Findings from long-term studies demonstrate the sustained therapeutic success of the toll-like receptor agonist imiquimod in the indication area of small superficial basal cell carcinomas. Early detection and treatment is critical to the progression of this common form of white skin cancer.
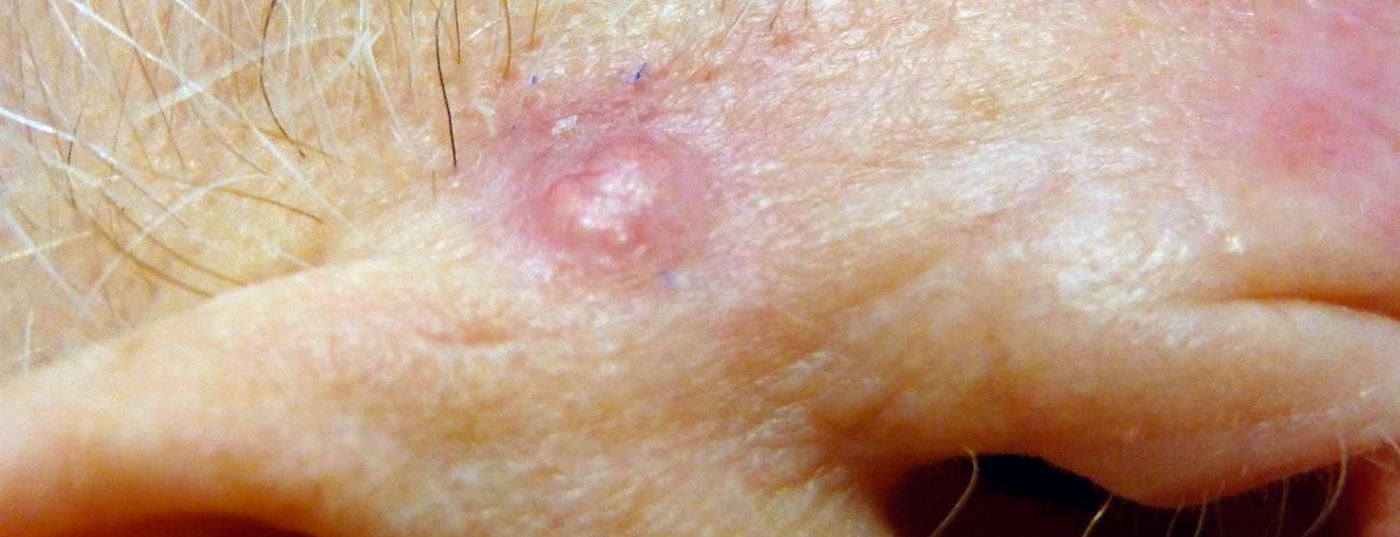
In Central Europe, basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common subtype of non-melanocytic skin cancer with a prevalence of about 80%. The remaining 20% are distributed between squamous cell carcinomas and its precursor, actinic keratoses [1]. In addition to genetic predisposition (fair skin type), UV exposure of the skin through excessive sunlight exposure is an important etiopathogenetic factor. While surgical excision is the treatment of choice for nodular and cirrhotic BCC, superficial BCC can be treated alternatively with cryotherapy, photodynamic therapy, or Imiquimod cream [2].
High success rate in 5-year long-term study
Imiquimod, a substance belonging to the class of synthetic immunomodulators, led to durable treatment success in the indication area of superficial basal cell carcinoma in several recently published long-term studies [3]. The efficacy of this Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonist is based on antiviral, antitumor, and immunoregulatory effects [4]. Stimulation of TLR-7 and TLR-8 induces various immunological processes that play an important role in antitumor effects [5]. TLR-stimulated plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDC) play a key role in the induction and modulation of immune responses. DC are antigen-presenting cells at the interface between innate and acquired immune systems, with pDC activated by TLR7 secreting mainly type I interferons (IFN-alpha/beta) [12].
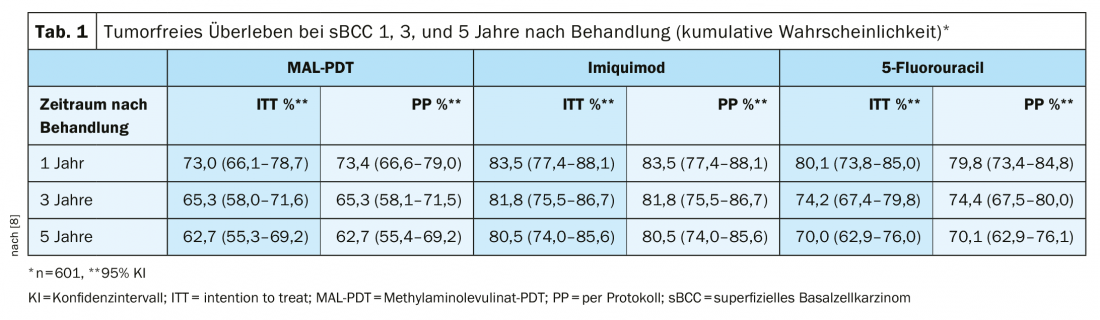
According to the current s2k guideline, the use of Imiquimod 5% cream [6] is recommended for the treatment of superficial basal cell carcinoma, especially in cases of contraindications to surgical removal [7]. The suggested treatment frequency is once-daily application for five days per week, and the treatment duration should be six weeks. In a long-term study published in 2018 (n=601), a proportion of 80.5% of patients with primary sBCC achieved tumor-free survival 5 years after baseline with imiquimod 5%. Thus, this agent proved superior to methyl aminolevulinate (MAL-PDT) and 5-fluorouracil [8] (Table 1) . This is consistent with the results of Williams et al. in patients with superficial and nodular BCC, where the proportion of patients with tumor-free survival 3 and 5 years, respectively, after treatment with imiquimod was approximately 80-85% [9].
High histological cure rate
Complete freedom from lesions 5 years after treatment was reported in a study by Micali et al. detected in a proportion of 77.9-80.4% of patients with sBCC and in 71-76% of those with nBCC [10]. The data from Williams et al. and Micali et al show that there is evidence that imiquimod is also effective in nodular BCC [4]. Imiquimod cream 5% is currently approved in Switzerland and the EU for adults for the treatment of superficial basal cell carcinoma less than 2 cm in diameter in low-risk localizations [6,7]. The histologic cure rate for sBCC is approximately 80% [5,11].
Literature:
- Dermatologikum Wien: White skin cancer, www.dermatologikum.at/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/weisser-hautkrebs.pdf
- Dummer R, et al: Modern management of skin tumors. Swiss Medical Forum 2017, https://medicalforum.ch
- Deinlein T: Therapeutic options for actinic keratoses. Update. Derma 2/2019, www.oeadf.at/images/e-learning/ccDerma_0319_dfp.pdf
- de Rie M: Topical Immune-activation, Prof. Menno de Rie, PhD, MA Amsterdam UMC, EADV Madrid, 12.10.2019.
- Nägeli M, Imhof L, Läuchli S: White skin cancer. Which tumors to cut, which to treat locally, which to irradiate? DERMATOLOGIE PRAXIS 2017; 27(2): 15-18, www.zora.uzh.ch
- Swiss Drug Compendium, www.compendium.ch
- Lang BM, et al: S2k guideline basal cell carcinoma of the skin (2017/18 update), www.awmf.org
- Jansen MHE, et al: Five-Year Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Effectiveness of Photodynamic Therapy, Topical Imiquimod, and Topical 5-Fluorouracil in Patients with Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma. JID 2018; 138: 527-533.
- Williams HC, et al: Surgery Versus 5% Imiquimod for Nodular and Superficial Basal Cell Carcinoma: 5-Year Results of the SINS Randomized Controlled Trial. J Invest Dermatol 2017; 137: 614-619.
- Micali G, et al: Topical pharmacotherapy for skin cancer: part II. Clinical applications. J Am Acad Dermatol 2014; 70(979): 1-12.
- Arits AH, et al: Photodynamic therapy versus topical imiquimod versus topical fluorouracil for treatment of superficial basal-cell carcinoma: a single blind, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 2013; 14: 647-654.
- Drobits B, Holcmann M, Sibilia M: Dendritic cells, Toll-like receptors: Effect of imiquimod in tumor therapy. Spectrum Oncology 3/2012: 143-144.
DERMATOLOGY PRACTICE 2020; 30(3): 31