Pathological obesity is associated with complications in various organ systems. In addition to lifestyle measures and medications, there are several endoscopic procedures to aid in weight loss. However, the long-term benefit is often a critical issue.
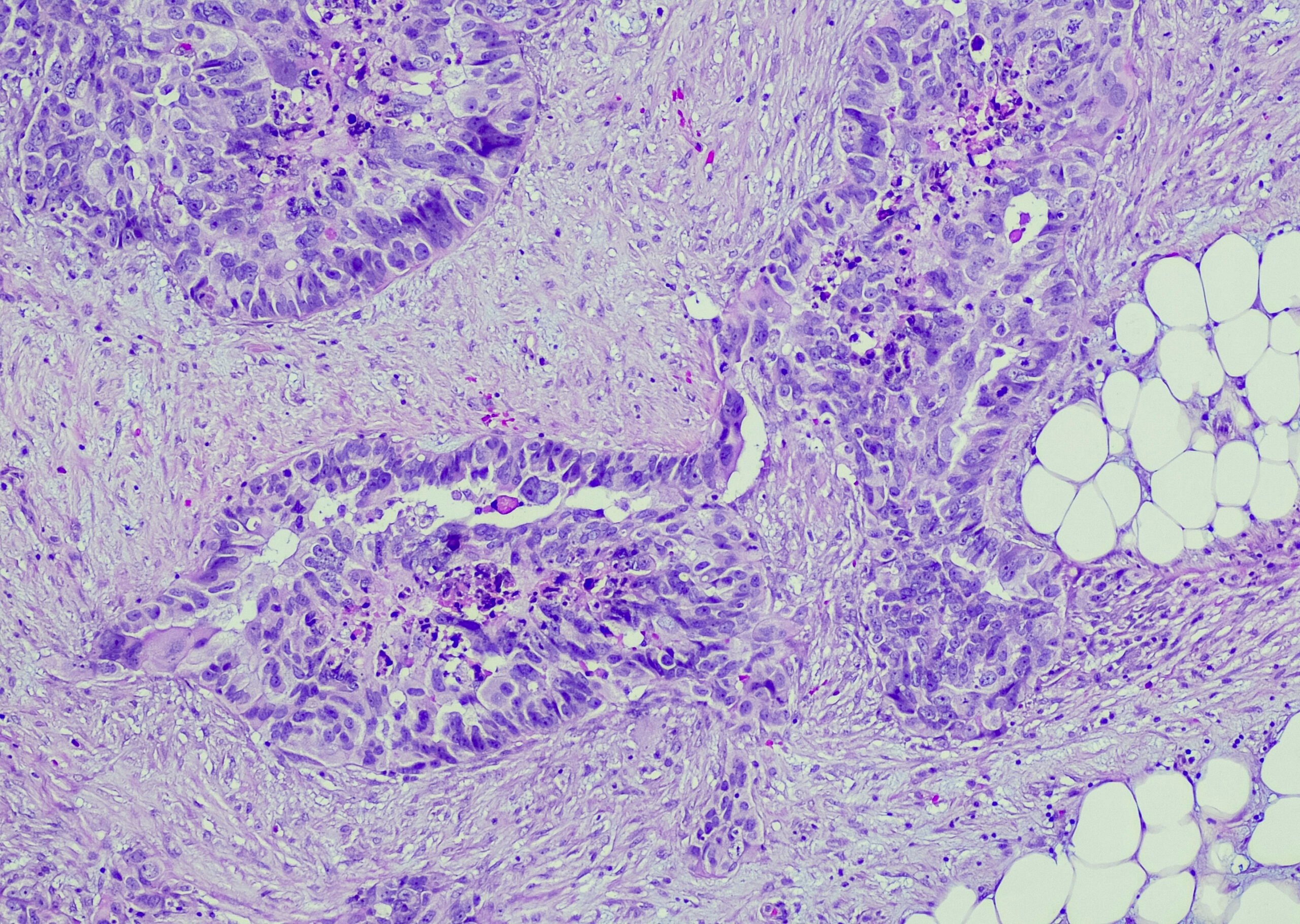
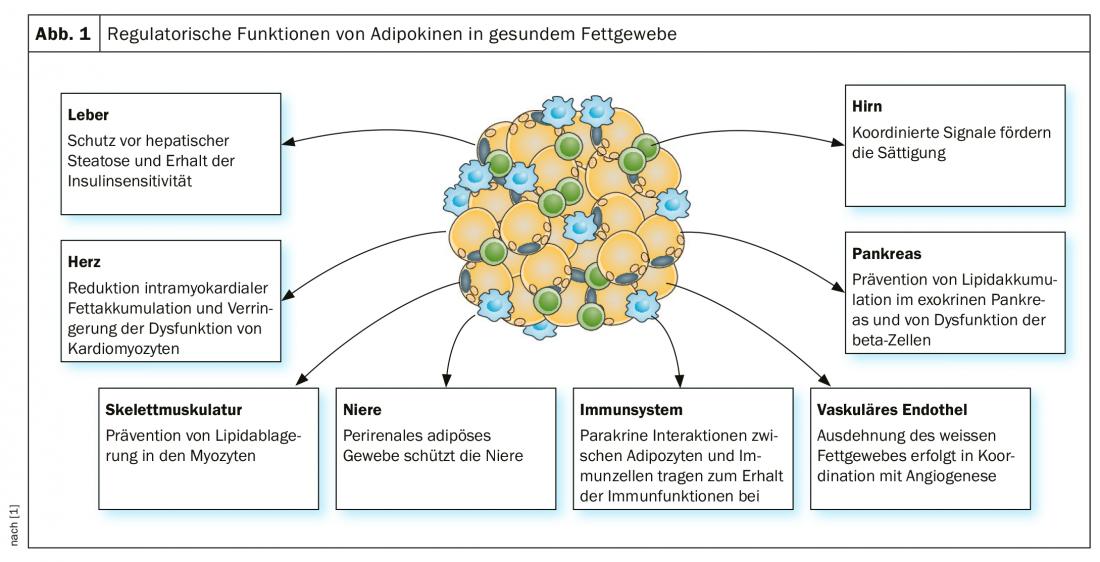
Fatty tissue is not only an energy store, but also fulfills many other functions in the organism. Adipose tissue regulates numerous physiological processes whose dysfunctions in obese individuals are associated with disturbances in metabolic homeostasis, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes [1] (Fig. 1) . Adipokines regulate not only metabolism but also a variety of other processes such as appetite and inflammation. In his presentation, PD Dr. med. Jörn M. Schattenberg, University Medicine Mainz (D), explained the metabolic basis of interactions between obese tissue and other organ systems [2].
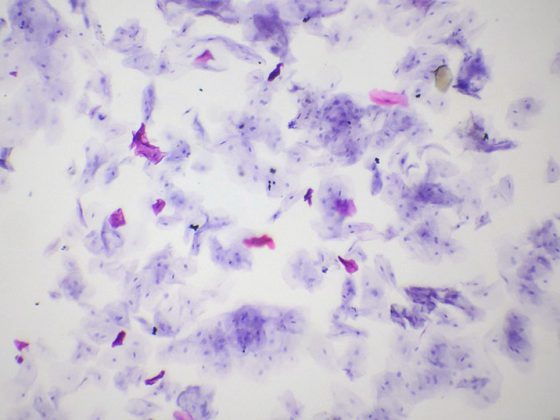
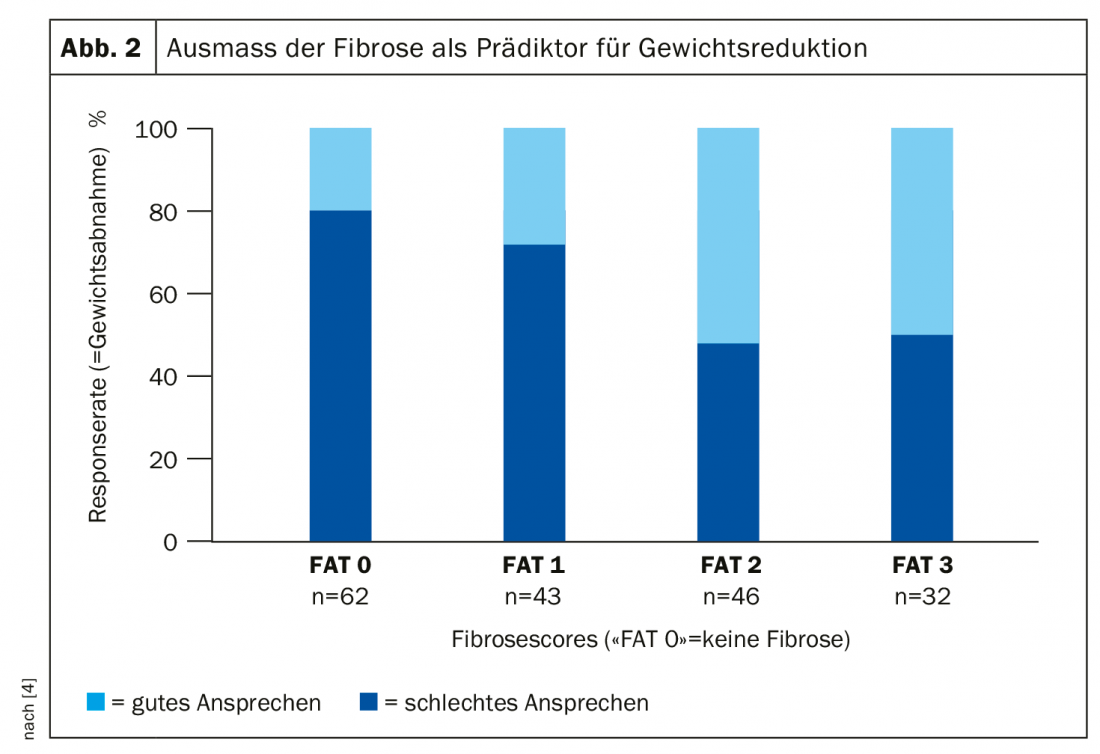
Fibrosis as a predictor of weight loss after bariatric surgery.
In obesity, adipose tissue, mediated by pro-inflammatory mediators, is involved in increased atherogenesis and tumor growth [3]. A distinction is made between brown adipose tissue, which plays an important role in thermogenesis, among other things, and white adipose tissue, which is more strongly involved in inflammatory processes. Among other things, TNF-α, an inflammatory mediator that promotes the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, is secreted by white adipose tissue. The speaker points out that inflammatory processes also play a central role in other health limitations associated with obesity, such as sleep disorders and mood swings/depressive symptoms. At the metabolic level, fibrosis is a possible consequence of chronic inflammation that can occur in various organs. It has been shown that in obese patients, the extent of fibrosis is a predictor of successful weight loss after bariatric surgery by assigning biopsies of subcutaneous adipose tissue to a score (0-3; 0=no fibrosis) and correlating with response rate (weight loss) [4] (Fig. 2).
All endoscopic methods have advantages and disadvantages
Prof. Dr. med. Ralf Kiesslich, Helios HSK Wiesbaden, presented current findings on various endoscopic procedures [5]. An endoscopic tube stomach (“endosleeve”) is a minimally invasive method of assisting weight loss in obesity. In this procedure, the ventriculus is folded in during gastroscopy using a special suturing technique, resulting in a volume reduction of up to 70%. Stomach passage for food is slowed, promoting a quick and long-lasting feeling of satiety. It could be empirically proven that patients with “endosleeve” or gastric balloon achieved a higher weight loss with appropriate diet than patients without these interventions, but in the long term a yo-yo effect often set in, the speaker explained [5].
After realizing that it is crucial for the food pulp to reach deeper layers of the small intestine, a procedure was developed using a plastic tube based on the principle of a stent (“endobarrier”). In contrast to 2016 when, due to short-term positive effects on weight as well as on diabetes-related parameters, the opinion prevailed that “Endobarrier” should be used as primary therapy in obese diabetic patients, there is now much skepticism. This is because long-term data showed that the rates of liver abscesses were significantly higher in patients with “endobarriers”, so that this procedure was withdrawn from the market again [5]. The speaker mentions a procedure using a swallowable gastric balloon as another method to aid weight loss. This system has led to positive effects on weight reduction and other parameters in a study, but has not yet been approved for the market, the speaker said. According to a comparative study published in 2018 [6], all four procedures result in similar weight loss within a 12-month period – none of the methods showed significant superiority. The speaker pointed out that when interpreting the results, it should be noted that this was not a randomized study.
Lifestyle modification alone can also theoretically be useful for weight loss in individuals with morbid obesity, but the hurdles are high. For longer-term positive effects, dietary changes must take place over a period of at least 12 months, so that a reprogramming of relevant metabolic processes occurs, the speaker said. With regard to exercise, at least 12,000 steps per day were required for a measurable benefit in terms of weight reduction.
Source: DGIM Wiesbaden (D)
Literature:
- Kusminski CM, Bickel PE, Scherer PE: Targeting adipose tissue in the treatment of obesity-associated diabetes. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2016; 15(9): 639-660.
- Schattenberg JM: Obesity: the endocrine active fat cells or: the different shades of fat, slide presentation, PD Jörn M. Schattenberg, MD. Universitätsmedizin Mainz (D), Obesity and its consequences in gastroenterology, DGIM May 5, 2019, Wiesbaden (D).
- Stulnig T: Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ, Journal of Nutritional Medicine, www.jem-online.at/expertenbericht/fettgewebe-als-endokrines-organ-189.html
- Bel Lassen P, et al: The FAT Score, a Fibrosis Score of Adipose Tissue: Predicting Weight-Loss Outcome After Gastric Bypass. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2017; 102(7): 2443-2453.
- Kiesslich R: Obesity and endoscopy: what to consider? Slide presentation, Prof. Dr. med. Ralf Kiesslich, Helios HSK Wiesbaden (D), Obesity and its consequences in gastroenterology, DGIM May 5, 2019, Wiesbaden (D).
- Lopez-Nava G, et al: Comparison of 4 Bariatric Endoscopy Techniques: Is there any one better at 1 year? Gastrointestinal Endoscopy 2018; 87(6); Supplement AB67-AB68.
HAUSARZT PRAXIS 2019; 14(11): 26-27 (published 11/21/19, ahead of print).