An 80-year-old patient with dysphagia and upper abdominal discomfort is evaluated radiologically. Diagnosis: paraesophageal gastric hernia. What therapy should the patient receive?
Background: The 80-year-old patient complains of dysphagia and upper abdominal discomfort. Due to a myocardial infarction in the immediate family, the patient is very worried. He also complains of sleep disturbances.
History and Diagnosis: The patient shows no abnormalities on comprehensive cardiac examination. Referral to the radiologist and examination of the function of the esophageal phase by means of esophageal breakthrough swallow reveals coarsened mucosal relief of the distal esophagus, DD inflammatory alteration possible (Fig. 1) . The diagnosis of paraesophageal gastric hernia is made.
Therapy: Which therapy would you choose?
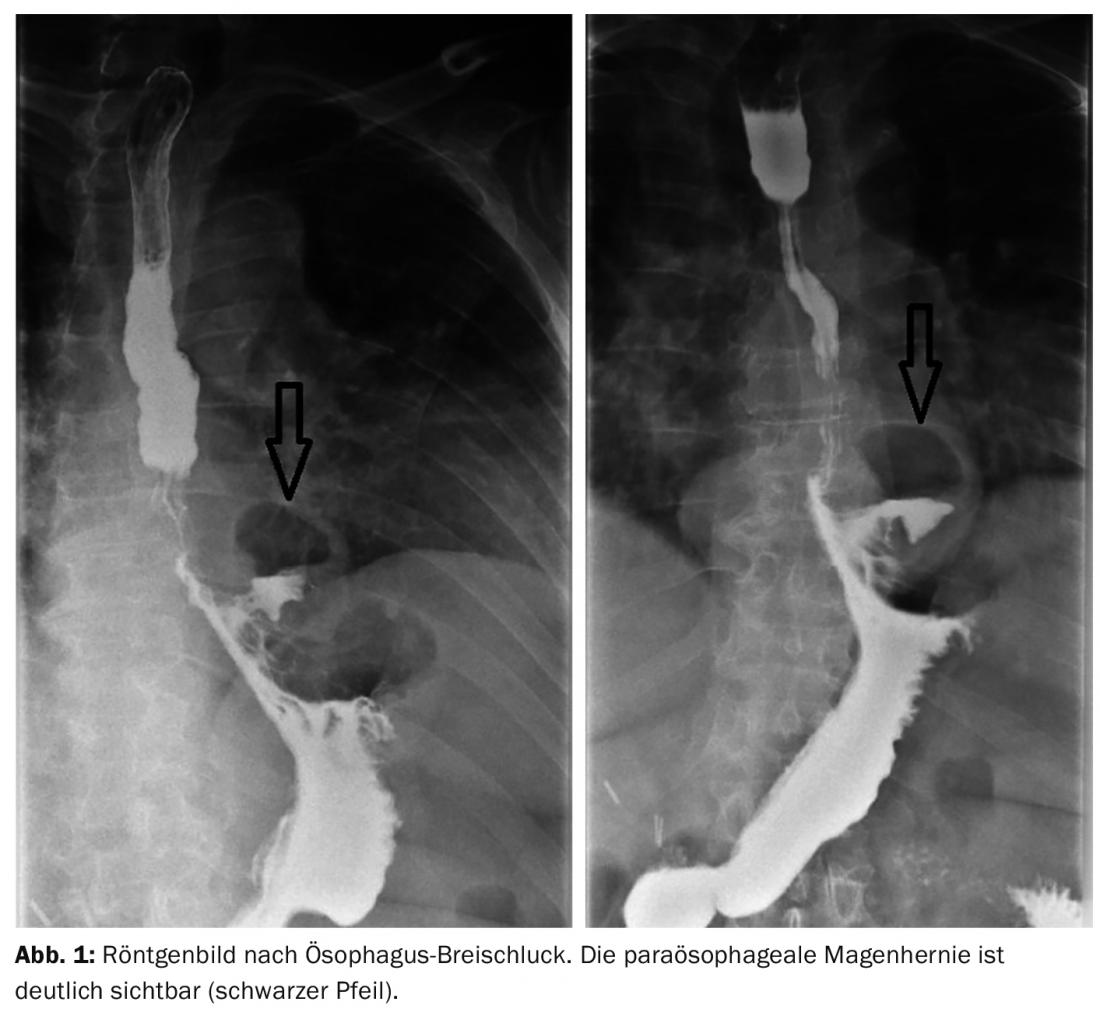
Answer: While an axial hiatal hernia can initially be treated conservatively with proton pump inhibitors and the indication for rehabilitation is only given after unsuccessful PPI therapy, intolerance and risk of bleeding, paraesophageal hiatal hernia requires immediate surgery due to the high risk of complications. Remediation is performed by laparoscopic fundoplication in combination with hiatoplasty.
GP PRACTICE 2019; 14(5): 38