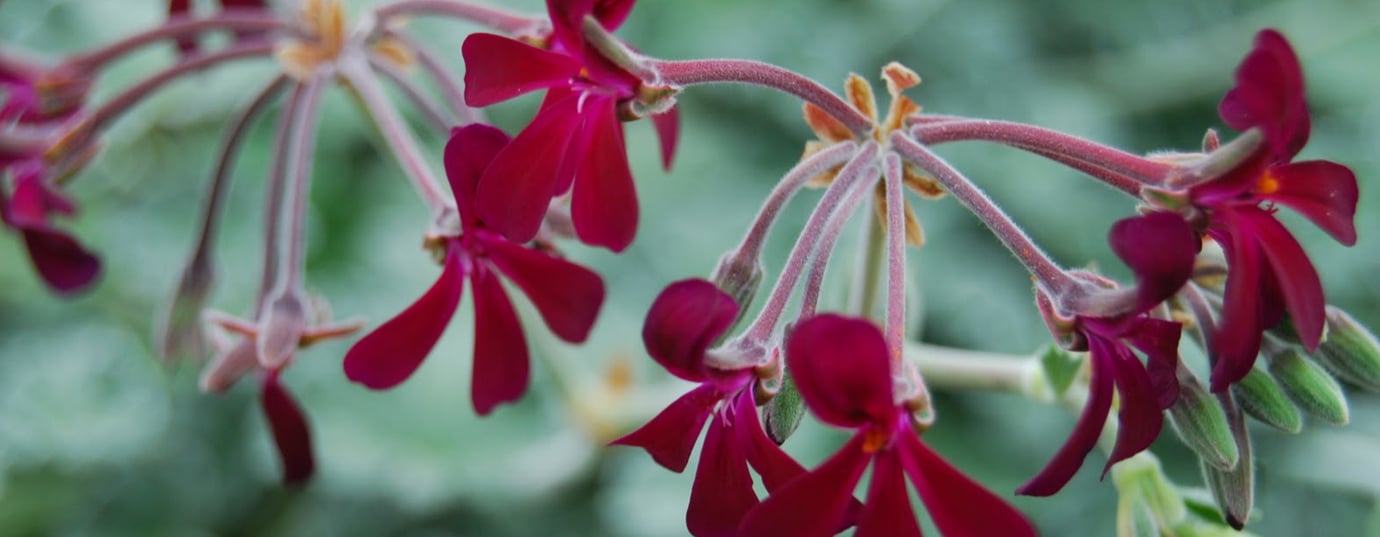
Pelargonium sidoides, a plant native to southern Africa, has been studied by various research teams since the 1990s. Folk application against bronchitis gave the medical evidence, also a meta-analysis confirmed the effectiveness. All studies were made with the standardized extract EPs 7630.
Although most respiratory infections have viral causes, antibiotics are very often prescribed. These are known to be ineffective against viruses. This, too, contributes to rising antibiotic resistance, even though effective and clinically proven medicinal plant extracts, among others, exist that could be used to treat these diseases. In the treatment of bronchitis, for example, the standardized extract EPs 7630 (Tab. 1) from the South African medicinal plant Pelargonium sidoides has proven effective.

Pelargonium sidoides
It is a shrub found in South Africa in many areas, about 50 cm high. For centuries, this has been used by the indigenous population against various diseases such as colds, bronchitis, as well as against tuberculosis. For about 20 years, the plant has been scientifically researched.
Scientific studies
The literature list of clinical studies done with EPs 7630 is very large. In 2007 and 2008 alone, seven clinical trials, two reviews, and one meta-analysis have been published.
Mathys and Heger [1] demonstrated the efficacy of EPs 7630 in an open multicenter study in adults with acute bronchitis using the BSS (“bronchitis specific symptoms”) scale classification. Mathys et al. [2] included children in another study, some of whom were ≤3 years of age, and were again able to show that the extract was effective in children using the BSS.
This efficacy was confirmed by Haidvogl and Heger [3], who included in their study only children in whom the BSS score indicated complete or at least partial remission of bronchitis, as in the other studies.
Again, Mathys and Heger published another study in 2007, but this one was randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled [4]. The decrease on the BSS scale was significantly greater in the verum group than on placebo, and the safety of EPs 7630 was also documented. These results were also reported by the authors Lizogub et al. [5] confirmed.
In 2008, a meta-analysis by Agbabiaka et al. [6]. The authors evaluated the results of 1012 patients from four RCTs (“Randomized Controlled Trial”) and were able to reconfirm the significant superiority of the extract over placebo.
Kamin et al. [7] again confirmed the efficacy in children and determined the effective dosage for different age groups in their study (Table 1).
Sinusitis maxillaris
Further, there are studies that provide evidence for efficacy in maxillary sinusitis. Schapowal has published a review article on this [8]. Since this publication, another study has already appeared [9]. However, EPs 7630 has not received approval for acute maxillary sinusitis in Germany or Switzerland.
Literature:
- Mathys H, Heger M: EPs® 7630-solution – an effective therapeutic option in acute and exacerbating bronchitis. Phytomedicine 2007; 14: SVI 65-68.
- Mathys H, et al: Pelargonium sidoides preparation (EPs® 7630) in the treatment of acute bronchitis in adults and children. Phytomedicine 2007; 14: SVI 69-73.
- Haidvogl M, Heger M: Treatment effect and safety of EPs® 7630-solution in acute bronchitis in childhood: Report of a multicentre overvantional study. Phytomedicine 2007; 14: SVI60-64.
- Mathys H, Heger M: Treatment of acute bronchitis with a liquid herbal drug preparation from Pelargonium sidoides (EPs® 7630): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, mutlicentre studiy. Current Medical Research and Opinion 2007(2); 23: 323-331.
- Lizogub VG, et al: Efficacy of a Pelargonium sidoides preparation in patients with the common cold: a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Explore (NY) 2007(6); 3: 573-584.
- Agbabiaka T, et al: Pelargonium sidoides for acute bronchitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytomedicine 2007(5); 15: 378-385.
- Kamin W, et al: Efficacy and tolerability of EPs 7630 in children and adolescents with acute bronchitis. Int Clin Pharmacol Ther 2010(3); 48: 184-191.
- Schapowal A: Phytotherapy in acute maxillary sinusitis. Phytotherapy 2006(5); 6: 9-11.
- Bachert C, et al: Treatment of acute rhinosinusitis with the preparation from Pelargonium sidoides EPs® 7630: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Rhinology 2009; 47: 51-58.