The fact that most type 2 diabetics today aim for an HbA1c value of <7% is partly due to the results of the UKPDS. This landmark study showed that the risk of microvascular complications could be significantly reduced as a result. Another milestone was the launch of GLP-1-RA and SGLT-2-i – state-of-the-art drugs that not only have glucose-lowering effects, but also have independent cardio- and nephroprotective effects.
“Symptomatic therapy is something you should aim for in all patients with diabetes,” recalled PD Dr. med. Matthias Betz, specialist in endocrinology and diabetology, University Hospital Basel [1]. The “UK Prospective Diabetes Study” (UKPDS) was one of the first large prospective studies to demonstrate the benefits of intensified therapy for type 2 diabetes [2,3] (box). Only recently has it become clear that the aim in type 2 diabetes should not only be to reduce microvascular complications, but also to reduce macrovascular complications [2,3].
| In the period 1977-1997, 5102 patients with newly manifested type 2 diabetes were included in the UKPDS**. The study made it clear that a stage-adapted drug therapy for diabetes, in which insulin is also used as required, leads to a reduced incidence of microvascular complications. 25-65-year-old type 2 diabetics were randomized into a control group (CG) with conventional therapy (target value for fasting glucose: ≤15 mmol/l) or an intervention group with intensified blood glucose-lowering therapy (stricter HbA1c target values than in CG). The intensified therapy consisted of therapy with insulin or a sulfonylurea for normal-weight participants, and overweight participants received insulin or sulfonylureas and metformin. An average reduction in HbA1c from 7.9% to 7.0% with intensified glucose-lowering therapy resulted in a 25% reduction in the rate of microvascular complications and a 12% reduction in all diabetes-related endpoints. Since then, intensified glucose-lowering therapy has established itself as the standard in international guidelines. |
| ** UKPDS = “UK Prospective Diabetes Study” |
| to [1–3] |
What is the learning of large-scale cohort studies?
The bottom line of an analysis of a large dataset of Swedish registry data published in 2018 was that in type 2 diabetics, an HbA1c -value outside the target range was the strongest predictor of stroke and acute myocardial infarction in type 2 diabetics. In total, this cohort study included data from 271,174 type 2 diabetics and 1,355,870 controls matched by age, sex and region [4]. And a publication by Sattar et al. published in 2023, which used data sets from the Swedish National Diabetes Register from 2001-2019 – 679,072 type 2 diabetics and 2,643,800 matched controls – showed that the rates of atherosclerotic complications (e.g. coronary heart disease) and heart failure in type 2 diabetics are generally declining, although the risk is still increased compared to the general population without diabetes [5]. The realization that, in addition to well-controlled diabetes (HbA 1c value), systolic blood pressure and BMI are also modifiable risk factors that reduce the risk of atherosclerotic complications and heart failure, has also been incorporated into the treatment concept for type 2 diabetes [5].
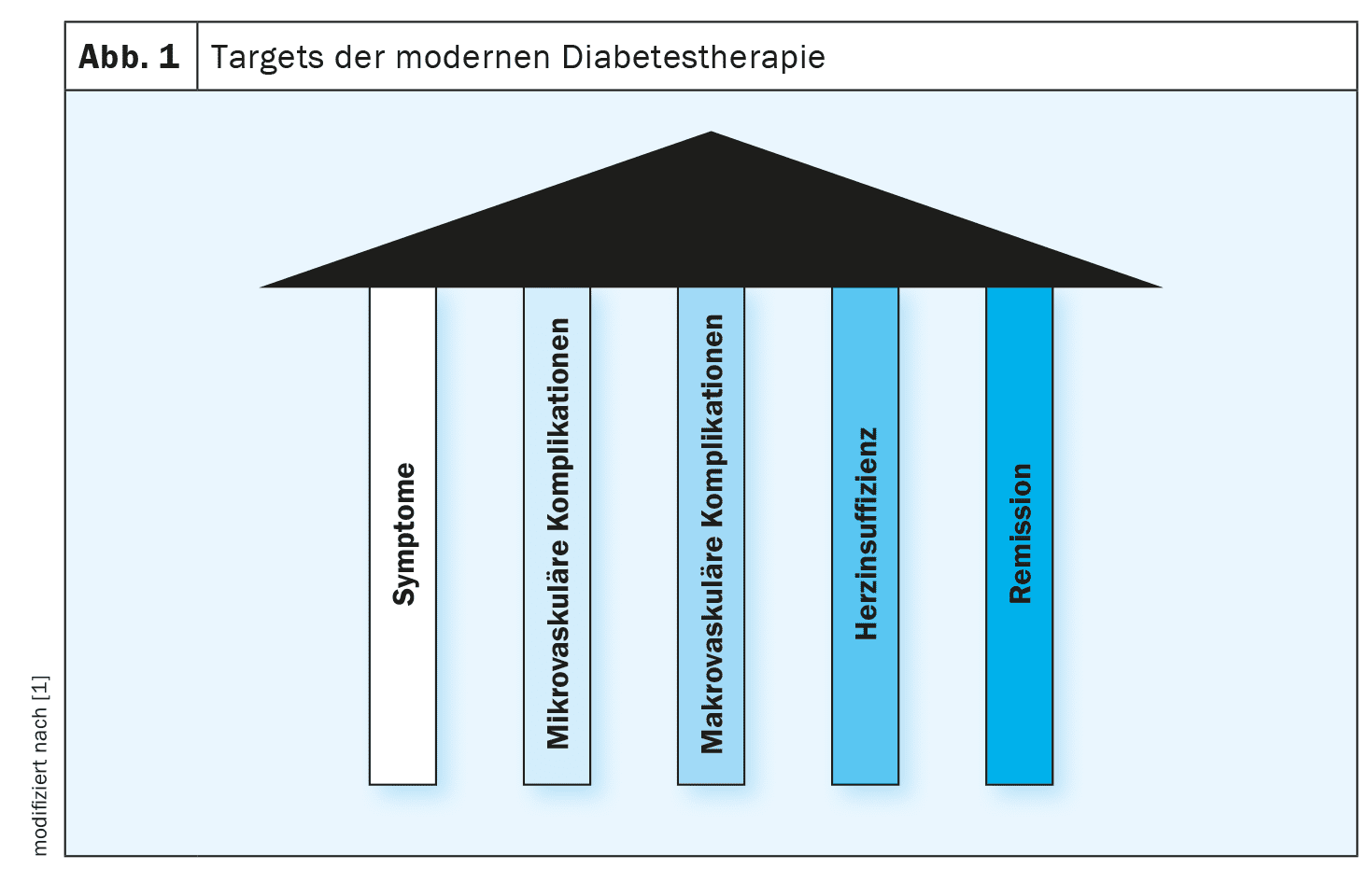
Reduction of microvascular and macrovascular complications: high priority
Nowadays, the management of type 2 diabetes is not only focused on glucose control, but also on reducing microvascular and macrovascular complications. Various therapeutic tools are available to achieve these goals. Recently, attention has focused on the fact that heart failure ( HF) plays a major role in type 2 diabetes, reported Dr. Betz [1]. Many people with type 2 diabetes are obese, which can promote HF. But diabetes can also lead to HF via CHD or myocardial infarction. “And we have also obtained new tools for this in recent years,” said the speaker, adding: “We have seen that SGLT-2 inhibitors reduce hospitalization rates in heart failure and that mortality decreases” [1].
Define individualized treatment goals
The basic therapy for type 2 diabetes consists of diet, exercise and metformin. However, every type 2 diabetic should be asked whether there is an increased cardiovascular risk, whether they already have heart failure and what their kidney status is, emphasized Dr. Betz [1]. Depending on this, it is advisable to expand pharmacotherapy with medications that lower the cardiovascular risk and reduce the risk of HF and renal insufficiency. “Ultimately, these are GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT-2 inhibitors, possibly in combination,” said the speaker [1]. If the HbA1c cannot be reduced below 7% despite these modern medications, consideration should be given to whether a basic or bolus insulin is indicated. The question of whether a patient needs insulin should be asked at the beginning of therapy, but also repeatedly in the further course. “Being overweight or obese significantly increases the risk of insulin resistance,” Dr. Betz pointed out [1]. In most cases, slim diabetes patients do not have insulin resistance, but reduced insulin secretion. “Insulin has much more effect than just lowering blood sugar,” the speaker stated, adding: “Insulin is there to store energy, to promote protein production, and an acute insulin deficiency makes you feel bad” [1]. In summary, it is all about using the right tools from the diabetes therapy toolbox. Today, incretin mimetics and SGLT-2 inhibitors play an important role in the modern treatment of type 2 diabetes:
- GLP-1-RA: reduce the HbA1c value very effectively and promote weight reduction; if they are used without insulin or sulphonylureas, no hypoglycaemia is induced. “And they have been shown to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality,” said the speaker [1]. In terms of side effects, gastrointestinal complaints are relatively common.
- SGLT-2-i: also lead to very effective blood glucose lowering, do not induce hypoglycaemia and are well tolerated. “They protect against nephropathy and heart failure,” emphasized the speaker [1].
In general, the aim of blood glucose-lowering therapy is to achieve an HbA1c target value of ≤7%. However, this is not a strict rule. While remission may be the goal for younger type 2 diabetics, an HbA1c <8% may already be considered a satisfactory goal for an 80-year-old patient. The fact that remission in type 2 diabetes is in principle not an unattainable goal has been mentioned in the guidelines for several years. Specifically, this means that a reduction in HbA1c below 6.5% can be maintained for at least three months without having to use insulin or other glucose-lowering agents [6]. The DIRECT study showed that this can be achieved by overweight type 2 diabetics reducing their body weight by >15%.
Congress: medArt Basel
Literature:
- “Diabetes mellitus”, PD Dr. med. Matthias Betz, State of the Art Lecture 5, medArt, Basel, 17-21.06.24.
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998; 352: 837-885.
- “Studies that changed clinical practice. UKPDS: United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study”,
www.pcdsociety.org,(last accessed 22.07.2024) - Rawshani A, et al: Risk Factors, Mortality, and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med 2018; 379(7): 633-644.
- Sattar N, et al: Twenty Years of Cardiovascular Complications and Risk Factors in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Swedish Cohort Study. Circulation 2023; 147(25): 1872-1886.
- Riddle MC, et al: Consensus Report: Definition and Interpretation of Remission in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021; 44(10): 2438-2444.
HAUSARZT PRAXIS 2024; 19(8): 28–29 (published on 22.8.24, ahead of print)