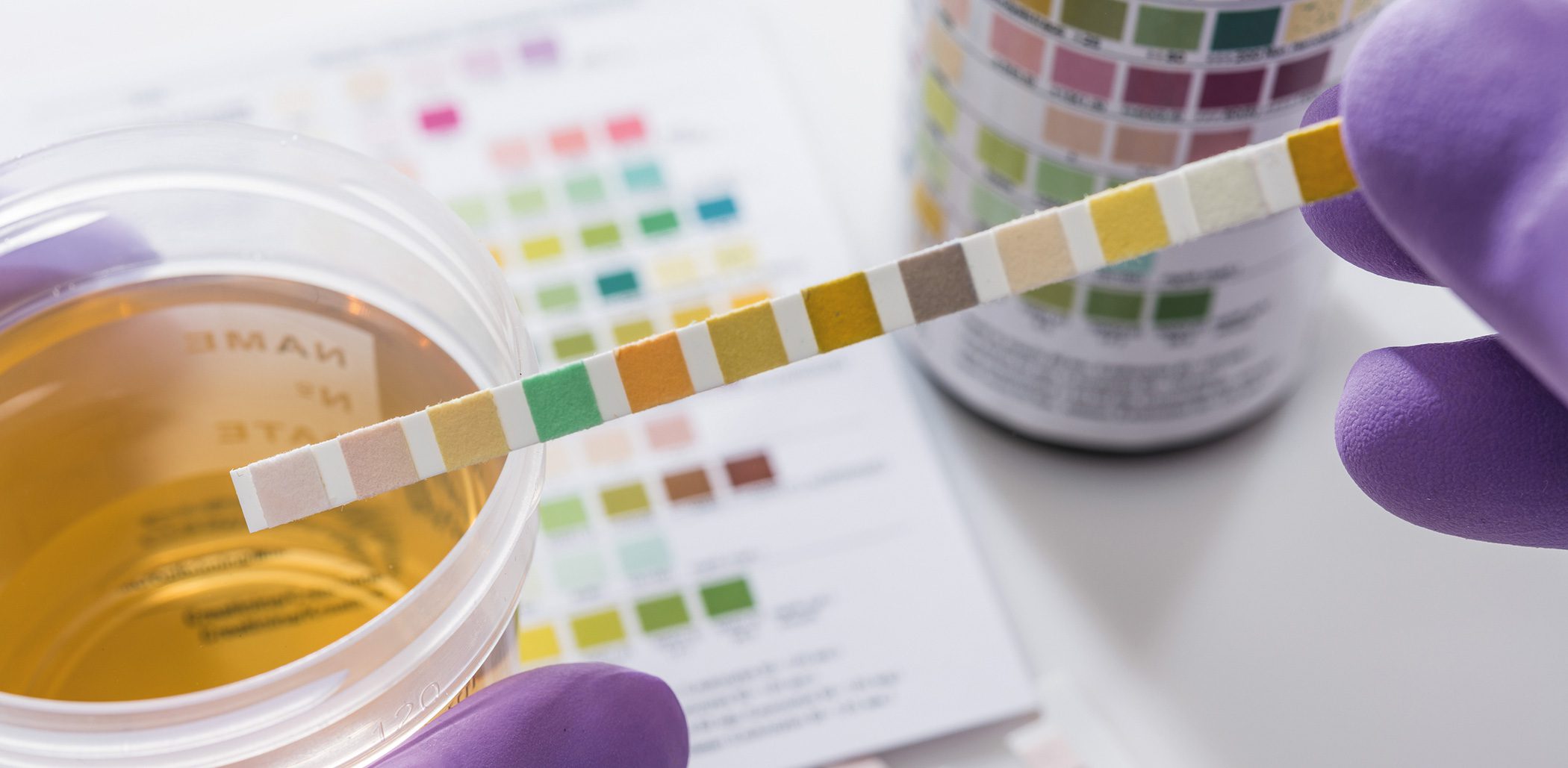
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most common infectious diseases worldwide and represent a considerable burden for patients and healthcare systems, particularly in the hospital context. While uncomplicated infections can usually be treated reliably with standard antibiotics, complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI) require differentiated diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. The following article highlights the epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical presentation and current management approaches of cUTI – with a particular focus on high-risk populations, resistance issues and innovative treatment options.
Autoren
- Tanja Schliebe
Publikation
- Nephrologie-Special
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- Findings from research on the generalization of exposure therapy
Treatment of comorbid anxiety
- Symptom-free despite asthma?
Asthma treatment requirements have increased
- Phytotherapy for rhinosinusitis
Evidence, active substances and clinical classification for medical practice
- Contact eczema
Causes and prevention at work
- Pulmonary hypertension
PH and lung diseases
- Respiratory infections: viral bronchitis or bacterial pneumonia?
Old crucial question in the light of current findings
- What biomarkers reveal about "biological youth" - and what not (yet)
Epigenetic ageing
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and nutrition