Interleukin-23 and interleukin-17A play an important role in the inflammatory process of plaque psoriasis. A comparison of two agents directed against these targets in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis led to interesting results.
Back to “Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis news”.
As the pharmaceutical company AbbVie Inc. in a press release, the IL23 inhibitor risankizumab (Skyrizi™) [1] proved superior to the IL17A inhibitor secukinumab (Cosentyx®) [2] in this double-blind, randomized, active-controlled, open-label phase III multicenter study with regard to various primary and secondary endpoints after a treatment period of 52 weeks [3]. Subjects were randomized 1:1 to the Skyrizi™ 150 mg* (n=164) or Cosentyx® 300 mg** (n=163) condition as subcutaneous injections. The two primary endpoints were defined as non-inferiority at week 16 and superiority at week 52 with respect to PASI90. Secondary endpoints were the values of the following parameters at week 52: PASI 100, sPGA 0/1, and PASI 75.
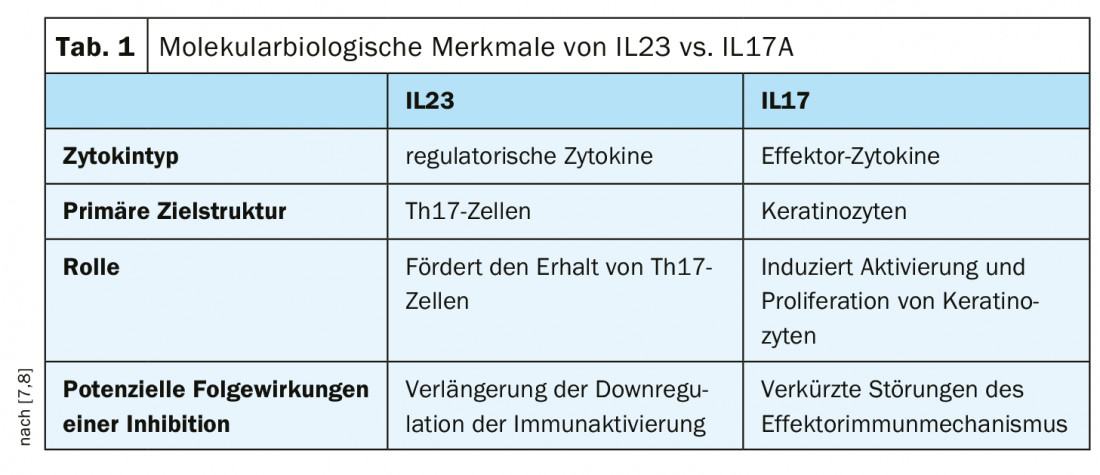
Under treatment with risankizumab, a proportion of 74% of patients reached PASI90 at week 16, compared with only 66% in the secukinumab condition [3]. Risankizumab also met the second primary endpoint (87% PASI 90 response vs. 57% with secukinumab, p<0.001) [3]. The IL23 inhibitor risankizumab also proved superior to the IL17A inhibitor secukinumab in all measured secondary endpoints in this study, including PASI 100, PASI 75, and sPGA 0/1 at week 52 (p<0.001) [3]. The safety profile of Skyrizi™ was consistent with that of previous studies, with no new safety signals reported over the 52-week study period (4-6). The biologics Skyrizi™ (risankizumab) [1] and Cosentyx® (secukinumab) [2] are approved in Switzerland for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults. These are two of the successively expanded spectrum of interleukin-antagonistic treatment options for psoriasis patients in recent years. The two cytokines IL-23 and IL17A differ with respect to various molecular biological characteristics (Table 1).
* Condition Skyrizi™ 150 mg: 2 subcutaneous 75 mg injections each at weeks 0, 4, and 12; thereafter at 12-week intervals.
** Condition Cosentyx® 300 mg: 2 subcutaneous 150 mg injections each at week 0,1,2,3,4; thereafter at 4-week intervals.
Source: AbbVie Inc.
Literature:
- Skyrizi [Summary of Product Characteristics]. AbbVie Ltd. Available at: www.ema.europa.eu.
- Cosentyx: https://compendium.ch, last accessed 12.02.2020
- AbbVie press release: https://news.abbvie.com/news/press-releases/new-head-to-head-phase-3-data-show-skyrizi-risankizumab-superior-to-cosentyx-secukinumab-across-primary-and-all-ranked-secondary-endpoints-in-adults-with-moderate-to-severe-plaque-psoriasis-at-52-weeks.htm
- Gordon K, et al: Efficacy and safety of risankizumab in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis (UltIMMa-1 and UltIMMa-2): results from two double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled and ustekinumab-controlled phase 3 trials. The Lancet 2018; 25; 392(10148): 650-661.
- Reich K, et al: Risankizumab compared with adalimumab in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis (IMMvent): a randomised, double-blind, active-comparator-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019; 394(10198): 576-586.
- Blauvelt A, et al: Efficacy and Safety of Continuous Q12W Risankizumab Versus Treatment Withdrawal: 2-Year Double-Blinded Results from the Phase 3 IMMhance Trial. Poster #478. 24th World Congress of Dermatology. 2019.
- Gooderham MJ, et al: Shifting the focus – the primary role of IL-23 in psoriasis and other inflammatory disorders. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2018; 32: 1111-1119.
- Girolomoni G, et al: The role of IL-23 and the IL-23/TH17 immune axis in the pathogenesis and treatment of psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2017; 31: 1616-1626.
DERMATOLOGIE PRAXIS 2020; 30(1): 27 (published 2/22/20, ahead of print).