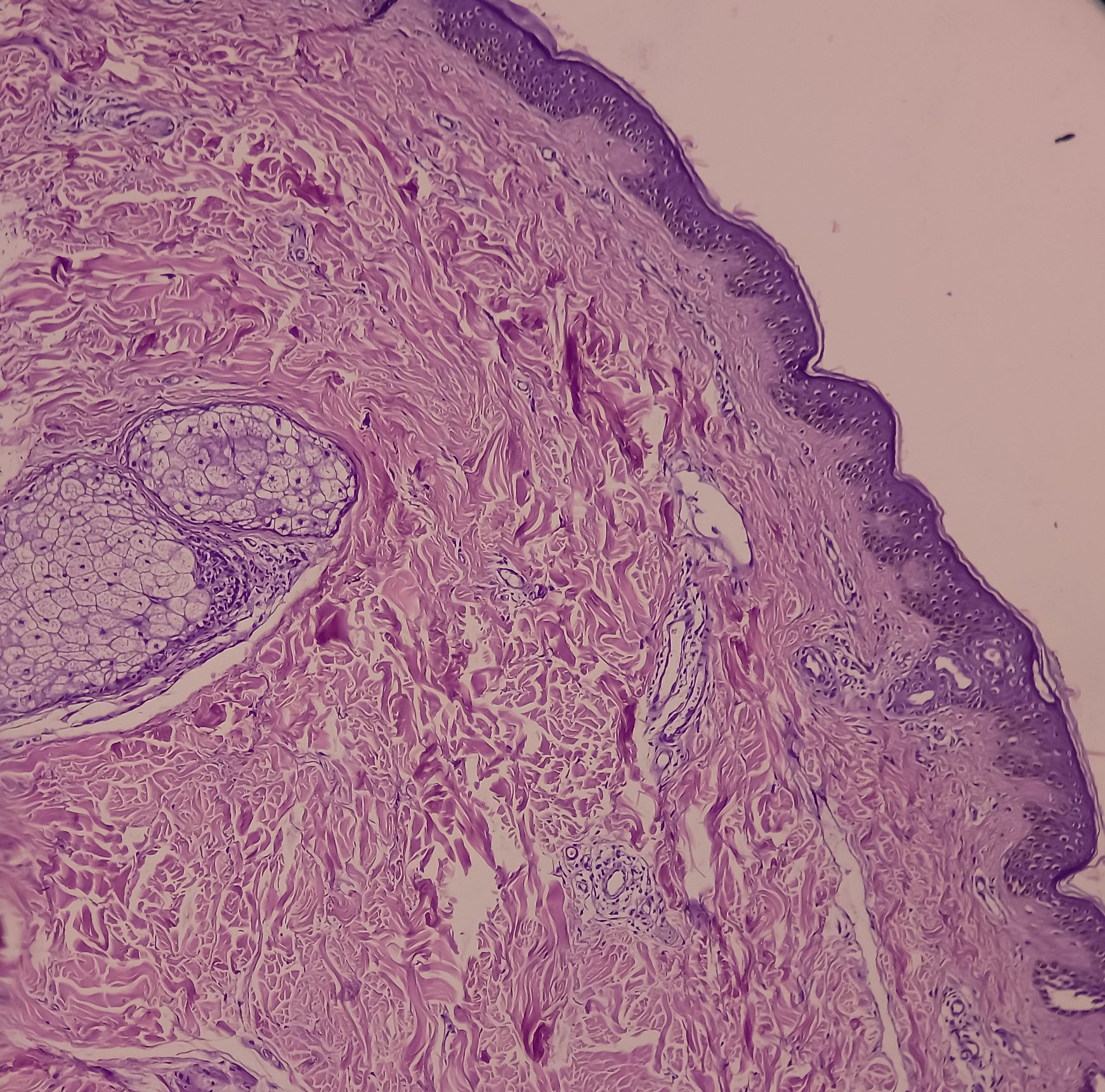
Pemphigus diseases are potentially life-threatening, blistering autoimmune diseases. Acantholysis is detected by skin or mucosal biopsy. In this case study, an 82-year-old man was referred for a dermatological examination due to a generalized exanthema affecting the oral mucosa. The skin and mucosal changes had started two months ago and were accompanied by blistering, pain and pruritus.
Autoren
- Mirjam Peter, M.Sc.
Publikation
- DERMATOLOGIE PRAXIS
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- Oncology
Study updates from the ESMO Congress
- High-dose influenza vaccine
Lower hospitalization rates – even with heart failure
- From statins to metformin
Preventive pharmacology and longevity
- Important basics and studies on cancer and the psyche
Interplay between cancer and mental illness
- From symptom to diagnosis
Abdominal pain – angiosarcoma
- Pediatric epilepsy
Diazepam nasal spray for infants
- Findings from research on the generalization of exposure therapy
Treatment of comorbid anxiety
- Symptom-free despite asthma?