The main therapeutic domain of botulinum is in the upper third of the face, not the lower third. The treatment of the lower third of the face should be reserved for doctors with a lot of experience. For an optimal result, it has proven effective to combine different therapy options.
The SGEDS column “Aesthetic Dermatology” now has a permanent place in DERMATOLOGIE PRAXIS. I am pleased to present to you in this issue already the third part of the botulinum advanced training as part of the “Advanced Training Series in Aesthetic Dermatology”. In the first part (DP 01/2015) we discussed the basics, the second part (DP 02/2016) was dedicated to aesthetic indications in the upper third of the face. In the third part of the series, we will now discuss the application in the lower third of the face. In a later issue we will conclude the topic “Botulinum” with the treatment of hyperhidrosis. You will then have in your hands a fully comprehensive overview of the possible applications of botulinum in dermatology.
Botulinum in the lower third of the face is difficult
The domain of botulinum treatment in facial aesthetic treatment is in the upper third of the face (see DP 02/2016). The reason for this is the anatomical conditions of the mimic musculature. While we have just four relevant muscles in the upper third of the face (three depressors and one levator), we find a multitude of larger and smaller muscles in the lower third of the face, which control the fine facial expressions in their complex interaction. With each unit of botulinum, we weaken a specific muscle in this very balanced system of agonists and antagonists. In addition, the different muscles are sometimes very close to each other and the drug botulinum is known to have a certain diffusion capacity. Improper injections, be they too deep or too far laterally, or even a not quite correct dilution or Inaccurate injection amounts of the toxin very quickly lead to a co-impairment of an adjacent muscle with sometimes aesthetically unattractive results or (worse) functional impairment (“crooked laughter”, “drooling”, speech disorders, etc.). There are repeated reports of the risk of “mask expression” after excessive botulinum treatment in the upper third of the face. It is forgotten that the mimic expression is only influenced by the muscles of the upper third of the face to a vanishingly small extent. A young child is not yet capable of adjusting the mimic musculature in the upper third of the face (in the narrower sense, glabella and forehead) according to the emotions. But also toddlers (or: especially toddlers) have a partly distinctive mimic facial language and can convey sadness, anger, joy or astonishment extremely well mimic. This is due to the fact that the essential part of facial mimic speech is performed in the lower third of the face.
In summary, it can be stated: Botulinum in the upper third of the face is relatively safe, botulinum in the lower third of the face is difficult and should only be performed by well-trained dermatologists or plastic surgeons who are well grounded in the subject.
The aging of the lower third of the face – What happens?
Not only the anatomical muscular conditions are complex in the lower third of the face. The aging processes are also multifactorial, especially in this area. While the upper third of the face is dominated by osseous structures, the lower third of the face consists mainly of soft tissue structures, in the narrower sense fat pads, muscles and skin. It is well known that the main factor of the aging process is due to atrophy, especially of soft tissues. In addition, actinic elastosis due to chronic UV radiation and increasingly static wrinkles due to mimic musculature. The main factors in this multifactorial process include lipatrophy and increasing elastosis of the skin, which are then responsible for the sagging face. In somewhat simplified terms, there is too much facial skin with age, as the volume to be covered decreases. The third factor, static wrinkles due to mimic activity, is less critical to the visual aging of the lower third of the face. In addition to the technical anatomical difficulties of botulinum treatment, this is another reason why the lower third of the face is less the domain of botulinum therapy. The improvement of the aesthetic facial expression is only marginal even with perfect technique. The lower third of the face is the domain of augmentation and, if necessary, medium-deep to deep peeling, depending on the severity of actinic elastosis.
However, there are also suitable indications for botulinum therapy in the lower third of the face.
“Gummy smile”
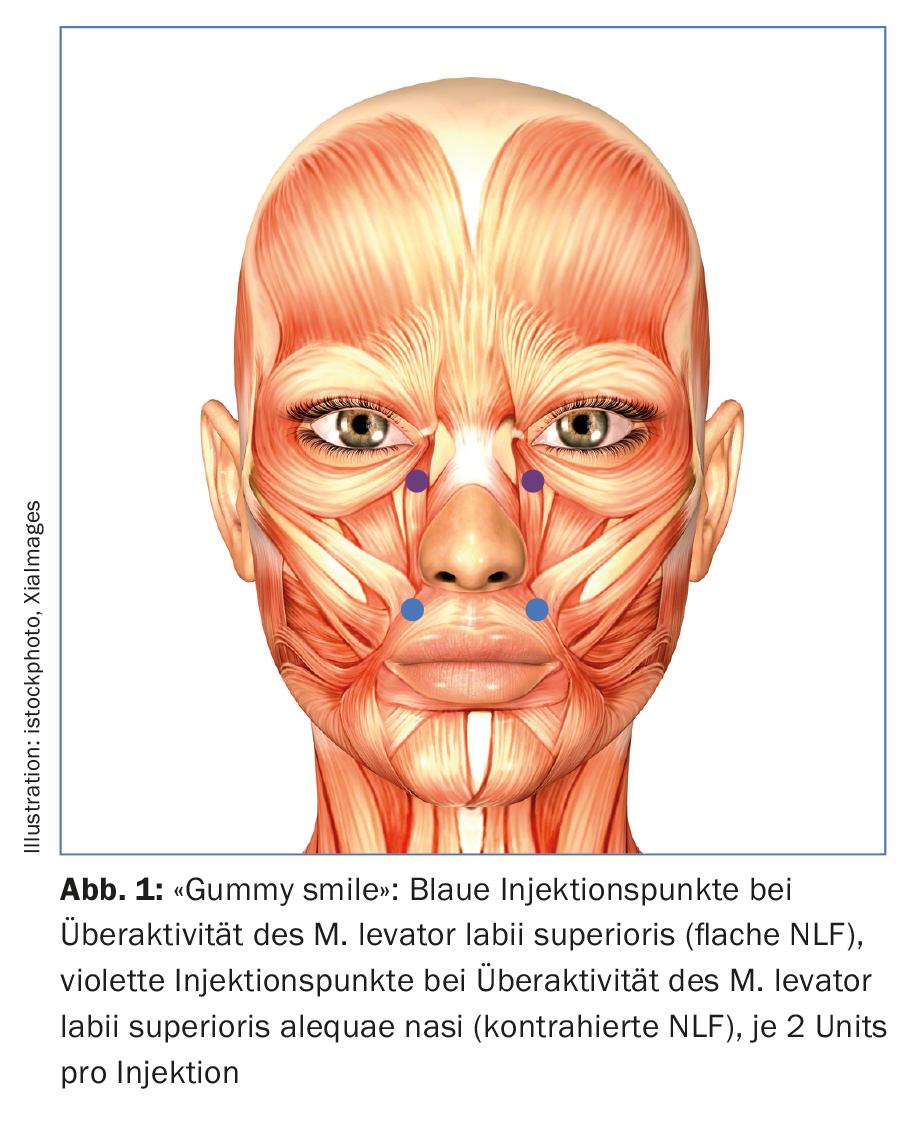
One speaks of “gummy smile” when not only the upper incisors but also the gums are presented when laughing. We distinguish between two different types:
- Overactivity of the levator labii superioris muscle results in frontal pointing of the gingiva without the posterior molars being visible. The nasolabial fold is not contracted and remains flat.
- In case of overactivity of the levator labii superioris alequea nasi muscle, the upper lip is pulled maximally cranially. In addition to the gum pointing, there is also a lateral mouth opening with the appearance of the posterior molars. The nasolabial fold is contracted.
Depending on the clinical appearance, either the M. levator labii superioris or the M. levator labii superioris alequae nasi must therefore be treated with 2 U botulinum toxin each (resolution and different units depending on the botulinum product, see “Botulinum I – Basics” DP 01/2015). (Fig.1). The danger of this treatment is a “flat laugh” (M. levator labii superioris alequae nasi) resp. a functional mouth opening disorder when the levator labii superioris muscle is injected, since the orbicularis oris muscle lies directly below the levator labii superioris muscle.
“Smoker lines” or “barcode wrinkles”
This is a very frequently complained about problem on the part of patients. Due to the increasing atrophy of the skin in this area with the circularly closing muscle, vertically directed wrinkles occur mainly in women, first in the area of the upper lip, later also in the lower lip. In advanced cases, increasing actinic elastosis plays an additional important role. According to Glogau, we distinguish four degrees of severity:
- No wrinkles
- Wrinkles only with mimic activity
- Wrinkles even at rest
- Deep furrows
Grade 1 and grade 2 can be treated with botulinum, whereas grade 1 is a prophylactic therapy in young patients with clearly thin skin. Grade 3 and 4 are more difficult to address and usually require a combination treatment with botulinum, hyaluronic acid and possibly peeling, and any therapy must be performed very carefully and at low doses to achieve a good aesthetic and functional result. Since the mouth closure is not only crucial for articulation (e.g. words with P like “police station”), but also for food intake (drinking from a straw resp. “drooling”), the orbicularis muscle must not be weakened too tightly in its function.
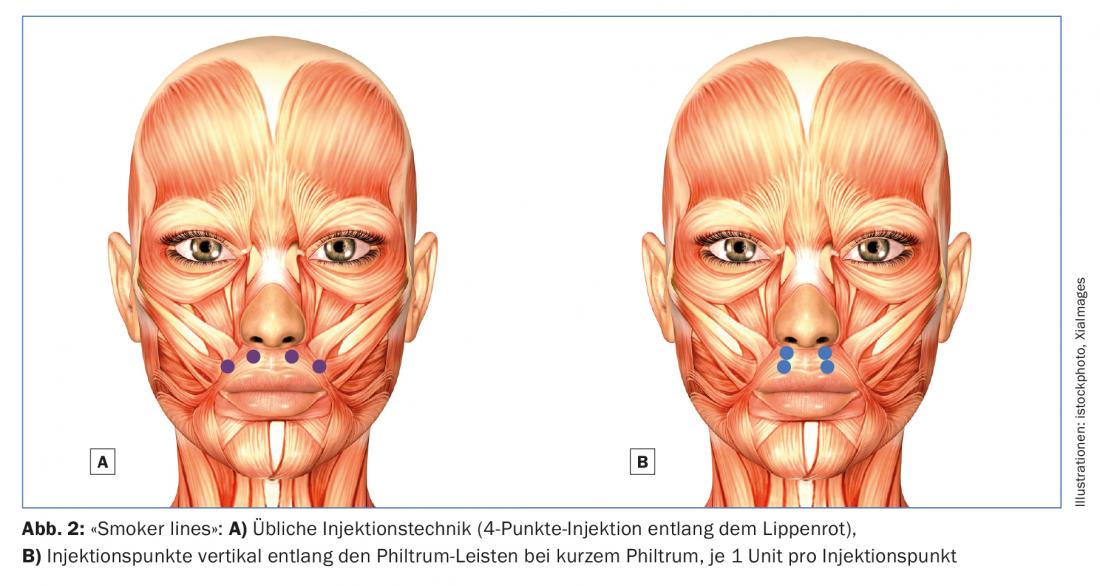
The usual injection technique is a 4-point injection along the red of the lip, with only 1 U of botulinum injected per injection point (Fig. 2A). As a desirable side effect, the upper lip is rotated slightly outward, resulting in a slightly fuller lip. In rare cases with a very short philtrum, the injection points can also be placed vertically along the philtrum ridges, which lengthens the philtrum (Fig. 2B). Since the injection doses must be kept very small in this indication, the duration of effect is limited. Regular re-injections every six to eight weeks are therefore required for a lasting good result. However, if these treatment cycles are followed for a longer period of time, extremely beautiful results with a long-term effect can be achieved (prophylactic therapy).
“Marionette lines” (“puppet folds”)
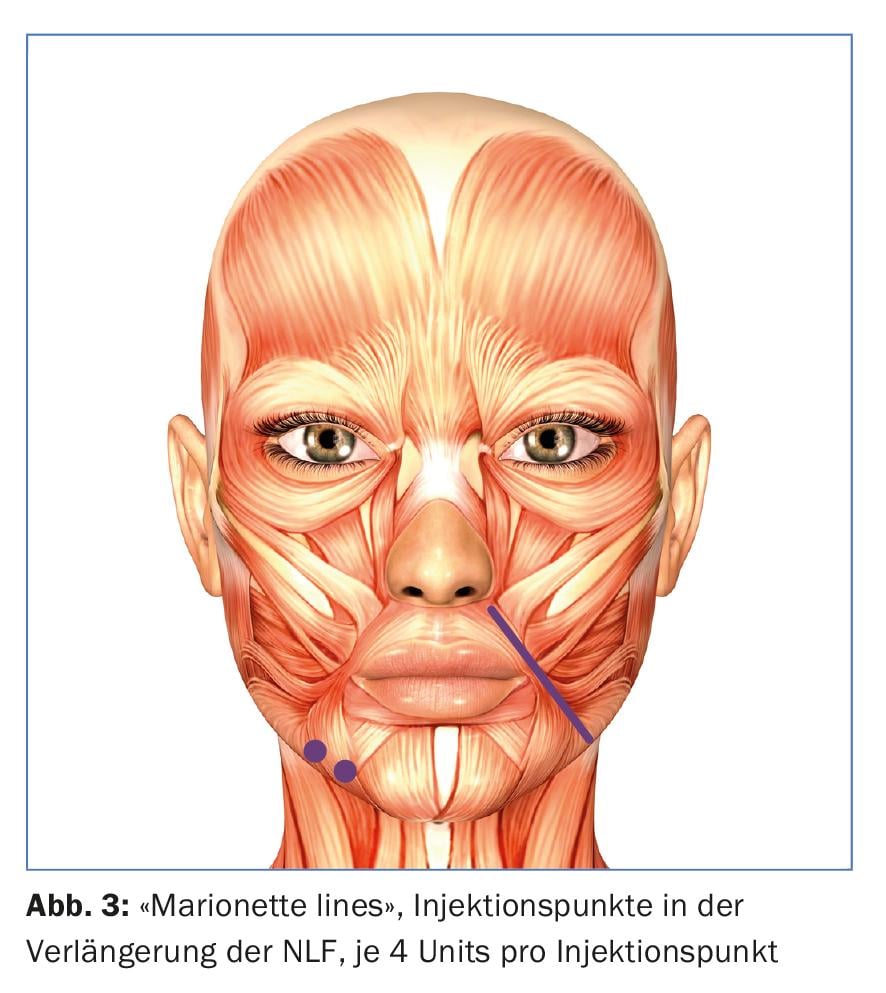
The name “Merkel wrinkle” has also become established in German usage. Etiologically, in principle, this is not a mimic wrinkle. It is rather caused by lipatrophy of the local adipose tissue on the one hand and by sagging of the midface due to lipatrophy of the malar fat pads on the other hand. However, in young patients, this fold can be reduced by activity reduction of the depressors in this area. The most powerful depressor in the lower mouth region is the depressor anguli oris (DAO) muscle. The muscle originates at the margo inferior of the mandible and radiates into the corner of the mouth. At its origin, it is fused to the platysma, and at its attachment, its muscle fibers interweave with those of the risorius and orbicularis oris muscles. The muscle pulls the corner of the mouth down. Botulinum treatment weakens it and the corners of the mouth are pulled up, the marionette wrinkles disappear.
One point is treated 1 cm laterally from the corner of the mouth at the level of the mandibular edge and additionally laterally from this point the fibers of the irradiating platysma are treated with 4 U botulinum each. A somewhat easier localization is achieved by selecting the first point on the mandibular edge in the extension of the nasolabial fold (Fig. 3).
The main danger is that the inferior labial depressor muscle may be affected by incorrect placement of the injection site. The muscle lies medial to the DAO. In this case, the result is an unsightly “crooked mouth” with possible impairment of the mouth closure. Treatment of DAO should be reserved for experienced physicians and is not recommended in cases of advanced “sagging” resp. Elastosis contraindicated.
“cobblestone chin”
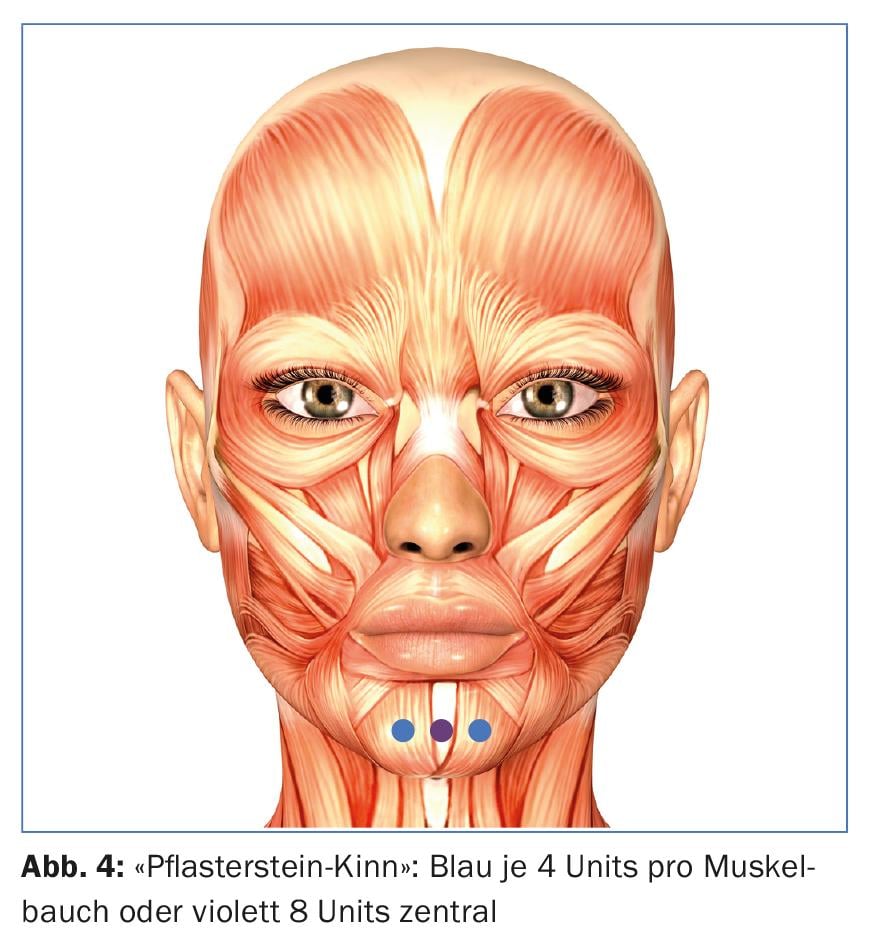
If the mentalis muscle is overactive, an unsightly “cobblestone chin” may result during facial expressions. With two deep injections of 4 U botulinum, the mentalis muscle can be weakened in such a way that the cellulite-like bumps during facial expressions disappear. This has the pleasant side effect of slightly flattening the chin, which often results in a more harmonious image in the side view. This effect is all the more pronounced the more advanced the so-called “hamster cheeks” are. Since the mentalis muscle is a two-bellied muscle, the 2-point injection with 4 U botulinum each has proven to be effective (Fig. 4). Some authors prefer a singular central injection with 8 U to avoid diffusion of the botulinum into the depressor labii inferioris muscle as much as possible. The latter runs superficially over the mentalis muscle. Thus, there is also an application error if the injections are chosen too superficially.
Nefertiti lift (after Philippe Lévy)
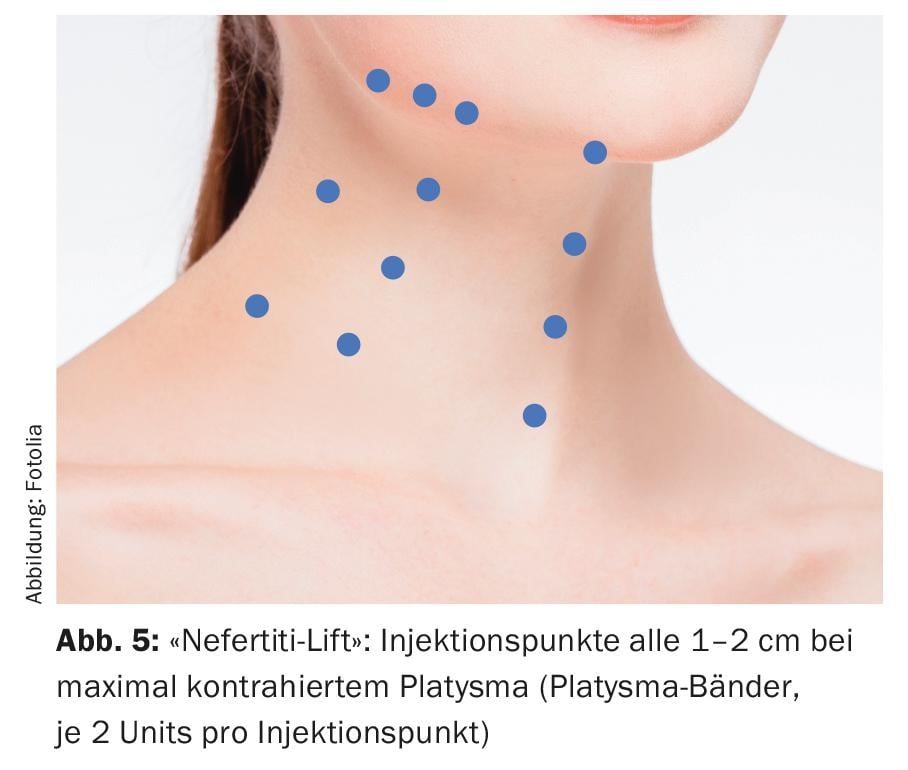
With increasing age, for the above-mentioned reasons, the jaw angle on the one hand becomes deformed and on the other hand the fat pads are lowered with consequent excess skin in the area of the ventral jawline (“hamster cheeks”). In younger patients, treatment of the platysma, a major depressor of the lower perioral region, can significantly reduce “hamster cheeks.” The injection points in the platysma ligaments are chosen at maximum contraction with a distance of 1-2 cm (Fig. 5). 2 U of botulinum are used per injection point. The disadvantage of this method is that a relatively large amount of botulinum must be used and the technique reaches its limits with advanced “sagging” of the jawline. However, extremely satisfactory results can still be achieved in younger patients with incipient “hamster cheeks”. As with the above-mentioned forms of therapy, strict attention must be paid to impairment of the depressor labii inferioris muscle.
The treatment of the different forms of hyperhidrosis will be the topic of the next and last training block on “Botulinum”. Look forward to it, it will be exciting again!
Take-Home Messages
- The main domain of botulinum treatments is certainly in the upper third of the face, not the lower third.
- Due to degradation processes, primarily of the fat pads, as well as general skin aging in the sense of increasing elastosis, the most important forms of therapy here are augmentation with hyaluronic acid and medium-deep to deep peels. However, in selected cases or for specific problems such as “gummy smile” or “smoker lines”, botulinum treatments can be an essential pillar in aesthetic treatment.
- Botulinum treatment in the lower third of the face should necessarily be reserved for doctors with a lot of experience in aesthetic forms of treatment. For an optimal result, it has proven effective to combine different therapy options. Especially in combination with hyaluronic acid treatments, the additional therapy with botulinum certainly has its firm place.
DERMATOLOGIE PRAXIS 2017; 27(4): 34-38