Adalimumab (anti-TNF-α) is currently still the only approved biologic for the treatment of moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). In a recent “real world” 52-week study, treatment with adalimumab resulted in significant reductions in disease severity, which was associated with improvements in quality of life and productivity.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (alternative name: acne inversa) is a disease of the terminal hair follicles associated with lympho-histiocytic inflammation, granulomatous reactions, and the formation of sinus tracts and scars, and the deep areas of the follicles seem to be particularly involved [1,2]. Histologic studies of hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) consistently report follicular occlusion, attributed to hyperkeratosis [3]. Regardless of the duration of the disease, inflammation and possible secondary infections occur as a result of the closure of the apocrine glands and subsequent rupture of the follicles. Strong expression of the cytokines IL-1β, CXCL9 (MIG), IL-10, IL-11, BLC, and IL-17A and a decrease in the expression of IL-20 and IL-22 have been demonstrated in skin lesions of patients with HS [4,5].
Severity of the disease is associated with quality of life
Patients with HS suffer from a significant reduction in quality of life due to their disease, especially when a high degree of morbidity is present [6]. Empirical data show that there is a direct relationship between disease severity and loss of quality of life [7]. HS-associated pain has the greatest negative impact on quality of life. Work-related productivity losses have also been documented [3]. For the classification of the severity of the disease, the classification into stages I-III according to Hurley is available [8]. Grade I is characterized by localized disease with singular or multiple abscesses without fistula tracts and scarring. In grade II, recurrent abscesses with fistula tracts and incipient scarring, both singular and multiply separated, are present. Diffuse involvement of the entire anatomic region with abscesses, communicating fistulous tracts, and marked scarring to the point of limited mobility is classified as grade III. Horvath et al. published a revised version of the Hurley classification in 2017 [9].
Important therapeutic goals in HS are to improve severity and quality of life within 12 weeks [3].

“Real World” study of adalimumab: sustained clinical response
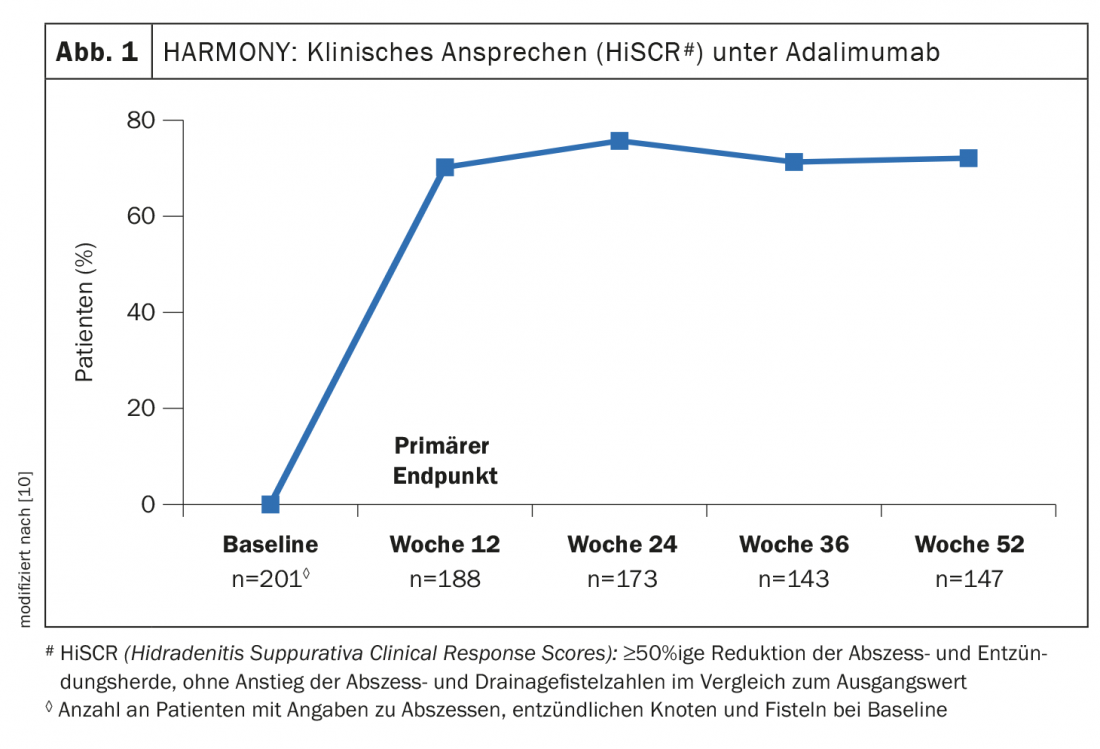
To investigate the efficacy and safety of adalimumab (box) in real-life settings, the HARMONY (Effectiveness of Adalimumab in Moderate to Severe HidrAdenitis SuppuRativa Patients – a Multi-cOuNtry studY in Real Life Setting) study was conducted – a multicenter observational study in adult patients with moderate to severe HS [10]. Disease severity and changes in quality of life were assessed at 12-week intervals during 52 weeks of treatment using validated measurement tools. The primary endpoint was the proportion of study participants who achieved a clinical response according to HiSCR (≥50% reduction in abscess and inflammatory foci, with no increase in abscess and drainage fistula counts compared with baseline) at 12 weeks. Secondary endpoints were HiSCR (Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response Scores), quality of life, and productivity at 24, 36, and 52 weeks. Analyses were performed using as-observed data. Quality of life was assessed using the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI)*, the Patient Health 9-Item Questionnaire (PHQ-9)#, and the Euro Quality of Life 5 Dimensions (EQ-5D).
$
assessed. The Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI) questionnaire was used to assess productivity.
* DLQI: 0=highest quality of life, 30=lowest quality of life.
# PHQ-9: each aspect is rated with values between 0 (not disturbed at all in the last two weeks) and 3 (disturbed almost every day in the last two weeks)
$
EQ-5D: 0=worst possible health status, 100=best possible health status.
The proportion of study participants (n=188) who met the HiSCR endpoint at week 12 was 70.2% and remained ≥70% through the end of the study ( Fig. 1). There were statistically significant reductions in HS-related skin pain (p<0.0001) [10]. In all quality-of-life measures collected, treatment with adalimumab resulted in a significant improvement from baseline to week 52 (p< 0.0001). DLQI and PHQ-9 scores decreased by approximately 50%, and components of the EQ-5D also showed significant improvement from baseline to week 52. All four domains of the WPAI-presenteeism, absenteeism, total impairment of work productivity, and total impairment of activity-improved significantly from baseline to week 52 with treatment with adalimumab.
Adalimumab was generally found to be well tolerated. The most common adverse events were cutaneous and subcutaneous disorders (7.5%). A total of 5.5% of study participants terminated adalimumab treatment prematurely in association with adverse events. Severe adverse events occurred in 11.4% of patients, resulting in hospital readmission or prolongation of hospital stay.
Literature:
- Jansen T, Altmeyer P, Plewig G: Acne inversa (alias hidradenitis suppurativa). J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2001; 15: 532-540.
- Kurzen H, Schönfelder-Funcke S, Hartschuh W: Surgical treatment of Acne inversa at the University of Heidelberg. Int J Coloproct 2000; 22:76-80.
- Zouboulis CC, et al: S1 guideline on the therapy of hidradenitis suppurativa / acne inversa. AWMF register number 013-012.
- van der Zee HH, et al: Adalimumab (anti-TNF-α) treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa ameliorates skin inflammation: an in situ and ex vivo study. Br J Dermatol 166 2012; 31: 298-305.
- Wolk K, et al: Deficiency of IL-22 contributes to a chronic inflammatory disease: pathogenetic mechanisms in acne inversa. J Immunol 2011; 186: 1228-1239.
- Matusiak U, Bieniek A, Szepietowski JC: Psychophysical aspects of hidradenitis suppurativa. Acta Derm Venereol 2010; 90: 264-268.
- Sartorius K, et al: Objective scoring of hidradenitis suppurativa reflecting the role of tobacco smoking and obesity. Br J Dermatol 2009; 161: 831-839.
- Hurley HJ: Axillary hyperhidrosis, apocrine bromhidrosis, hidradenitis suppurativa, and familial benign pemphigus; surgical approach. In: Roenigk RK, Roenigk HH, editors. Dermatologic surgery. New York Marcel Dekker 1989. pp. 729-739.
- Horváth B, et al: Hurley staging refined: a proposal by the Dutch Hidradenitis Suppurativa Expert Group. Acta Derm Venereol 2017; 97(3): 412-413.
- Hafner A, et al: Improvement in Hidradenitis Suppurativa and quality of life in patients treated with adalimumab: Real-world results from the HARMONY Study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2021; 35(11): 2277-2284.
- Kimball AB, et al: Two phase 3 trials of adalimumab for hidradenitis suppurativa, N Engl J med 2016; 375; 422-434.
DERMATOLOGY PRACTICE 2022; 32(4): 36-38