Polyneuropathies are generalized disorders of the peripheral nervous system and, with a prevalence of 5-8%, are most common in patients with chronic alcohol abuse, diabetes, or malignancies. In addition to therapy for the causative disease, analgesics, antidepressants, or anticonvulsants are usually used to alleviate symptoms.
In polyneuropathies (PNP), the motor, sensory and autonomic nerves all affect those parts of the nervous system that lie outside the central nervous system. Distal symmetric PNP is most common, starting in the legs, with a neuronal axonal length-dependent disease process as the causative factor. In addition, polyradiculoneuropathies with proximal and distal involvement or mononeuropathia multiplex with an asymmetric clinical picture may also occur. The pain associated with PNP occurs due to damaged or destroyed nerve fibers, which disrupts the transmission of stimuli.
Multiple causes
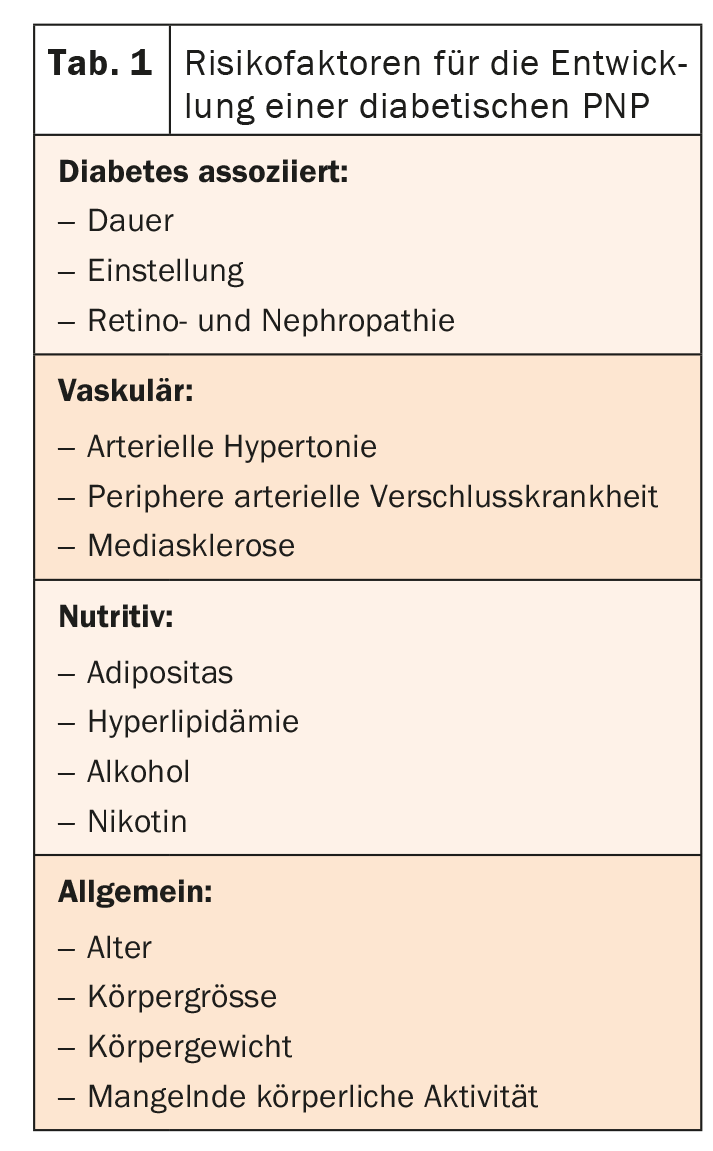
Often PNP are consequences of other diseases such as advanced diabetes. Diabetic neuropathy can be detected in nearly half of all type 2 diabetics. The increased blood sugar is held responsible, which damages the corresponding nerves. However, there are other risk factors (Table 1) . In PNP caused by chronic alcohol abuse, the nerves are toxically damaged. Malnutrition does the rest. The duration of abuse as well as the lifetime amount of alcohol play a role in the development. Chemotherapy-induced neuropathies are the most common neurologic side effect of tumor therapy. However, other drugs and environmental toxins can also trigger PNP (Table 2) .
Comprehensive diagnostics
The main focus of the S1 guideline “Diagnosis of polyneuropathies” is on possible triggers such as cancer drugs, the Zika virus, and gene mutations. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in particular can cause neurological side effects. However, organ transplantation, the hepatitis E and Zika viruses, the anti-FGF3 antibody, and mutations of the SCN9A, SCN10A, SCN11A (small fiber neuropathies) genes and the GLA gene can also cause various polyneuropathies. For diagnostic purposes, history, clinical examination, electrophysiology and standard laboratory are mandatory. In addition, an expanded laboratory, CSF diagnostics, muscle/nerve/skin biopsy, genetics, and diagnostic imaging are recommended.
Consistent therapy of the underlying disease and effective symptom control
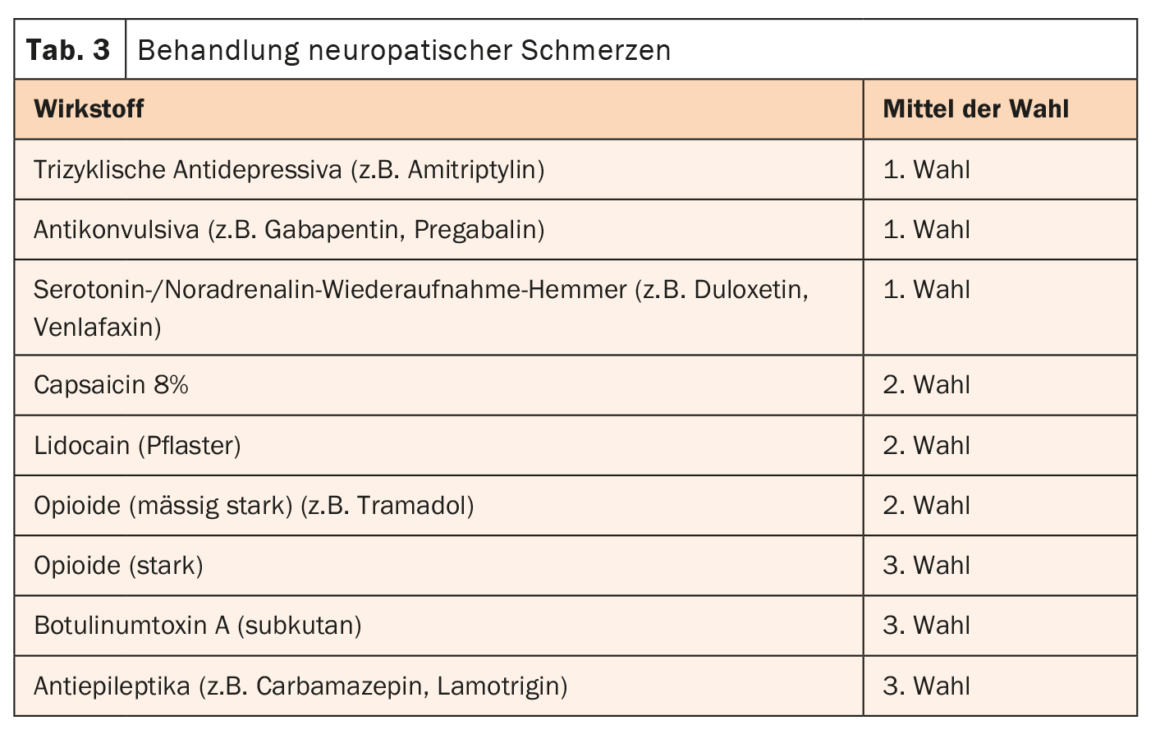
First and foremost, consistent treatment of the causative underlying disease is indicated. Well-controlled blood sugar or abstinence from alcohol can prevent further progression of nerve damage. In addition, the symptoms, first and foremost the pain, must be contained. However, the mechanisms of neuropathic pain are fundamentally different from those of nociceptive pain. Therefore, a special therapy concept is indicated. Analgesics are often not effective. The drugs of choice are primarily tricyclic antidepressants, serotonin/norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, and anticonvulsants (Table 3) .
Further reading:
- www.dgn.org/leitlinien/3754-ll-030-067-diagnostik-bei-polyneuropathien-2019 (last accessed on 25.05.2023)
- www.neurologen-und-psychiater-im-netz.org/neurologie/erkrankungen/polyneuropathie/was-ist-polyneurpathie (last accessed on 25.05.2023)
- Sommer C, Geber C, Young P, et al: Polyneuropathies – etiology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Dtsch Arztebl Int 2018; 115: 83-90. DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2018.008.
InFo NEUROLOGY & PSYCHIATRY 2023; 21(3): 24.