For years, Ginkgo biloba research focused on improving cognitive abilities or prevention. In this context, many studies with the Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 have shown positive results. Recently, mental disorders and behavioral problems have also been included.
The following article summarizes a recently published systematic review that investigated the efficacy of the Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 in dementia with psychological and behavioral symptoms of dementia (BPSD) [1]. These are also known as neuropsychiatric symptoms and are present in 80 to nearly 100% of patients affected by dementia.
Method
Studies that met the following criteria were sought for the review:
- randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials
- Patients with a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, or mixed forms (present for at least 22 weeks at recruitment).
- Patients with BPSD according to the Neuropsychiatric Inventory (NPI) or another recognized standard test.
- At least two of the following three parameters had to be included in the assessment: Cognitive functions, Activities of Daily Living (ADL), overall clinical assessment.
The methodological quality of the studies was considered sufficient if it met the standard for the following factors:
- Randomization, assignment, and blinding
- Sample size
- Number of patients who dropped out of the study early, and the rationale for this
- statistical analysis and evaluation.
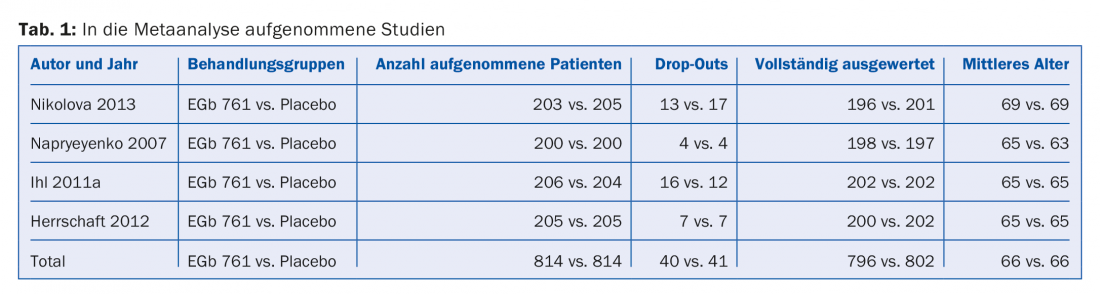
Studies
Four studies met the criteria (Table 1) [2–5]. All patients in these four studies were diagnosed with mild to moderate dementia according to TE4D-Cog (Test for the Early Detection of Dementia from Depression) and SKT (Short Cognitive Performance Test). The characteristics were:
- TE4D-Cog ≤35
- SKT between 9 and 12
- No major depression (HAMD ≤20).
- Age ≥50 years.
Results
The following dimensions were assessed:
- Cognitive functions
- BPSD
- ADL
- Overall assessment
- Quality of Life (QoL).
Cognitive functions: Results pooled with all four studies showed an improvement of 2.26 ± 3.15 scale points for the verum group versus 0.20 ± 3.48 for placebo. This indicates significant superiority of EGb 761 over placebo (p<0.001).
Neuropsychiatric symptoms (BPSD): All studies reviewed neuropsychiatric symptoms using the NPI or NPI caregiver distress (method for assessing caregiver stress symptoms). In all four studies, patients in the EGb 761 group showed an improvement of at least three scale points. In three of the four studies [2–4] this meant a significant improvement over placebo.
Pooled results from all studies showed significant improvement in both patients and caregivers (p<0.001) with EGb 761 versus placebo (patients: EGb 761 4.52 ± 6.56, placebo 0.71 ± 6.94; nurses: EGb 761 2.64 ± 4.44, placebo 0.33 ± 3.98).
Activities of daily living (ADL): Two studies [2,5] used the ADL subscale of the Gottfries-Bråne scale to assess activities of daily living, and the other two [3,4] used the ADL International Scale (ADL-IS). In all studies, competence for activities of daily living improved more in EGb 761 patients than in placebo patients. Pooling the results of the four studies showed a significant improvement with EGb 761 over placebo (p<0.001).
Overall Assessment: Overall assessment was performed using either the GBS [2,5] or the Alzheimer Disease Cooperative Study Clinical Impression of Change (ADCS-CGIC) [3,4]. In all four studies, EGb 761 patients performed better than placebo patients. In three studies, these values reached significance [2–4]. Pooling of all four studies showed significance for the EGb 761 groups (p<0.001).
Quality of life: Two studies determined health-related quality of life (DEMQOL-PROXY mean score) [3,4]. Significant improvements were found for the EGb 761 groups in both studies, which of course confirmed the pooling of the results of the two groups (p<0.001).
Subgroup evaluation: A subgroup evaluation with respect to the different dementia groups showed a significant improvement with EGb 761 in all three groups (AD, VaD, mixed form), except for the parameter QoL in the very small subgroup VaD.
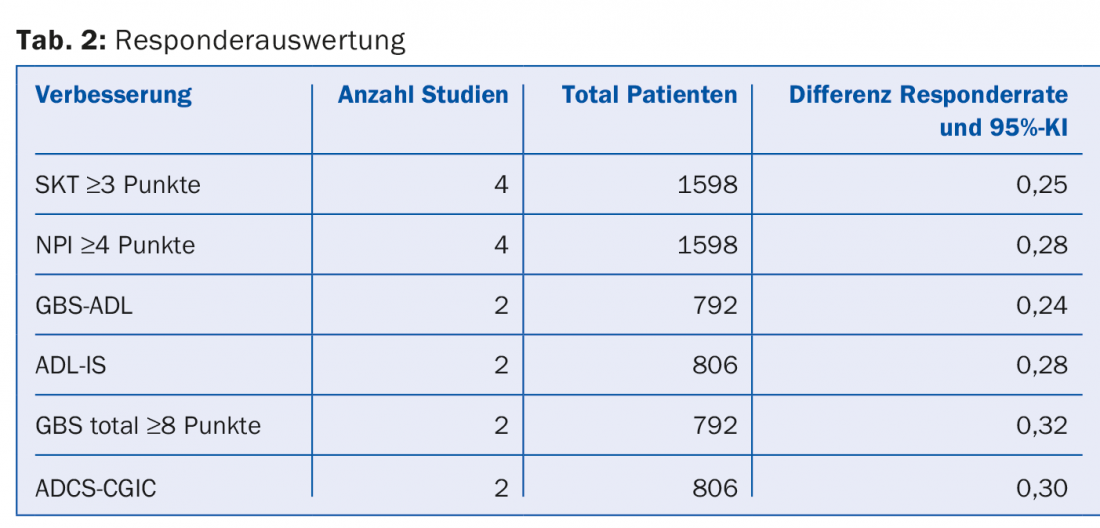
Responder analyses: Responders were defined as patients with the following improvements in accordance with international standards (Table 2):
- Cognitive functions: 4 points on the ADAS-cog scale.
- NPI: 4 points
- ADL: any improvement observed within five to six months by an independent physician.
- Global assessment: 8 points.
Safety and compatibility
Adverse events documented in the placebo groups were more numerous than in the EGb 761 groups, and none of these events could be linked to EGb 761.
Summary
The pooled results of the review illustrate the evidence-based efficacy of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 in the treatment of dementia patients with BPSD. Compared with placebo, EGb 761 was found to be statistically and clinically significantly superior in terms of improvement in cognitive function, BPSD, activities of daily living, quality of life, and in terms of global assessment. This significant superiority of EGb 761 was also evident in the individual analysis of three of the four studies [2–4].
Similarly, EGb 761 proved significantly superior in all but one of the subgroup evaluations.
For the treatment of dementia associated with neuropsychiatric symptoms (BPSD), Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 is not only an effective therapy, but is also characterized by its great safety and tolerability.
Literature:
- von Gunten A, Schlaefke S, Überla K: Efficacy of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 in dementia with behavioral and psychological symptoms: a systematic review. The World Journal of Biological Psychiatry 2015; 1-12. Doi:10.3109/156229975.1066513.
- Napryeyenko O, Borzenko I: Ginkgo biloba special extract in dementia with neuropsychatric features. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Drug Research 2007; 57: 4-11.
- Ihl R, et al.: Efficacy and safety of a once-daily formulation of Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761in dementia with neuropsychiatric features. A randomized controlled trial. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 2011a; 26: 1186-1194.
- Herrschaft H, et al: Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761 in dementia with neuropsychiatric features: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial to confirm the efficacy and safety of a daily dose of 240 mg. J Psychiatr Res 2012; 46: 716-723.
- Nikolova G, et al: Ginkgo biloba extract in dementia: a 22-week randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Bulgarian Neurology 2013; 14: 139-143.
HAUSARZT PRAXIS 2016; 11(6): 2-3