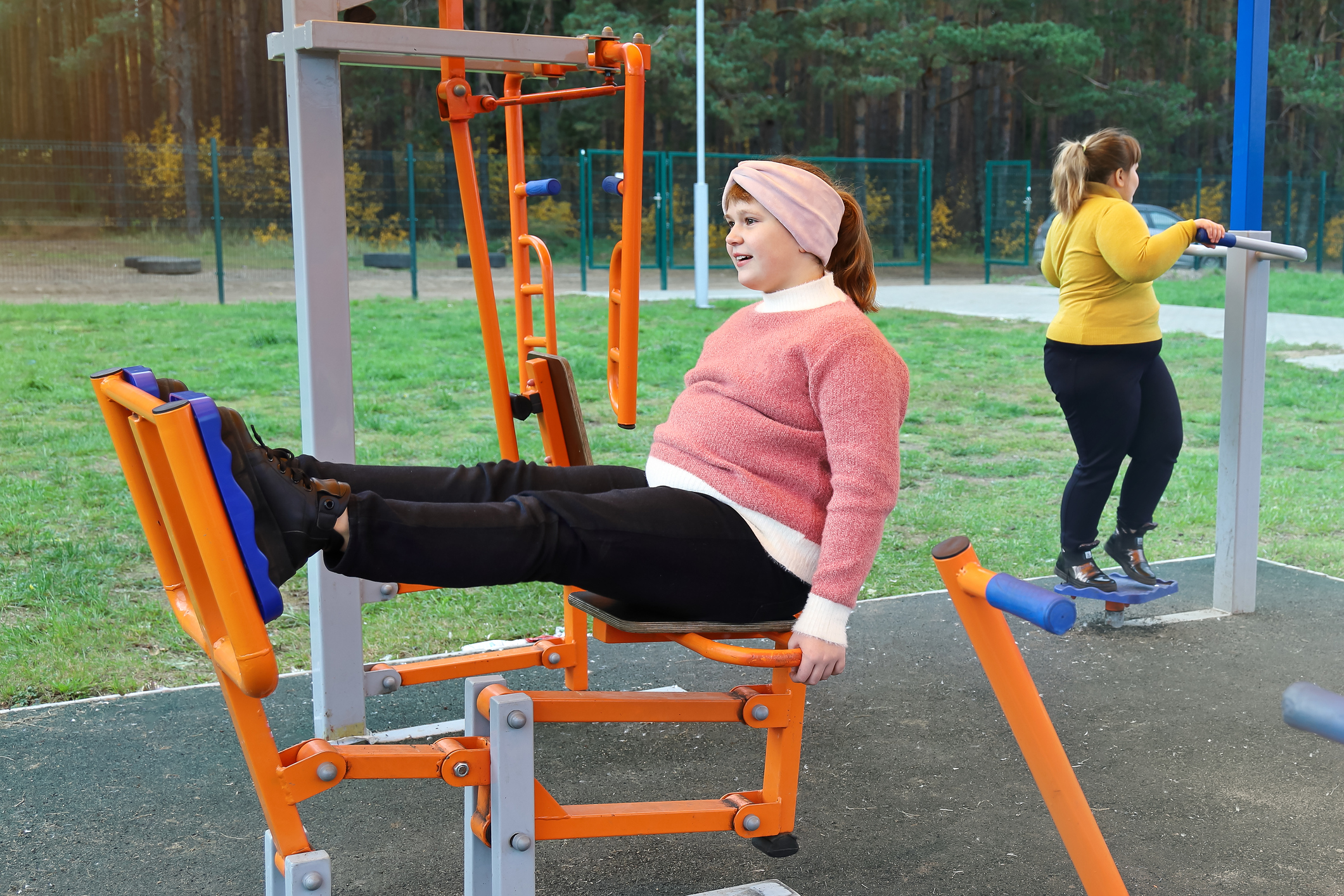
The prevalence of obesity in children and adolescents has risen in recent decades. The categorization of BMI is age- and gender-specific. Studies show that BMI status at a young age is predictive of adulthood. However, in some cases, weight management measures are successful, which also has important implications for the development of comorbidities. Multimodal treatment approaches aim to achieve a sustainable reduction in body weight and associated health risks.
Autoren
- Mirjam Peter, M.Sc.
Publikation
- HAUSARZT PRAXIS
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- Restless legs syndrome in children
Relationship between restless legs syndrome and growing pains
- Between hope and evidence gaps
Tinnitus and phytotherapy
- Case Report
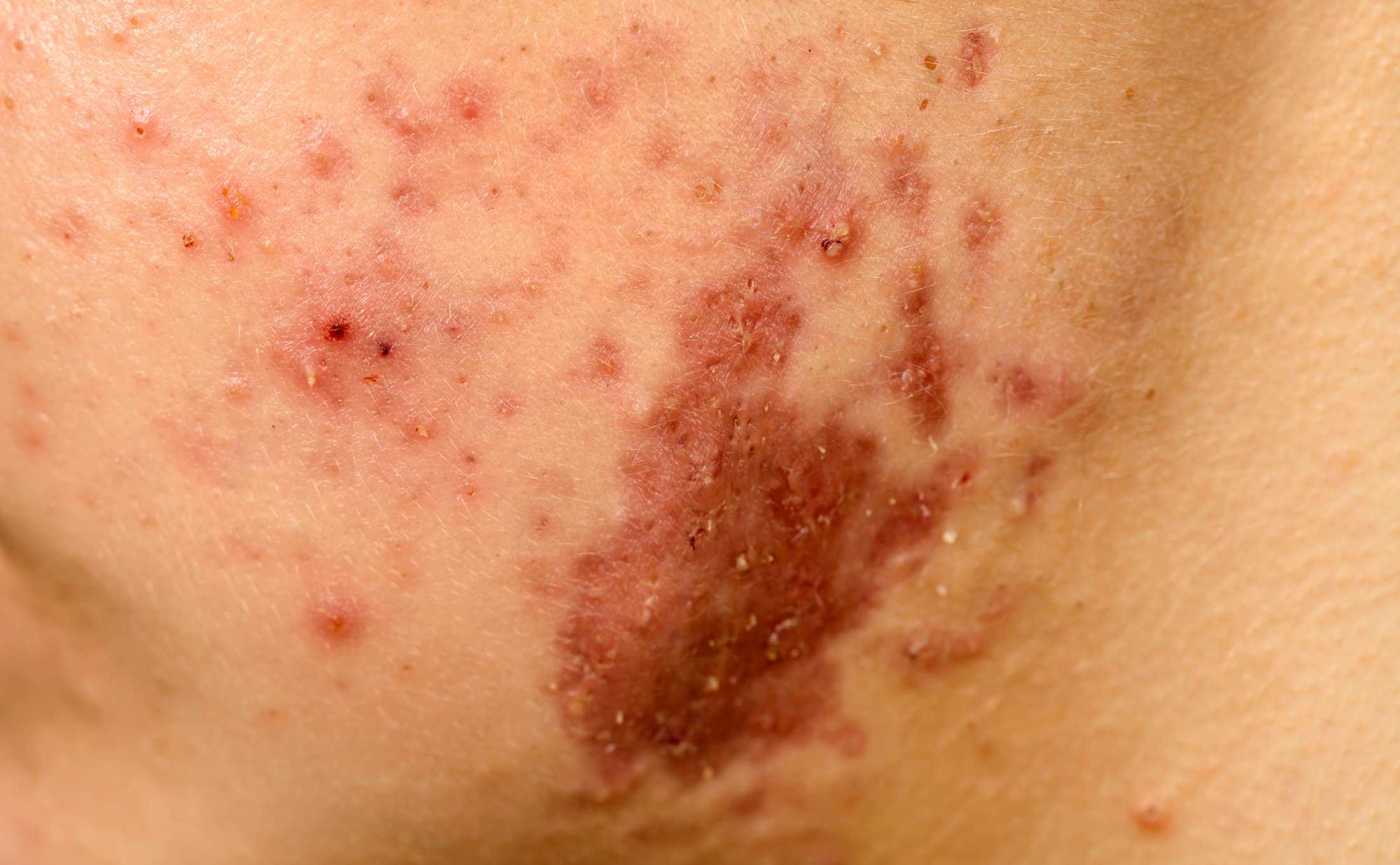
17-year-old patient with acne fulminans
- Oncology
Study updates from the ESMO Congress
- High-dose influenza vaccine
Lower hospitalization rates – even with heart failure
- From statins to metformin
Preventive pharmacology and longevity
- Important basics and studies on cancer and the psyche
Interplay between cancer and mental illness
- From symptom to diagnosis