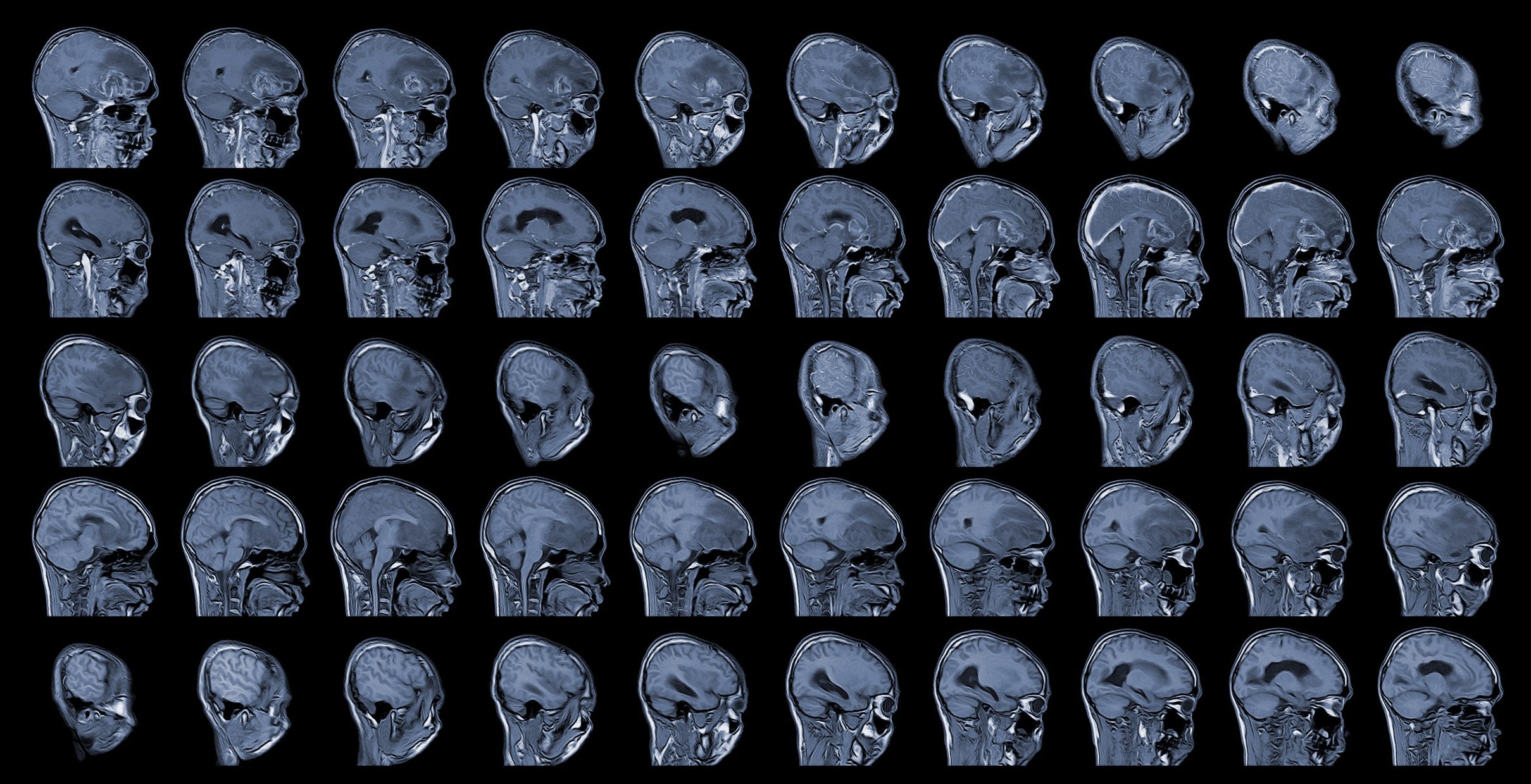
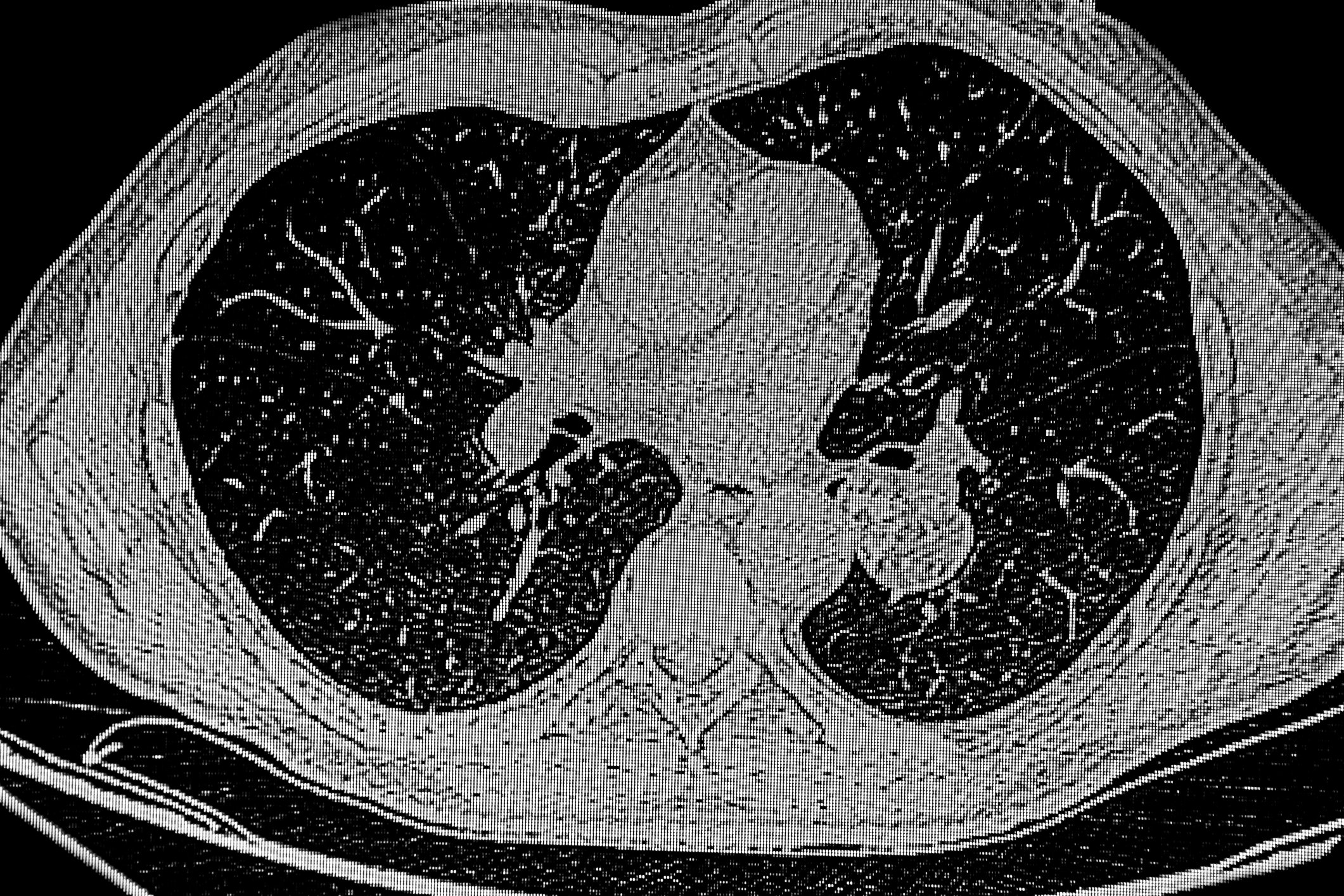
Glioblastomas (GBM) are among the most aggressive and therapy-resistant tumors of the central nervous system and present both clinicians and researchers with immense challenges. Despite significant advances in diagnostics and an improvement in standard therapy, which usually consists of surgical resection, subsequent radiotherapy and the administration of temozolomide, the survival prospects are still unsatisfactory. This is mainly due to the pronounced resistance, the complex tumor heterogeneity and the immunomodulating properties of glioblastoma cells and their microenvironment.
You May Also Like
- Side effects under opioid therapy
Is it possible to avoid the inevitable?
- Diagnostics of respiratory viral infections
What is tested when and on whom?
- From symptom to diagnosis
Dyspnea – pulmonary hamartomas
- Phobia
Propranolol and spider phobia: the time window is crucial
- Focus on prevention
Colorectal cancer screening – an update
- Rare diseases
Yellow nail and Swyer-James syndrome
- Contact eczema
Causes and prevention at work
- Diabetic ketoacidosis