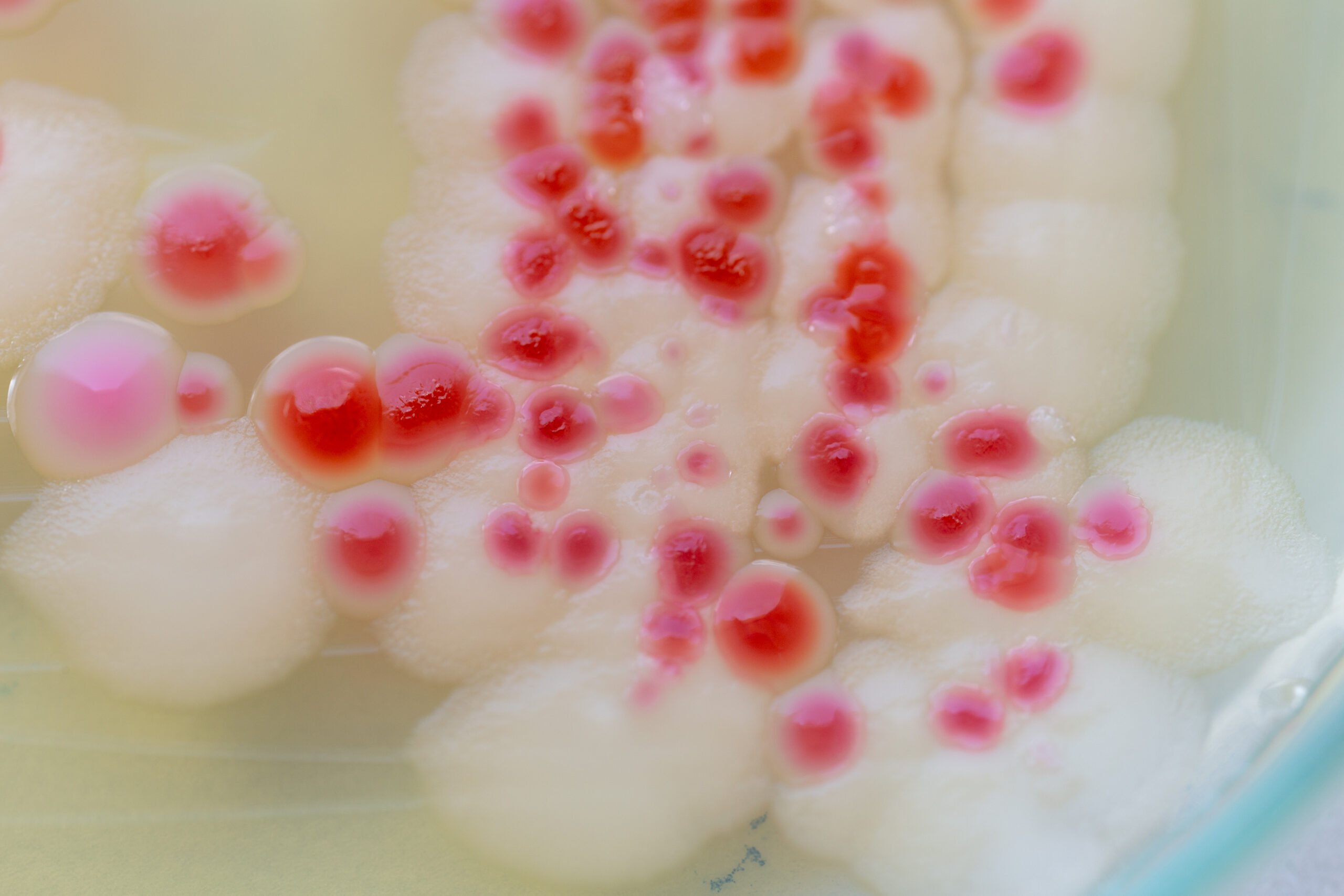
Immunocompromised individuals sometimes have a considerably increased risk of opportunistic infections. Serratia marcescens is a Gram-negative bacterium that belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family and was identified as the pathogen in this case in a 69-year-old woman with metastatic lung cancer who was undergoing chemotherapy and had various secondary diagnoses. After a week of antibiotic treatment, the patient’s condition improved and she was discharged from hospital.
Autoren
- Mirjam Peter, M.Sc.
Publikation
- HAUSARZT PRAXIS
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- "Forgotten axis" between plant substances, gut and systemic health
Microbiome and phytotherapy
- HIV: updated EACS guideline
Individualized approach to sustainable prevention and care
- Evidence-based diagnostics and treatment in the medical setting
Anxiety and depression disorders in adolescence
- Neuroenhancement
Can you swallow intelligence? Relevant substance classes times for healthy people
- Microbiome, inflammaging and affective/cognitive health
Gut-brain axis in old age
- Vitiligo - the level of suffering should not be underestimated
A lot can be achieved therapeutically nowadays
- Vector-borne infections with skin manifestations
Arboviruses and leishmaniasis in Europe
- Patient-centered rounds in medicine