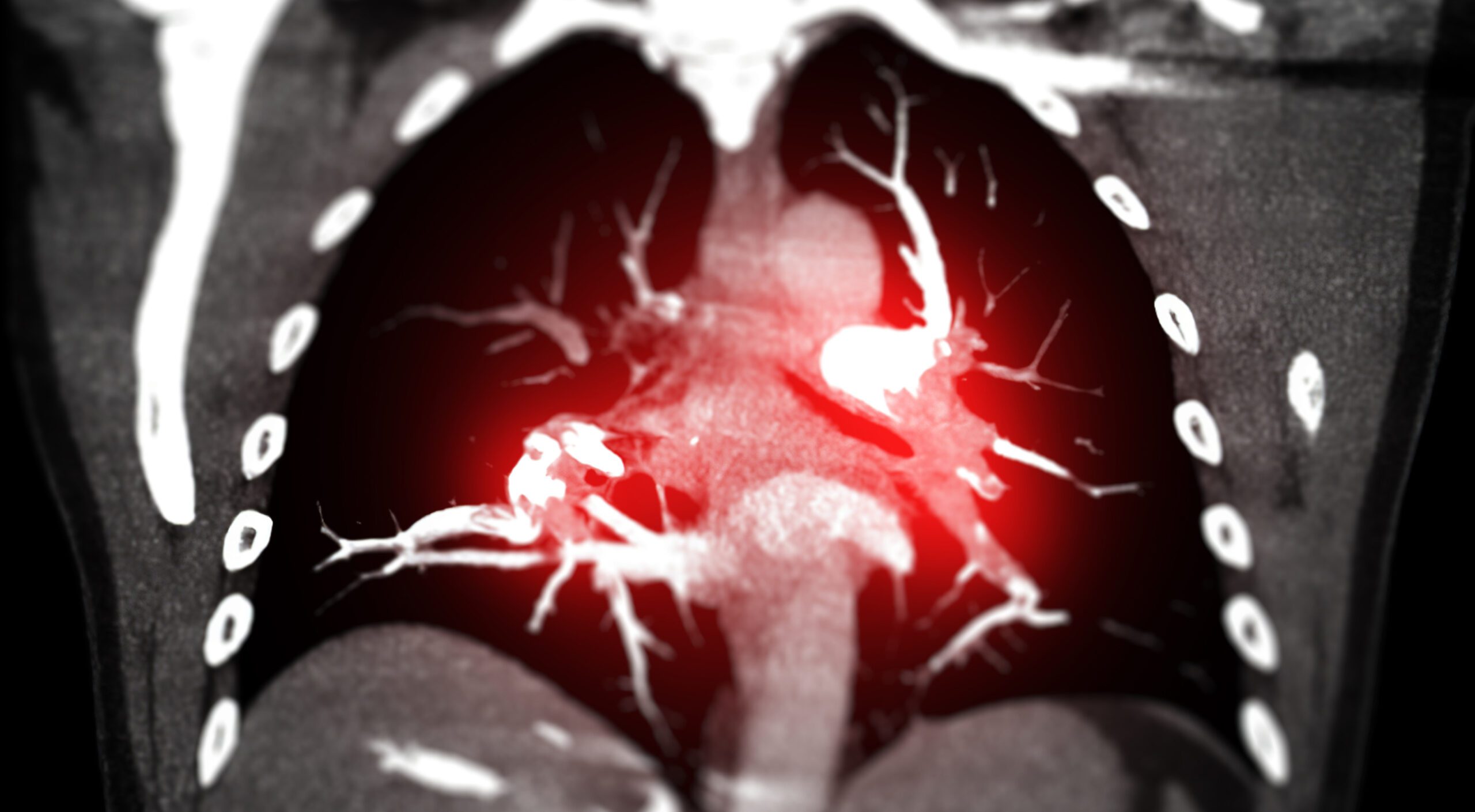
The most common symptoms include acute dyspnea, chest pain, syncope or presyncope and hemoptysis. The spectrum of clinical presentation ranges from asymptomatic patients to hemodynamic instability and shock. The clinical examination findings of the lungs are typically unremarkable. The suspected diagnosis of pulmonary embolism can be confirmed using imaging techniques.
Autoren
- Dr. med. Hans-Joachim Thiel
Publikation
- InFo PNEUMOLOGIE & ALLERGOLOGIE
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- Underestimated risk - findings from a US cohort
Heart failure after myocardial infarction
- AI in neurology
Control instead of a flood of data: AI makes big data and wearables usable
- From symptom to diagnosis
Abdominal pain – Sprue
- Case Report
76-year-old patient with pustular skin rash
- Sponsored Content: Psoriasis
Dauerhafte Erscheinungsfreiheit auch bei betroffenen speziellen Hautarealen
- Antithymocyte globulin in children with T1D
Old medicine, new hope
- Ginkgo biloba
Database of preclinical and clinical studies is becoming increasingly larger
- Digital biomarkers