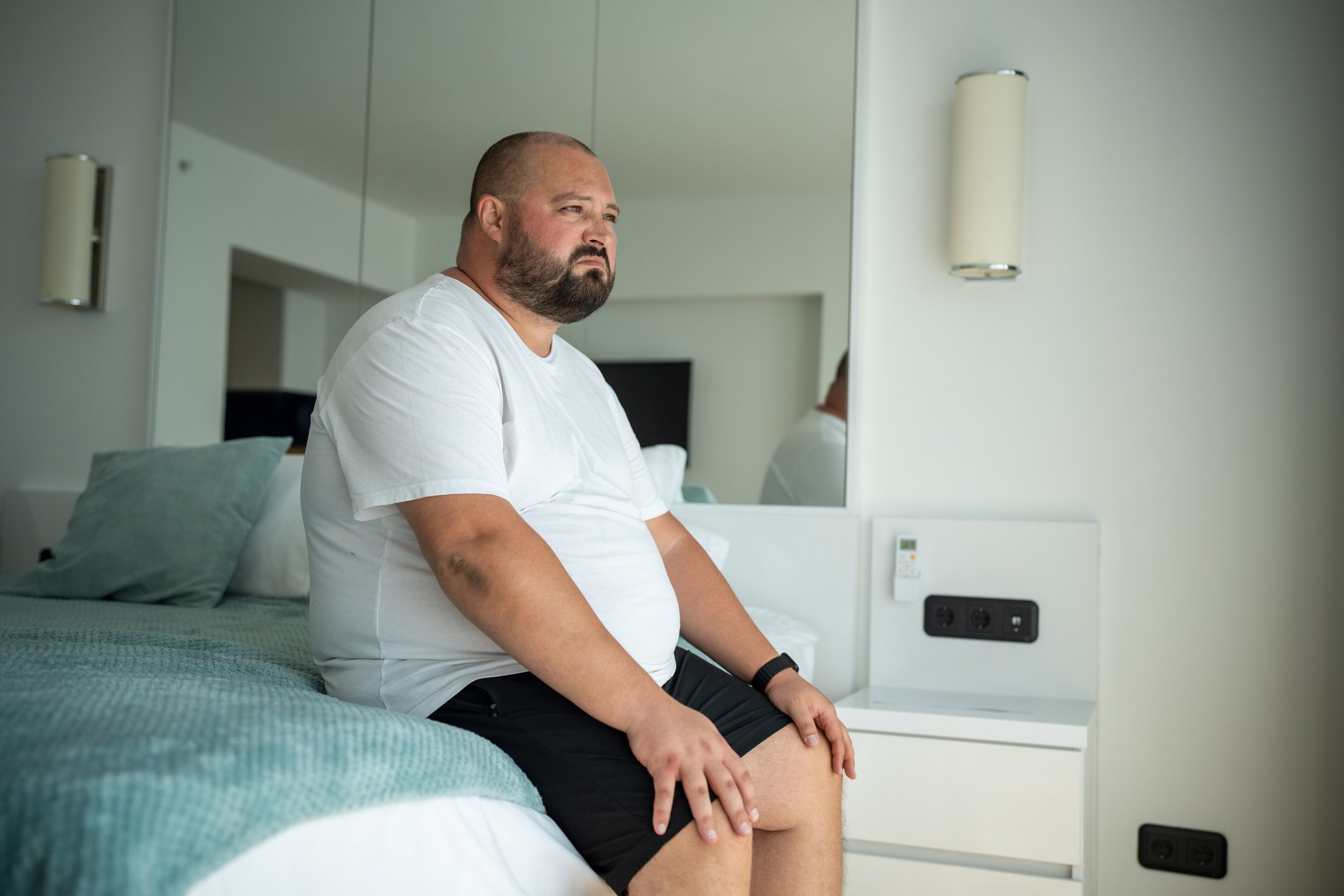
63-year-old patient presents with heartburn, volume reflux, and nocturnal cough, but symptoms respond inadequately to low-dose drug treatment.
Background: A 63-year-old male patient presented to his primary care physician with heartburn, volume reflux, and nocturnal cough. Initial treatment with low-dose proton pump inhibitors was given, resulting in little improvement in symptoms.
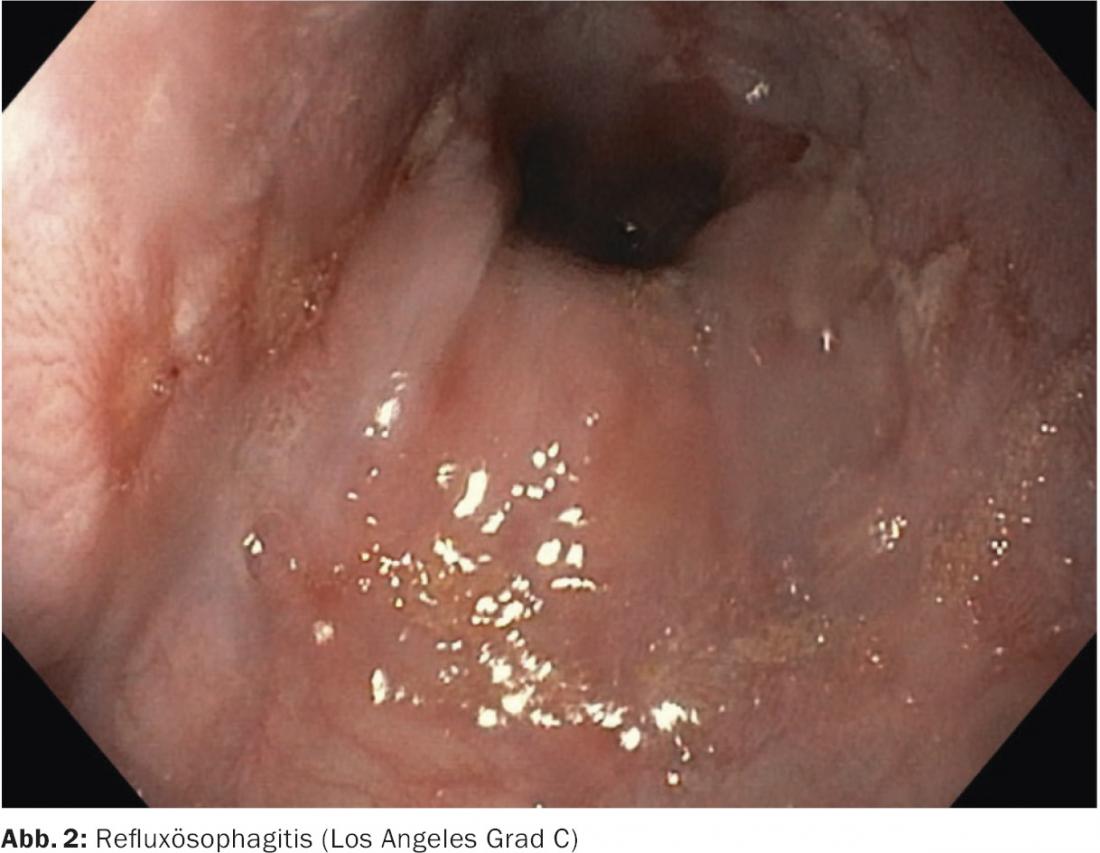
History and Diagnosis: The patient presented to the gastroenterologist due to inadequate symptom control and the presence of volume reflux. He stated that the complaints occurred mainly after sumptuous meals. Further medical history also revealed arterial hypertension and the risk factor obesity. Hypertension was treated by taking the antihypertensive combination drug Exforge HCT®. A trial of therapy with proton pump inhibitors and endoscopy were performed to establish the diagnosis. Endoscopy revealed a hiatal hernia measuring 3 cm and severe reflux esophagitis (Los Angeles classification grade C).
Therapy: The patient was then treated with a combination therapy of double-dose proton pump inhibitor and alginate for 4 weeks. This resulted in a rapid improvement in symptoms and subsequent switch to treatment with low-dose PPI and alginate as needed.
 Comment by Marcel Halama, MD: The present case demonstrates that a therapeutic approach with initial high-dose proton pump inhibitors is useful in cases of clear reflux esophagitis, which is favored by the two risk factors hiatal hernia and obesity. These should be reduced to the lowest possible dose during the course and supplemented by additional administration of Gaviscon® as needed.
Comment by Marcel Halama, MD: The present case demonstrates that a therapeutic approach with initial high-dose proton pump inhibitors is useful in cases of clear reflux esophagitis, which is favored by the two risk factors hiatal hernia and obesity. These should be reduced to the lowest possible dose during the course and supplemented by additional administration of Gaviscon® as needed.