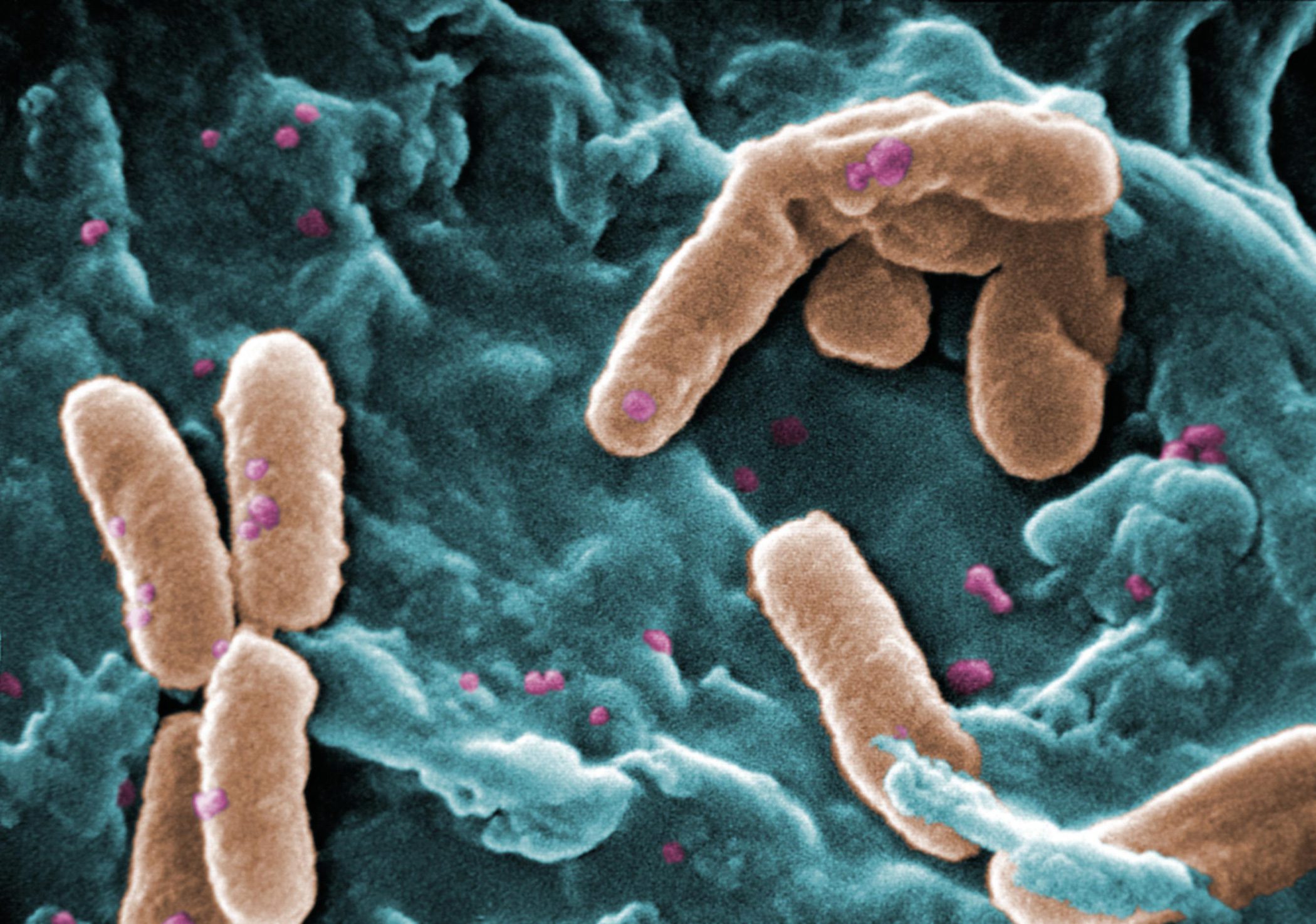
A chronic lung infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa is associated with an increased exacerbation and mortality rate in people affected by bronchiectasis. Inhaled antibiotics are frequently used in clinical practice to treat chronic infections with this bacterium. The PROMIS-I and PROMIS-II studies investigated the efficacy and safety of 12-month inhaled colistimethate sodium administration in patients with bronchiectasis and chronic P. aeruginosa infection.
Autoren
- Jens Dehn
Publikation
- InFo PNEUMOLOGIE & ALLERGOLOGIE
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- Pulmonary hypertension
PH and lung diseases
- CRC, AML and melanoma in focus
Molecular mechanisms of tumor plasticity
- Friedreich's ataxia
Interim analyses of the PROFA study show “Unmet needs”
- Study report
Sphingolipid profile in early-stage primary biliary cholangitis
- Angiosarcoma of the heart
A diagnostic and therapeutic “black box”
- Ataxias
Friedreich’s ataxia: when the energy metabolism attacks the nervous system
- Risk of osteoporosis in autoimmune liver diseases
Always determine bone density in PBC, PSC and AIH
- Neuroendocrine tumors