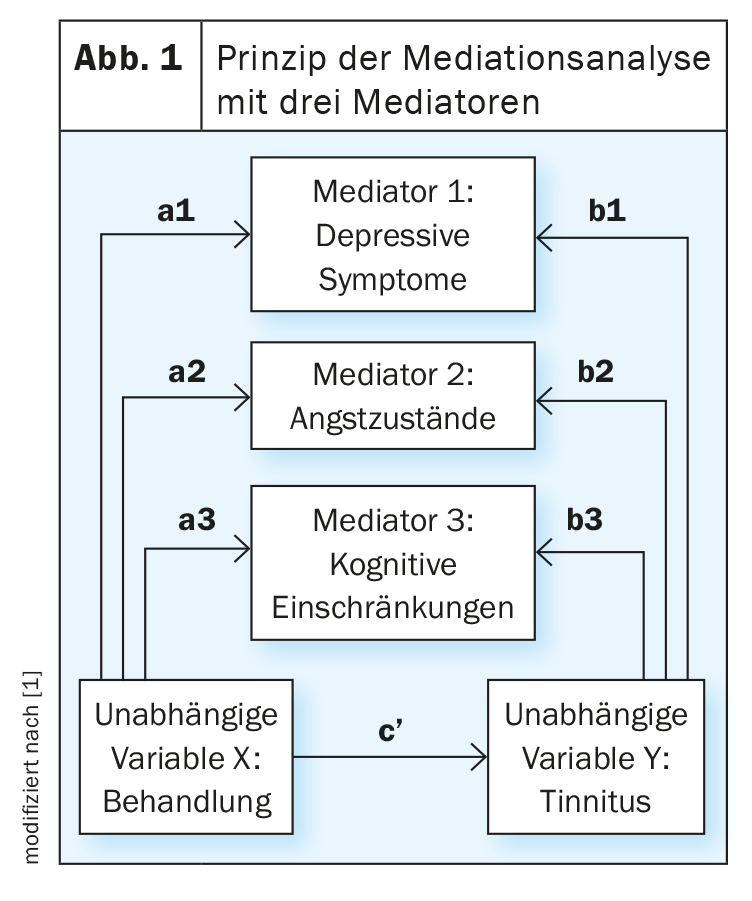
A research team involving the Tinnitus Center at Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin (D) demonstrated in a mediation analysis that tinnitus patients benefit from treatment with a high-quality Ginkgo biloba extract, with efficacy mediated in part by improvements in anxiety, depression, and cognitive impairment.
The high prevalence of tinnitus in patients with dementia is not surprising, as tinnitus-with or without hearing loss-affects a variety of cognitive functions and thus may contribute to the development of a dementia-related problem [1]. Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761® has been shown to be effective in reducing neuropsychiatric symptoms in elderly patients with dementia and tinnitus, and the underlying mechanism of action is multifactorial [1,2]. To determine how much of the overall effect of EGb 761® on tinnitus can be explained by direct effects and what proportion is brought about indirectly by improvement in depressive and anxious symptomatology, Brüggemann et al. performed a mediation analysis that appeared in the Journal of Clinical Medicine 2021 [1].
Pooled data from three RCTs
Included were three randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind studies of the efficacy of EGb 761® (240 mg/d; 22-24 weeks) in a total of 594 tinnitus patients with dementia and neuropsychiatric symptoms [1,3–5]. Tinnitus severity was assessed using the “11-point box” scale (0=no tinnitus, 10=extremely severe tinnitus) [6,7]. The “Neuropsychiatric Inventory” (NPI), an interview-based assessment of neuropsychiatric symptoms [8], was used to assess depression and anxiety. The extent of cognitive impairment was measured by the total score in the “Short Cognitive Performance Tests” (SKT) (low scores=better performance) [9,10]. In each of the three RCTs, EGb 761® was administered at the dose of 240 mg daily [11]. The duration of treatment was 22 or 24 weeks. Test-diagnostic measurements (“11-point box” scale, NPI, SKT) were taken at screening and baseline, respectively, and at study midterm and end of treatment (weeks 22 or 24).
Conclusion: EGb 761® especially useful for older tinnitus patients
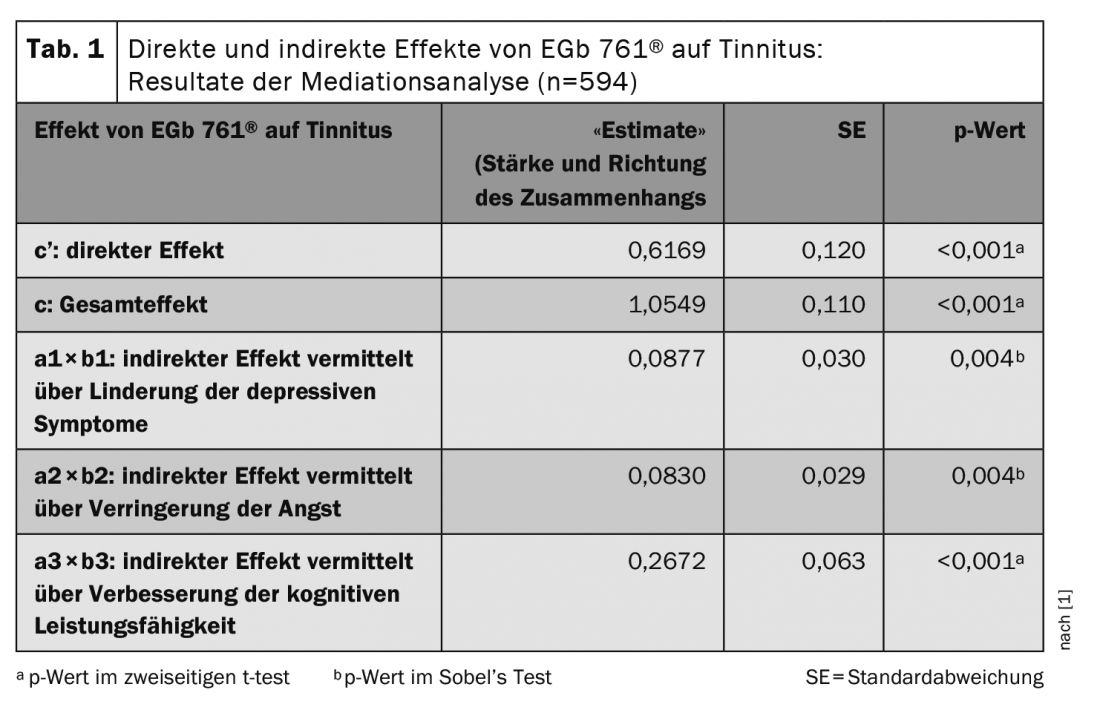
Mediation analyses aim to test whether the relationship between two variables is mediated by other factors (Fig. 1) [12]. The results of the work by Brüggemann et al. show that the direct effect of EGb 761® on tinnitus accounts for 58.5% of the total effect and 41.5% of the total effect is indirectly brought about by an improvement in neuropsychiatric symptoms (p<0.001 and p ≤0.004, respectively) [1]. Table 1 shows the strength and direction of the respective correlations (“Estimate”). From the results of the mediation analysis available at , it can be inferred that EGb 761® is useful as a supportive treatment for tinnitus in elderly patients with dementia, with an additional benefit in patients with depression or anxiety. Regarding mechanisms of action, it is known, among other things, that EGb 761® modulates neuronal signal transmissions and increases blood flow [2].
Literature:
- Brüggemann P, Sória MG, Brandes-Schramm J, Mazurek B: J Clin Med 2021; 10(14): 3151.
- Lang F, et al: In: Wagner H, Ulrich-Merzenich G (eds). Evidence and Rational Based Research on Chinese Drugs. Vienna 2013: Springer.
- Napryeyenko O, Borzenko I, GINDEM-NP Study Group: drug research 2007; 57: 4-11.
- Ihl R, et al; GOTADAY Study Group: Int J Geriatr Psychiatr 2010; 26: 1186-1194.
- Herrschaft H, et al: J Psychiatr Res 2012; 46: 716-723.
- Hawker GA, et al: Arthritis Care Res 2011; 63(Suppl. S11): S240-S252
- Adamchic I, et al: Am J Audiol 2012; 21: 215-225.
- Cummings JL: Neurology 1997; 48(Suppl. S6): 10S-16S.
- Erzigkeit HA: SKT Manual. Concise Version. Geromed GmbH; Castrop-Rauxel, Germany: 1992.
- Lehfeld H, et al: GeroPsych 2014; 27:75-80.
- Le Bars PL : Pharmacopsychiatry 2003; 36(Suppl. S1): S44-S49.
- Oostermeijer M, Boonen AJ, Jolles J: Front Psychol 2014; 5: 782.
HAUSARZT PRAXIS 2022; 17(2): 33