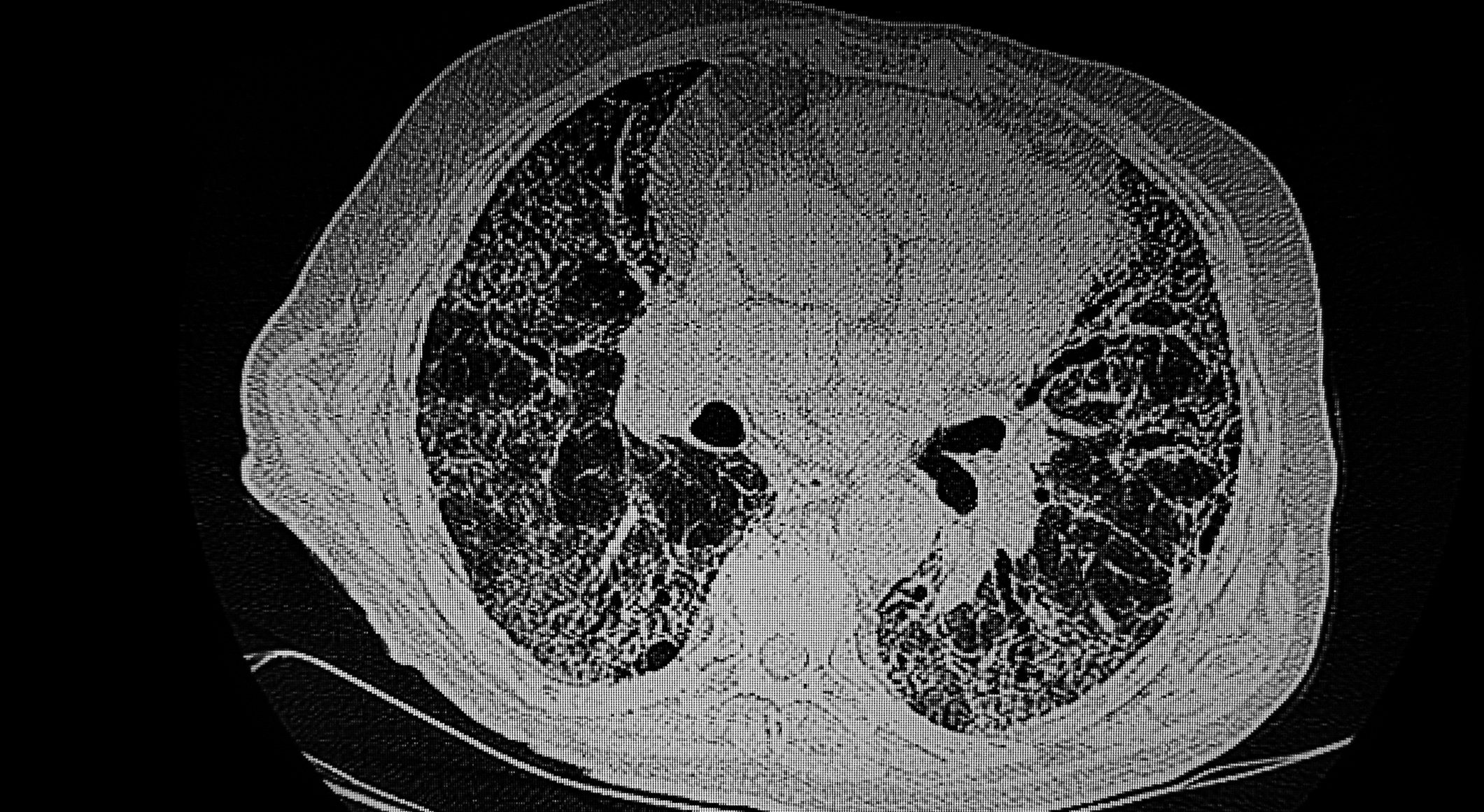
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic, progressive, fatal and age-related interstitial lung disease whose etiology and pathogenesis are still largely unknown. It is important to identify IPF patients at high risk of mortality so that early appropriate treatment can improve their prognosis. Therefore, the investigation of available and reliable prognostic biomarkers for IPF is crucial.
Autoren
- Jens Dehn
Publikation
- InFo PNEUMOLOGIE & ALLERGOLOGIE
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- Study report
Sphingolipid profile in early-stage primary biliary cholangitis
- Angiosarcoma of the heart
A diagnostic and therapeutic “black box”
- Ataxias
Friedreich’s ataxia: when the energy metabolism attacks the nervous system
- Risk of osteoporosis in autoimmune liver diseases
Always determine bone density in PBC, PSC and AIH
- Case report: Complication after type 2 diabetes
Topical corticosteroids lead to ketoacidosis
- NSCLC
Bispecific antibodies for rare EGFR mutations
- Type 2 diabetes - glycemic control and prevention of secondary diseases
Utilizing pleiotropic cardio- and nephroprotective effects of SGLT-2-i and GLP-1-RA
- Subsyndromal anxiety disorders: Family doctor as first point of contact