Tendovaginitis de Quervain is a tendovaginitis of the first dorsal tendon compartment of the hand, through which the two tendons of the extensor pollicis brevis muscle and the long abductor pollicis longus muscle pass. With regard to imaging examination procedures, magnetic resonance imaging is considered the gold standard.
The main causes of diseases of the tendon-ligament apparatus are chronic overload or concomitant inflammation in the context of rheumatic diseases [1]. Tendovaginitis, partial and complete tendon rupture, and muscular damage are all possible. Typing on the computer or knitting are common causes of mechanical overload. Tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain is a special form of tendovaginosis with isolated involvement of the extensor thumb tendon in the region of the styloid radial process, triggered by overloading of the tendon of the extensor pollicis brevis muscle and the abductor pollicis longus muscle. The criteria for tendovaginitis are listed in Table 1 .

As early as 1895, the Swiss physician de Quervain [2] described the symptoms of tendovaginitis stenosans in the radial portion of the wrist in this article. Symptomatology, pathology, and etiology were analyzed, differential diagnosis and therapeutic management were discussed, and the results of surgical treatment were presented. If immobilization has not resulted in regression of symptoms, tendovaginitis de Quervain may benefit from local injections under the retinaculum extensorum at the level of the radial styloid process. Cortisone injections into tendons should be avoided because tendon necrosis and rupture may develop [3].
Radiographs play no role in the diagnosis of tendovaginitis. However, in cases of localized pain and swelling of the wrist radially after trauma, they can be valuable in the differential diagnosis of bony injuries.
Computed tomographic ex aminations are also not suitable for visualizing inflammatory tendon changes because of poor soft tissue contrast in joint examinations. However, bony changes can be detected very well with this imaging.
Sonographically , high-frequency linear transducers (above 10 MHz) can detect tendon thickening and fluid proliferation in the tendon sheath of superficial structures with an echo-poor peritendinous fringe [1,4].
Magnetic reson ance imaging is the gold standard of imaging of inflammatory ligament and tendon changes. In particular, intravenous application of contrast agent shows a marked increase in signal and the exact extent and activity of the inflammatory event [1].
Case studies
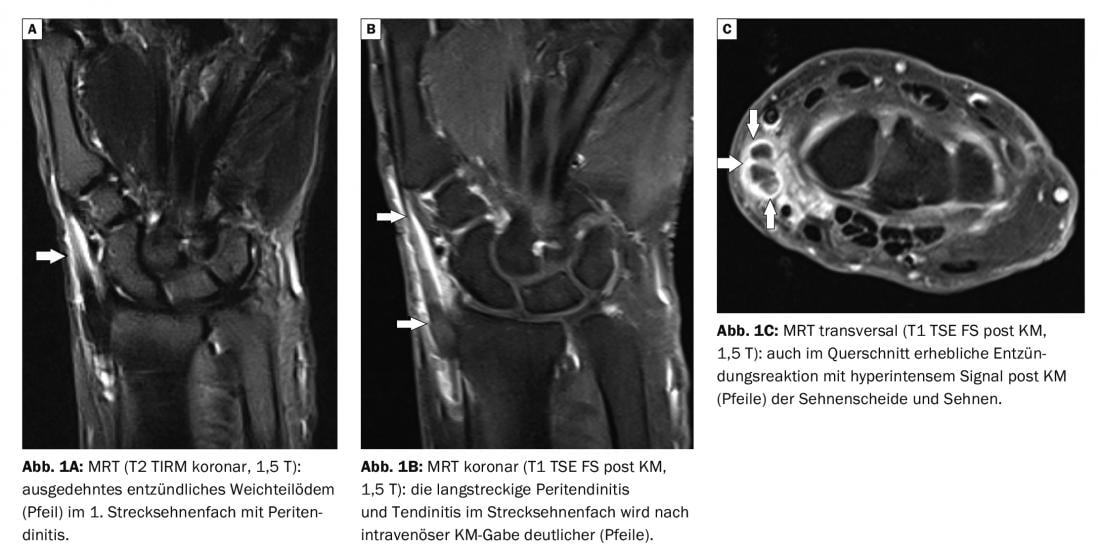
In case report 1 , a 64-year-old female patient was suspected of having tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain (Fig. 1A to C) . There was no trauma, but she complained of painful swelling in the radial left wrist and painful restriction of thumb extension. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) confirmed the suspicion; the inflammation in the 1st extensor tendon compartment was clear, especially in the contrast-enhanced sequences. Tendon rupture or significant bony alteration of the wrist could be excluded.
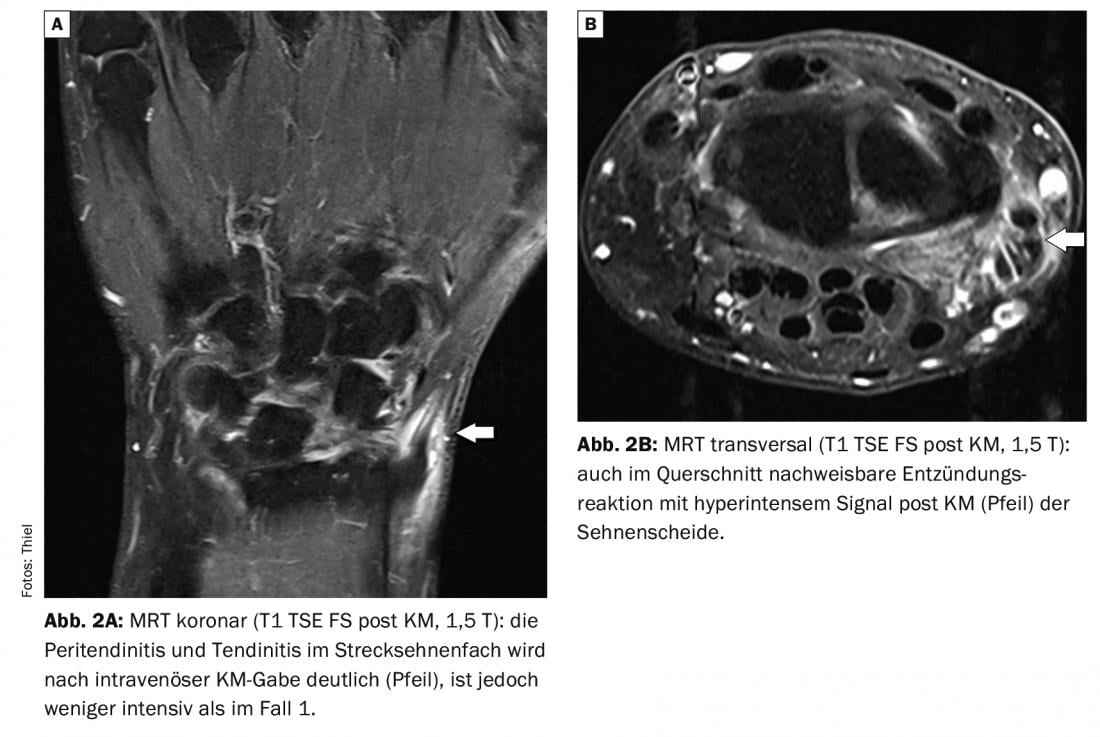
In case report 2 , tendovaginitis de Quervain was detected with radial swelling and pain in the left wrist with limited abduction of the thumb. The 52-year-old patient showed the inflammation loco typico in the radial portion of the joint on the MRI performed (Fig. 2A and B) .
Take-Home Messages
- Tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain shows the typical criteria of tendonitis or tendon sheath inflammation with swelling, pain and limited function.
- The local finding is radial at the wrist over the styloid process radii.
- Sonography can detect inflammation of the tendon and tendon sheath using high-resolution examination techniques.
- In MRI, the exact extent of inflammation and the active stage are visualized by the contrast sequences.
- Relieving, immobilizing and antiphlogistic treatment measures are indicated, rarely surgical therapy must be followed.
Literature:
- Treitl M, Stäbler A, Reiser M: Imaging diagnostics of the carpus. Radiology up2date 1, 2002: 93-120.
- De Quervain F: On a form of chronic tendovaginitis by Dr. Fritz
- de Quervain in la Chaux-de-Fonds. 1895. Am J Orthop 1997; 26(9): 641-644.
- Rehart S, Sell S, eds: Orthopedic Rheumatology. Georg Thieme Verlag Stuttgart, New York 2016: 135.
- Schueller-Weidekamm C: Sonography of the musculoskeletal system. Radiology up2date. 1, 2009: 15-28.
HAUSARZT PRAXIS 2022; 17(1): 38-39