Due to the immune escape of SARS-CoV-2 strains, the search for broad-spectrum antiviral agents remains an important research goal. A study published in 2023 shows that a phytopharmacological based on Pelargonium sidoides improves the course of the disease in hamsters infected with SARS-CoV-2. In addition, antiviral effects against the Delta AY.4 and Omicron BA.2 variants were detected in human nasal and bronchial epithelial cells.
The use of Pelargonium sidoides extract EPs® 7630 has proven to be an effective and safe treatment option for acute respiratory infections. Cell culture studies indicate that EPs® 7630 has comparable activity against SARS-CoV-2 as against other respiratory viruses. In an in-vitro study published in 2021, Papies et al. antiviral and immunomodulatory properties of EPs® 7630 in SARS-CoV-2 infected human lung cells [1]. To find out more about the properties of EPs® 7630 and its functionally relevant components in the context of phenotypically different SARS-CoV-2 variants, Emanuel et al. conducted another preclinical study [2]. On the one hand, they used an animal model – experimental studies on the Syrian hamster are considered a recognized model for analyzing the pathomechanisms of Covid-19 – and on the other hand, they analyzed treatment effects in a human in vitro model [2,3].
Effects of EPs® 7630 in SARS-CoV-2 infected hamsters
For the first experimental group, a prophylactic pre-treatment strategy was used in which the hamsters received oral treatment with a dose of 50 mg/kg body weight of EPs® 7630 twice daily, starting 24 hours before infection [2]. For the second test group, a combined oral (p.o.) plus intranasal (i.n.) treatment strategy was used, so that the hamsters received EPs® 7630 in addition to the oral dose (twice daily 50 mg/kg body weight from the time of infection), once intranasally 5 mg/kg body weight with the viral inoculum. The control group was also infected with SARS-CoV-2 and received a vehicle without EPs® 7630.
Virus replication in the lower respiratory tract was delayed: both the oral-only group and the oral plus i.n. treatment group showed an approximately tenfold reduction in SARS-CoV-2 plaque-forming units (PFU) on the second day after infection compared to the vehicle-treated controls [2]. Two days after infection, both EPs® 7630 trial groups showed a statistically significant reduction in viral titers and viral RNA of SARS-CoV-2 in the lower respiratory tract, with the effects being slightly more pronounced in the oral plus i.n. treatment group.
Delayed onset of pneumonia: Lung histopathology (paraffin-embedded tissue of the left-sided lungs; hematoxylin-eosin staining) was performed to determine whether treatment with EPs® 7630 also led to a change in Covid-19 pathology [2].
- Hamsters treated with EPs® 7630 had significantly fewer lung areas with signs of disease pathology 4 days post-infection than vehicle-treated controls.
- Hamsters treated with vehicle showed a peak of bronchitis 2 days after infection, whereas the hamsters treated with EPs® 7630 only showed a peak 4 days after infection.
- Both p.o. and i.n. EPs® 7630-treated hamsters had a significantly lower pneumonia score 4 days post-infection, but comparable scores to controls 7 days post-infection, suggesting an EPs® 7630-mediated delay in the onset of pneumonia.
- The hamsters treated with EPs® 7630 showed significantly less pulmonary edema compared to the vehicle-treated controls 4 days after infection. This was most pronounced in the combined oral and intravenous treatment group.
Antiviral properties of EPs® 7630 in human epithelial cells
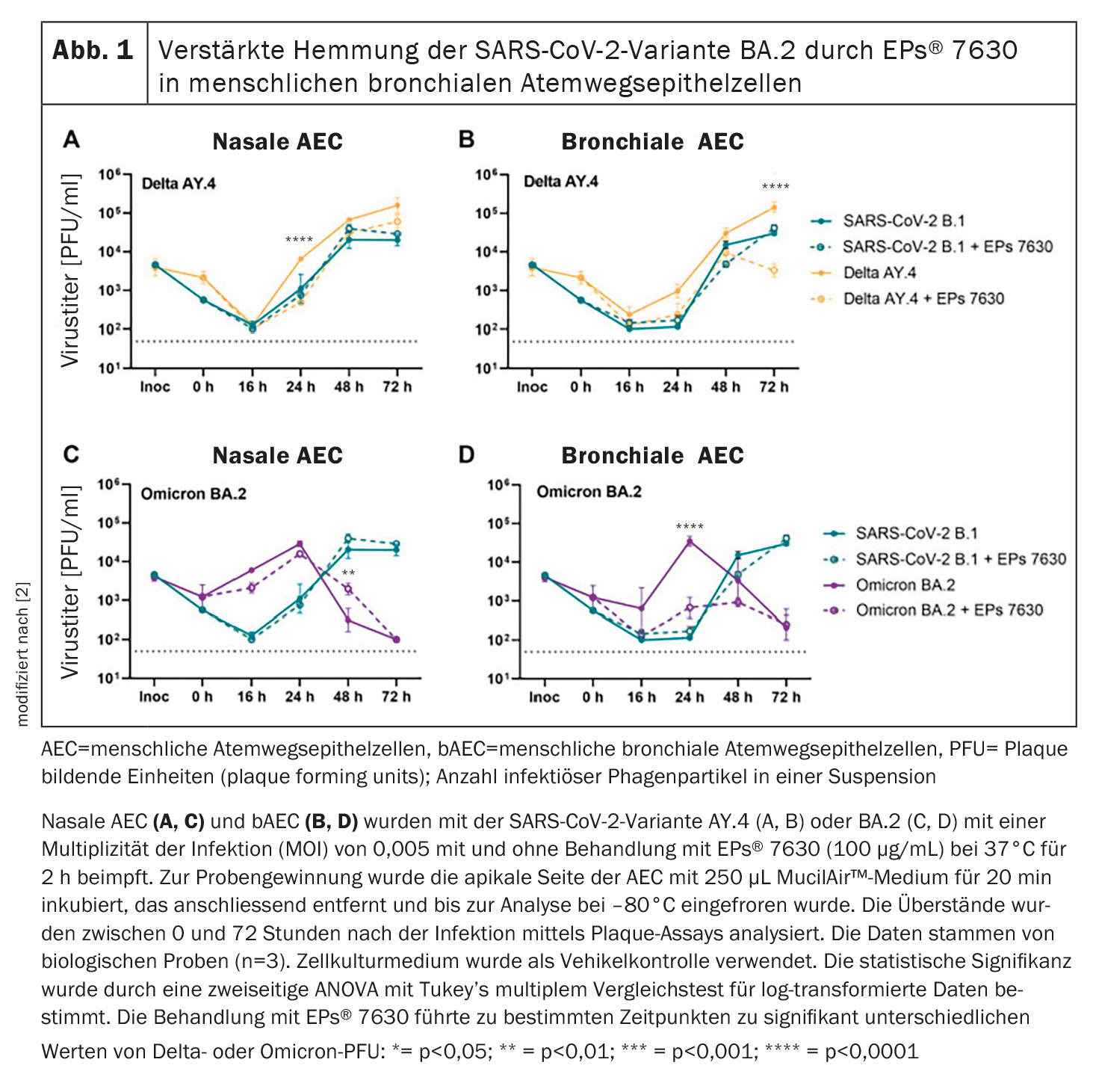
In human nasal and bronchial epithelial cells, EPs® 7630 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 variants differently [2]. Significant antiviral effects were observed against Delta AY.4 and Omicron BA.2 in both nasal and bronchial human epithelial cells (AEC), indicating a variant-specific antiviral effect (Fig. 1). According to the study authors, it seems plausible that the therapeutic efficacy of EPs® 7630 is based on a combination of inhibition of viral entry and direct anti-inflammatory effects. This is also consistent with the positive effects of EPs® 7630 observed in other respiratory tract infections in clinical settings [4–7].
In addition, at least two molecular components of EPs® 7630, namely (-)-epigallocatechin and (+)-taxifolin, were shown to have antiviral effects on SARS-CoV-2 replication and cell entry. It was also found that the mechanism by which epigallocatechin blocks SARS-CoV-2 is dependent on the SARS-CoV variant. Epigallocatechin and its component epigallocatechin gallate exhibited stronger entry inhibition against Omicron BA.2 compared to B.1 and Delta AY.117. This corresponds with the increased antiviral activity of EPs® 7630 and the two aforementioned ingredients against Omicron BA.2 (Fig. 1).
Literature:
- Papies J, et al: Antiviral and Immunomodulatory Effects of Pelargonium sidoides DC. Root Extract EPs® 7630 in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Human Lung Cells. Front Pharmacol 2021; 12: 757666. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1214351
- Emanuel J, et al: In vitro and in vivo effects of Pelargonium sidoides DC. root extract EPs® 7630 and selected constituents against SARS-CoV-2 B.1, Delta AY.4/AY.117 and Omicron BA.2. Front Pharmacol 2023 Jul 26; 14: 1214351.
- Osterrieder N, et al: Age-dependent progression of SARS-CoV-2 infection in Syrian hamsters. Viruses 2020; 12: 779. 10.3390/v12070779
- Kamin W, et al: Efficacy and tolerability of EPs 7630 in children and adolescents with acute bronchitis-a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter trial with a herbal drug preparation from Pelargonium sidoides roots. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2010a; 48, 184-191.
- Kamin W, et al: Efficacy and tolerability of EPs 7630 in patients (aged 6-18 years old) with acute bronchitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical dose-finding study. Acta Paediatr 99: 537-543.
- Matthys H, et al: Efficacy and tolerability of EPs 7630 tablets in patients with acute bronchitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled dose-finding study with a herbal drug preparation from Pelargonium sidoides. Curr Med Res Opin 2010; 26: 1413-1422.
- Riley DS, et al: Treatment with EPs 7630, a Pelargonium sidoides root extract, is effective and safe in patients with the common cold: results from a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Integr Med (Encinitas) 2019; 18 (1): 42-51.
FAMILY PHYSICIAN PRACTICE 2024; 19(1): 48-50