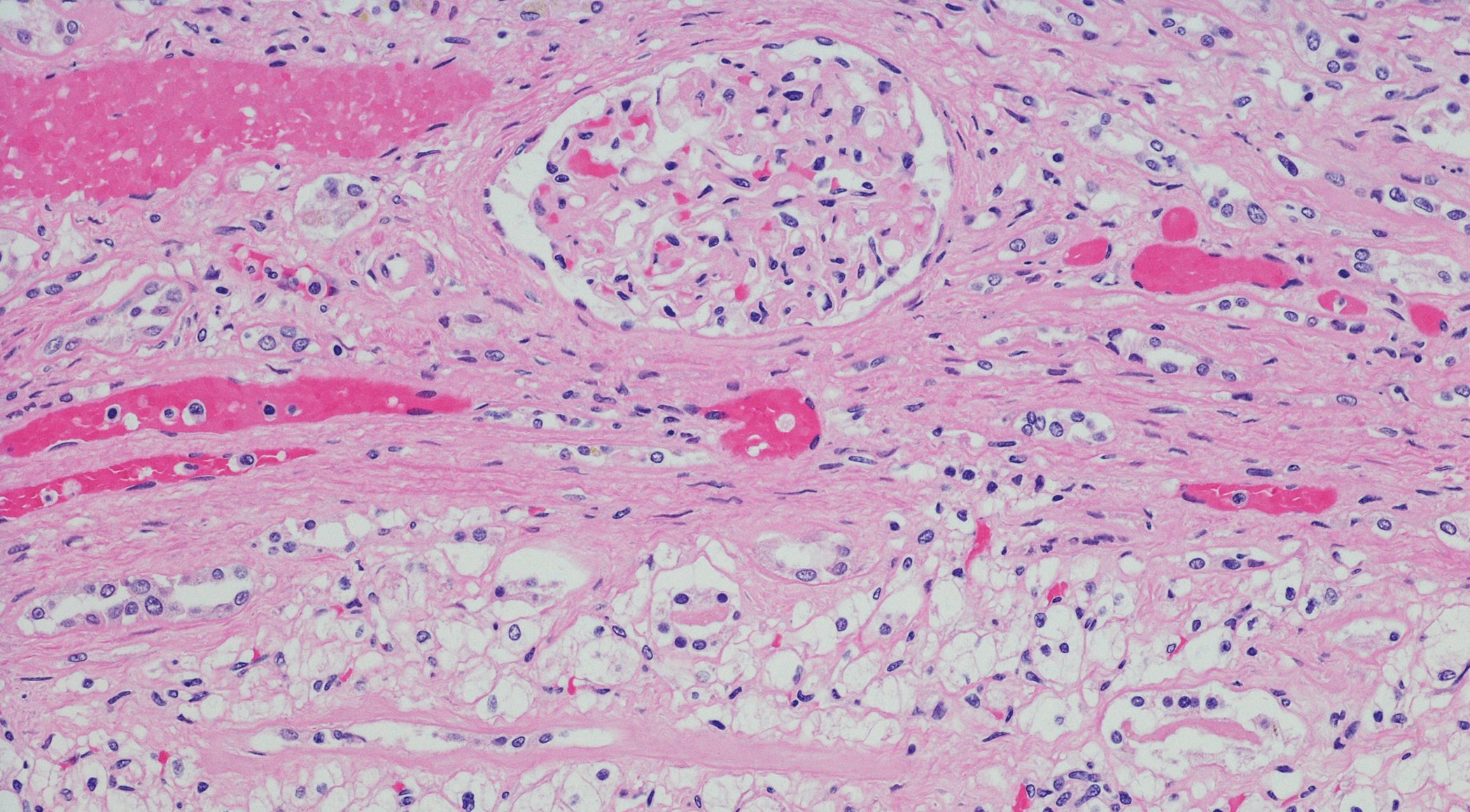
Benign prostatic syndrome (BPH) is one of the most common diagnoses in urological practice and is associated with a variety of lower urinary tract symptoms ( LUTS), which can severely impair the quality of life of affected men. In addition to hormonal factors, chronic prostatitis or prostatitis is increasingly coming into focus as an important risk factor for the progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Autoren
- Tanja Schliebe
Publikation
- Urologie-Special
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- Risk of osteoporosis in autoimmune liver diseases
Always determine bone density in PBC, PSC and AIH
- Case report: Complication after type 2 diabetes
Topical corticosteroids lead to ketoacidosis
- NSCLC
Bispecific antibodies for rare EGFR mutations
- Type 2 diabetes - glycemic control and prevention of secondary diseases
Utilizing pleiotropic cardio- and nephroprotective effects of SGLT-2-i and GLP-1-RA
- Subsyndromal anxiety disorders: Family doctor as first point of contact
Practical recommendations for diagnostics and therapy
- Patient-centered rounds in medicine
Aligning care with the patient
- Restless legs syndrome in children
Relationship between restless legs syndrome and growing pains
- Between hope and evidence gaps