Comorbid psychological symptoms are common in atopic dermatitis and can have serious consequences. The IgG4 monoclonal antibody dupilumab led to significant symptom reduction in subpopulations of this patient population, resulting in positive effects on mental health and quality of life.
Several efficacy studies on dupilumab in atopic dermatitis demonstrate the positive effects of this monoclonal antibody with anti-inflammatory and selective immunosuppressive properties. Bruin-Welleret et al. [1] investigated the effects of dupilumab in combination with topical corticosteroids in patients who showed intolerance to ciclosporin A. Simpson et al. [2] addressed the question of how dupilumab affects patients with moderate to severe dermatitis. In both studies, treatment with dupilumab resulted in symptom relief of atopic dermatitis as well as a reduction in comorbid psychological problems.
Positive effects in combination with topical corticosteroids
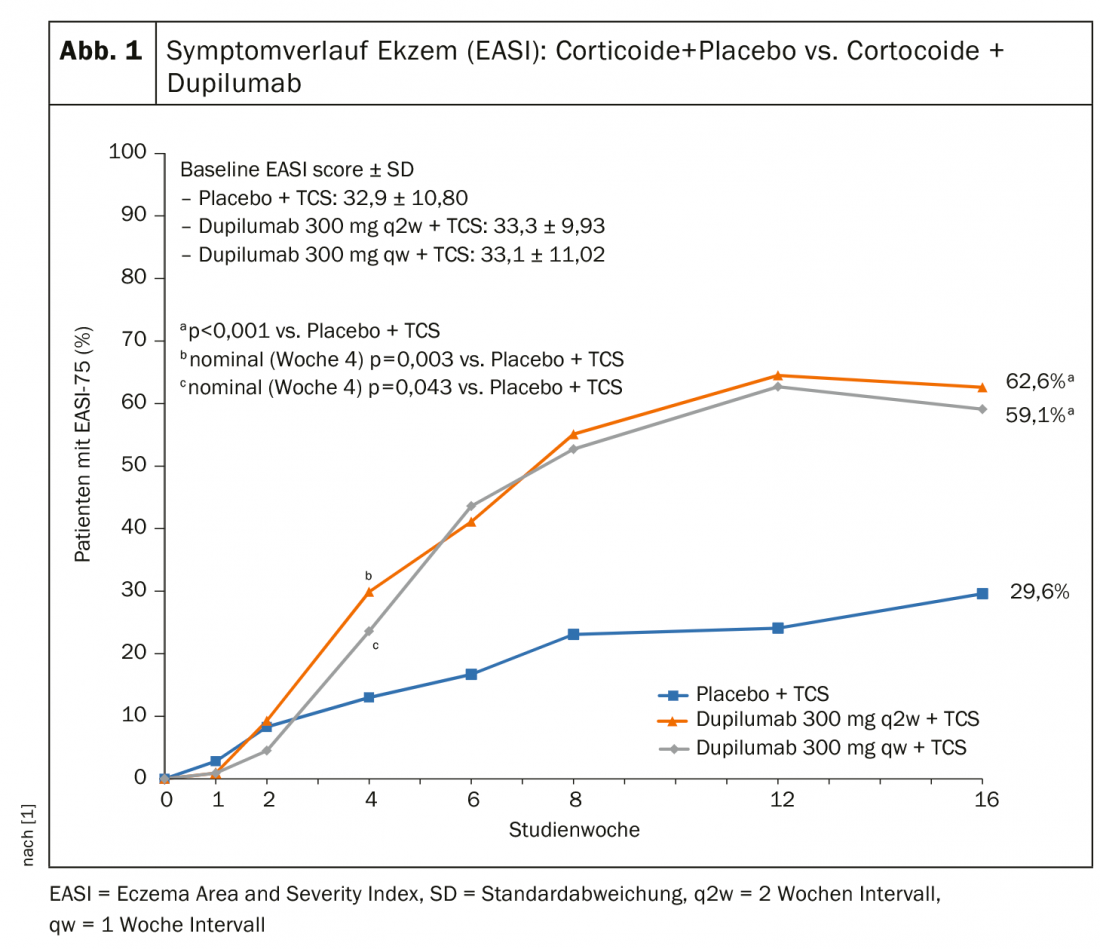
A double-blind, randomized-controlled phase III trial (n=325) published in 2018 evaluated the efficacy of dupilumab administered concurrently with topical corticosteroids with respect to comorbid psychological symptoms in patients with atopic dermatitis who had a history of inadequate response or intolerance to ciclosporin A [1]. In the two intervention conditions, dupilumab 300 mg was administered subcutaneously, with an interval of one week [qw] in one group of subjects and two weeks [q2w] in the other. Subjects in all three conditions (dupilumab_[qw]+TCS, dupilumab_[q2w]+TCS, placebo+TCS) had atopic dermatitis treated with medium-strength topical corticosteroids (TCS) during the study period, with dosing varying over time depending on the severity of the eczematous lesions [1].
After a period of 16 weeks, both conditions showed dupilumab_[qw]+TCS and dupilumab_[q2w] Significantly more patients ≥75% improvement in the primary endpoint Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) since baseline than in the placebo+TCS condition (59.1% and 62.6% vs. 29.6%; p<0.001) (Fig. 1) . Also, the proportion of patients with an improvement of ≥4 in the scores of DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) and POEM (Patient-oriented Eczema Measure) was higher in the dupilumab+TCS conditions compared to placebo+TCS [1]. With regard to symptom reduction of pruritus, there was a significant difference between the Dupilumab+TCS conditions compared to placebo already after two weeks. Reductions in anxiety symptoms and depressive symptoms were superior to the placebo condition in both intervention conditions, with significantly more patients achieving clinically meaningful symptom reductions (subscores <8) in Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) scores in the dupilumab_[q2w] condition than in the dupilumab_[qw] condition.
The rate of adverse events was comparable in all conditions (dupilumab_[qw]+TCS: 69.1%; dupilumab_[q2w]+TCS: 72.0%; placebo+TCS: 69.4%). Conjunctivitis was more frequent in dupilumab+TCS, whereas skin infections were more frequent in the placebo+TCS condition. The safety profile of dupilumab when used over a period of more than one year is being investigated in an open-label extension study addressing the same question [1].
Also effective for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis
Moderate to severe atopic dermatitis is very distressing for sufferers despite existing therapies. In a double-blind study (n=380), the effects of dupilumab were evaluated over a 16-week period in patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in whom symptoms were not adequately controlled by topical medications [2]. Subjects were randomly assigned to one of the conditions: [a] dupilumab 100 mg at 4 week intervals, [b] dupilumab 200 mg at 2 week intervals, [c] dupilumab 300 mg at 1 week intervals, [d] dupilumab 300 mg at 2 week intervals [e] placebo. Outcome parameters were pruritus (POEM and numerical rating scale), anxiety and depression (HADS), and quality of life (DLQI, EuroQol).
Dupilumab resulted in a significant reduction in pruritus 16 weeks after baseline (p<0,0001 [b,c,d] resp. p<0.05 [a]) and to a significant improvement in quality of life (p<0,05 [b,c,d], and of anxiety and depressive symptoms (p<0.05 in all dosages).
In summary, dupilumab rapidly produced positive, clinically meaningful effects on mental health and quality of life, with best efficacy at doses of 300 mg at intervals of one week [c] and two weeks [d], respectively.
Source: AAD Annual Meeting, Washington, March 2, 2019.
Literature:
- de Bruin-Welleret M, et al: Dupilumab with concomitant topical corticosteroid treatment in adults with atopic dermatitis with an inadequate response or intolerance to ciclosporin A or when this treatment is medically inadvisable: a placebo-controlled, randomized phase III clinical trial (LIBERTY AD CAFÉ). Br J Dermatol 2018 May; 178(5): 1083-1101. doi: 10.1111/bjd.16156. epub 2018 Mar 25.
- Simpson EL, et al: Dupilumab therapy provides clinically meaningful improvement in patient-reported outcomes (PROs): A phase IIb, randomized, placebo-controlled, clinical trial in adult patients with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (AD). J Am Acad Dermatol 2016 Sep;75(3):506-515. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2016.04.054. epub 2016 Jun 4.
- Printer A: Slide presentation. Atopic dermatitis comorbidities: what do derms need to know? AAD Annual Meeting 2019, San Francisco March 2, 2019.
DERMATOLOGIE PRAXIS 2019; 29(3): 33-34 (published 6/13/19, ahead of print).