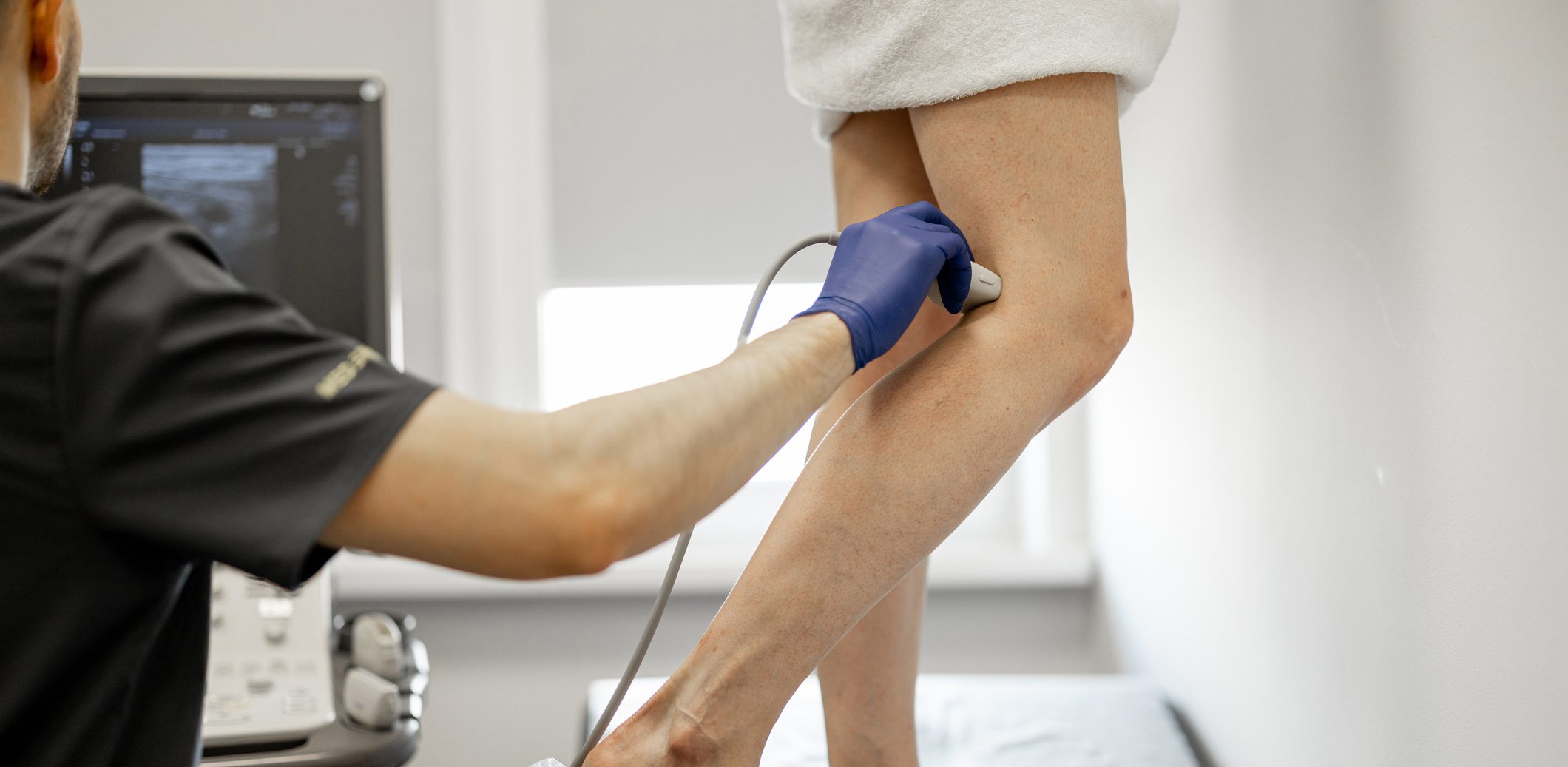
In recent years, the treatment of thrombosis patients has increasingly shifted to the outpatient sector. Provided that a reliable diagnosis and the application of anticoagulants in the correct dosage can be guaranteed, this often makes sense. However, there are cases where hospitalization and treatment is necessary, for example in cases of extensive pelvic vein thrombosis, severe venous congestion symptoms and in some other clinical situations.
Autoren
- Mirjam Peter, M.Sc.
Publikation
- HAUSARZT PRAXIS
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- Study report
Sphingolipid profile in early-stage primary biliary cholangitis
- Angiosarcoma of the heart
A diagnostic and therapeutic “black box”
- Ataxias
Friedreich’s ataxia: when the energy metabolism attacks the nervous system
- Risk of osteoporosis in autoimmune liver diseases
Always determine bone density in PBC, PSC and AIH
- Case report: Complication after type 2 diabetes
Topical corticosteroids lead to ketoacidosis
- NSCLC
Bispecific antibodies for rare EGFR mutations
- Type 2 diabetes - glycemic control and prevention of secondary diseases
Utilizing pleiotropic cardio- and nephroprotective effects of SGLT-2-i and GLP-1-RA
- Subsyndromal anxiety disorders: Family doctor as first point of contact