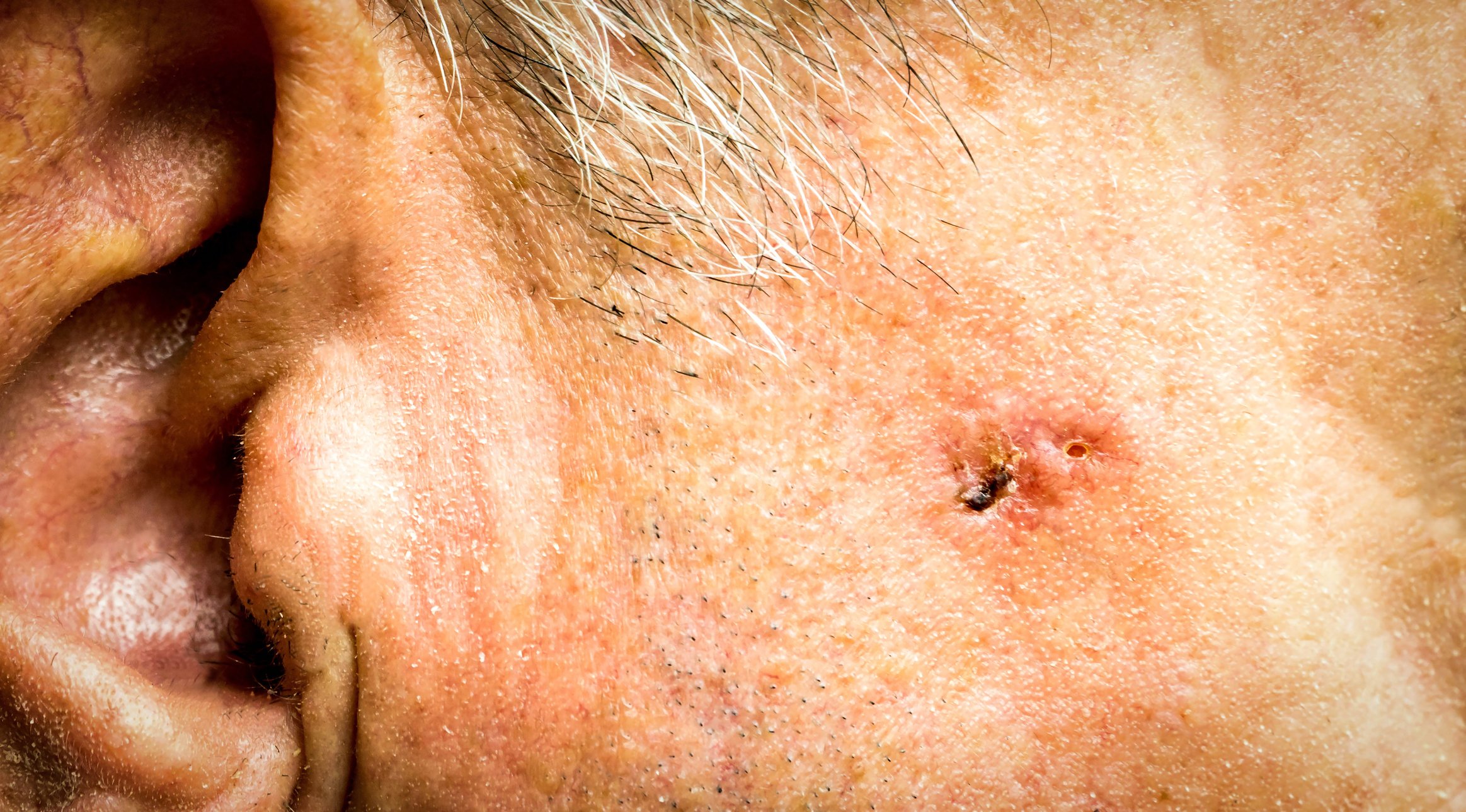
In the US cohort study published in JAMA Dermatology 2025, the risk of non-melanocytic skin cancer (NMSC) was reduced in patients who had received nicotinamide supplementation – especially if the supplementation took place after a first NMSC disease. The risk reduction was significantly higher for squamous cell carcinomas than for basal cell carcinomas.
Autoren
- Mirjam Peter, M.Sc.
Publikation
- DERMATOLOGIE PRAXIS
- InFo ONKOLOGIE & HÄMATOLOGIE
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- From symptom to diagnosis
Abdominal pain – Inguinal testicles
- Case series
Mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS)
- Gestational diabetes
Significant CVD prevention through five lifestyle factors
- Modern therapeutic approaches for melanoma
Innovative strategies to overcome immunotherapy resistance
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
“Best practice” recommendations for step-by-step clarification and stage-adapted therapy
- Nutritional supplements and cognition
5-HTP: The serotonin booster for cognition in old age
- Pulmonary hypertension
PH and lung diseases
- CRC, AML and melanoma in focus