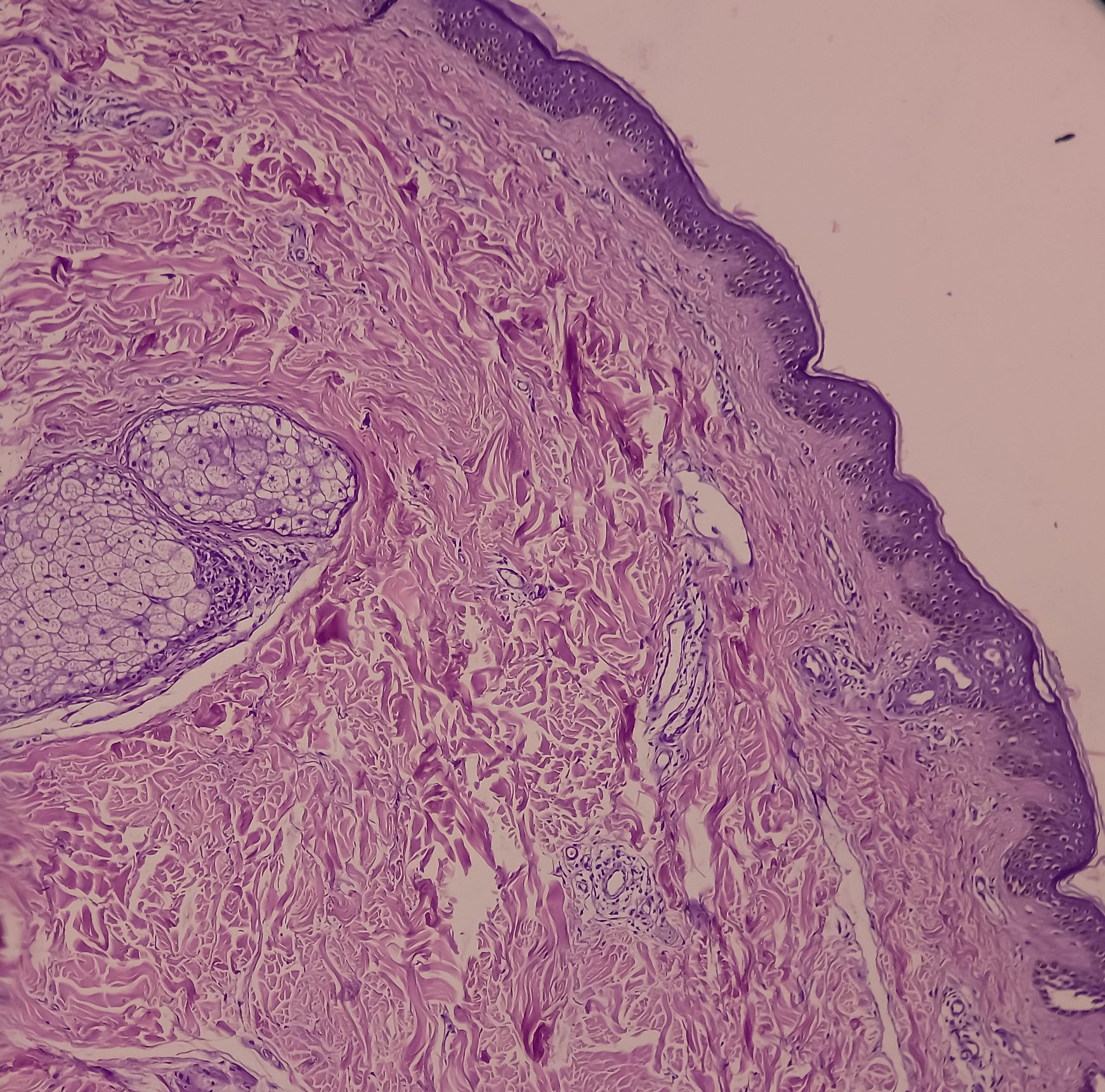
Pemphigus diseases are potentially life-threatening, blistering autoimmune diseases. Acantholysis is detected by skin or mucosal biopsy. In this case study, an 82-year-old man was referred for a dermatological examination due to a generalized exanthema affecting the oral mucosa. The skin and mucosal changes had started two months ago and were accompanied by blistering, pain and pruritus.
Autoren
- Mirjam Peter, M.Sc.
Publikation
- DERMATOLOGIE PRAXIS
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- GLA:D® program for back pain patients
Fewer consultations and reduction in the use of painkillers
- Nutrition for type 2 diabetes
Not such a great tuber
- From symptom to diagnosis
Abdominal pain – external hernias
- Mechanisms, evidence and therapeutic consequences
GLP-1 receptor agonists in cardiology
- MASLD/MASH
Drug therapy options on the rise: spectacular evidence
- New ways of neuroregeneration
CRISPR and artificial intelligence
- Asbestos victims
Federal Council has decided to amend the UVG
- Music as a cure for cancer?