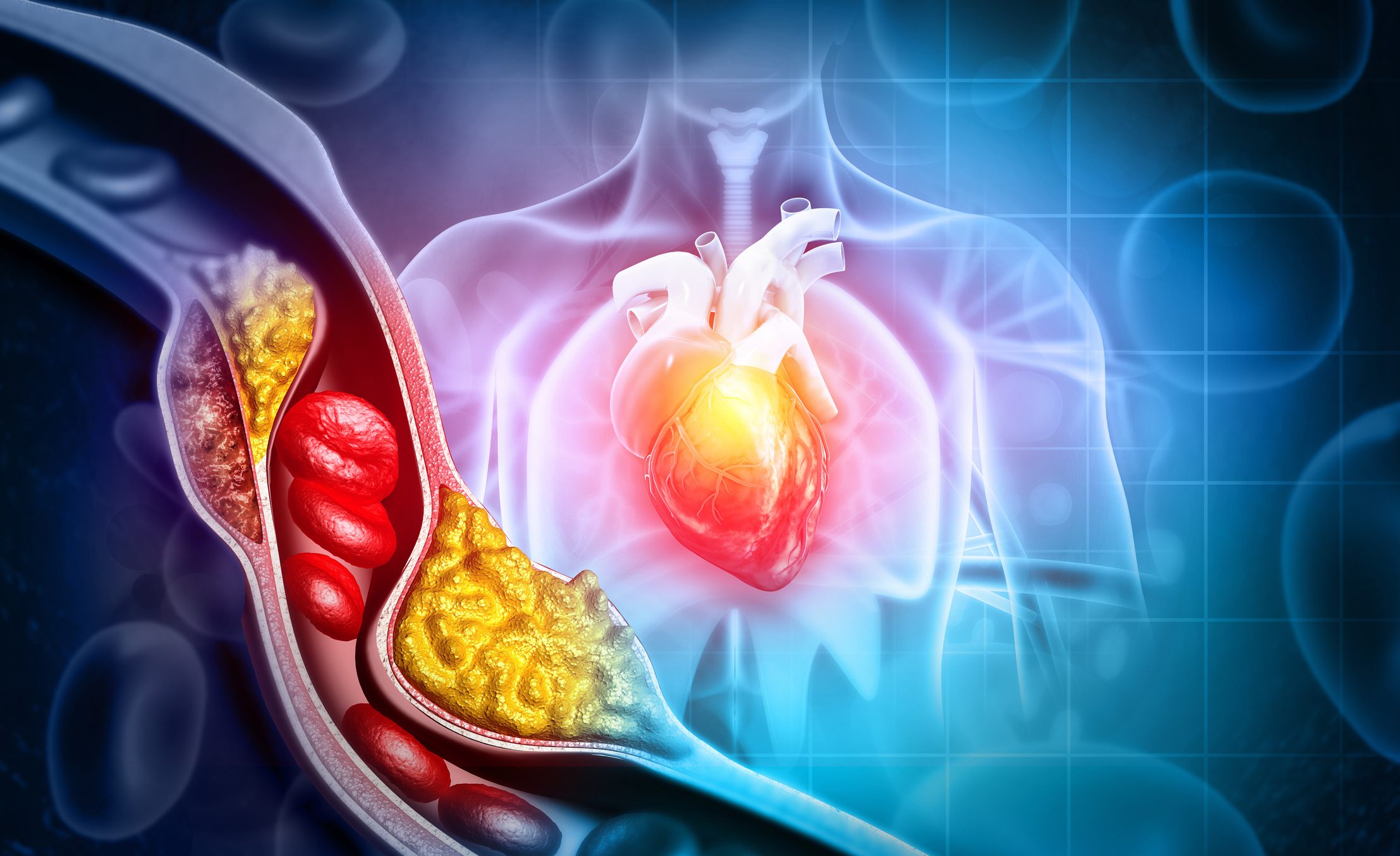
Angina pectoris is traditionally regarded as the leading symptom of coronary sclerosis. Nevertheless, observations show that a relevant proportion of patients with typical angina symptoms have no hemodynamically significant stenoses on invasive coronary angiography (coro). This constellation, often referred to as INOCA (Ischemia and Non-Obstructive Coronary Arteries) or ANOCA (Angina and Non-Obstructive Coronary Arteries), can have various mechanisms – one of which is coronary artery spasm ( CAS).
Autoren
- Tanja Schliebe
Publikation
- CARDIOVASC
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- Oncology
Study updates from the ESMO Congress
- High-dose influenza vaccine
Lower hospitalization rates – even with heart failure
- From statins to metformin
Preventive pharmacology and longevity
- Important basics and studies on cancer and the psyche
Interplay between cancer and mental illness
- From symptom to diagnosis
Abdominal pain – angiosarcoma
- Pediatric epilepsy
Diazepam nasal spray for infants
- Findings from research on the generalization of exposure therapy
Treatment of comorbid anxiety
- Symptom-free despite asthma?