions and reducing depressive symptoms in this study population of aMCI patients with an average age of 66 years. It should be emphasized that these beneficial effects were obtained at a dosage of 120 mg/d (the recommended dosage is 240 mg/d). The fact that no drug-associated adverse effects occurred underscores the good tolerability of this herbal drug even when used over a longer treatment period.
Literature:
- World Health Organization ICD-10. website cited, available: www.who.int/classifications (last accessed 07/22/2021).
- DGPPN/DGN: S3-Leitlinie “Demenzen”, 2016, long version. www.dgppn.de
- Ahmed OA, et al: Efficacy of sofosbuvir plus ribavirin with or without peginterferon-alfa in treatment of a cohort of Egyptian patients with hepatitis C virus infection. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2017; 17(2): 95-100.
- Tondo G, et al:Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Biomarker-based stability in limbic-predominant amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Eur J Neurol 2021; 28(4): 1123-1133.
- Ihl R, et al: World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of dementias in primary care. Int J Psychiatry Clin Pract 2015; 19: 2-7.
- Kandiah N, et al.: Treatment of dementia and mild cognitive impairment with or without cerebrovascular disease: Expert consensus on the use of Ginkgo biloba extract, EGb 761®. CNS Neurosci Ther 2019; 25(2): 288-298.
- Băjenaru O, et al.: Effectiveness and Safety Profile of Ginkgo Biloba Standardized Extract (EGb 761®) in Patients with Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2021, Feb 8, (online ahead of print), doi: 10.2174/1871527320666210208125524.
GP PRACTICE 2021; 16(8): 44
InFo NEUROLOGY & PSYCHIATRY 2021; 19(4): 32.