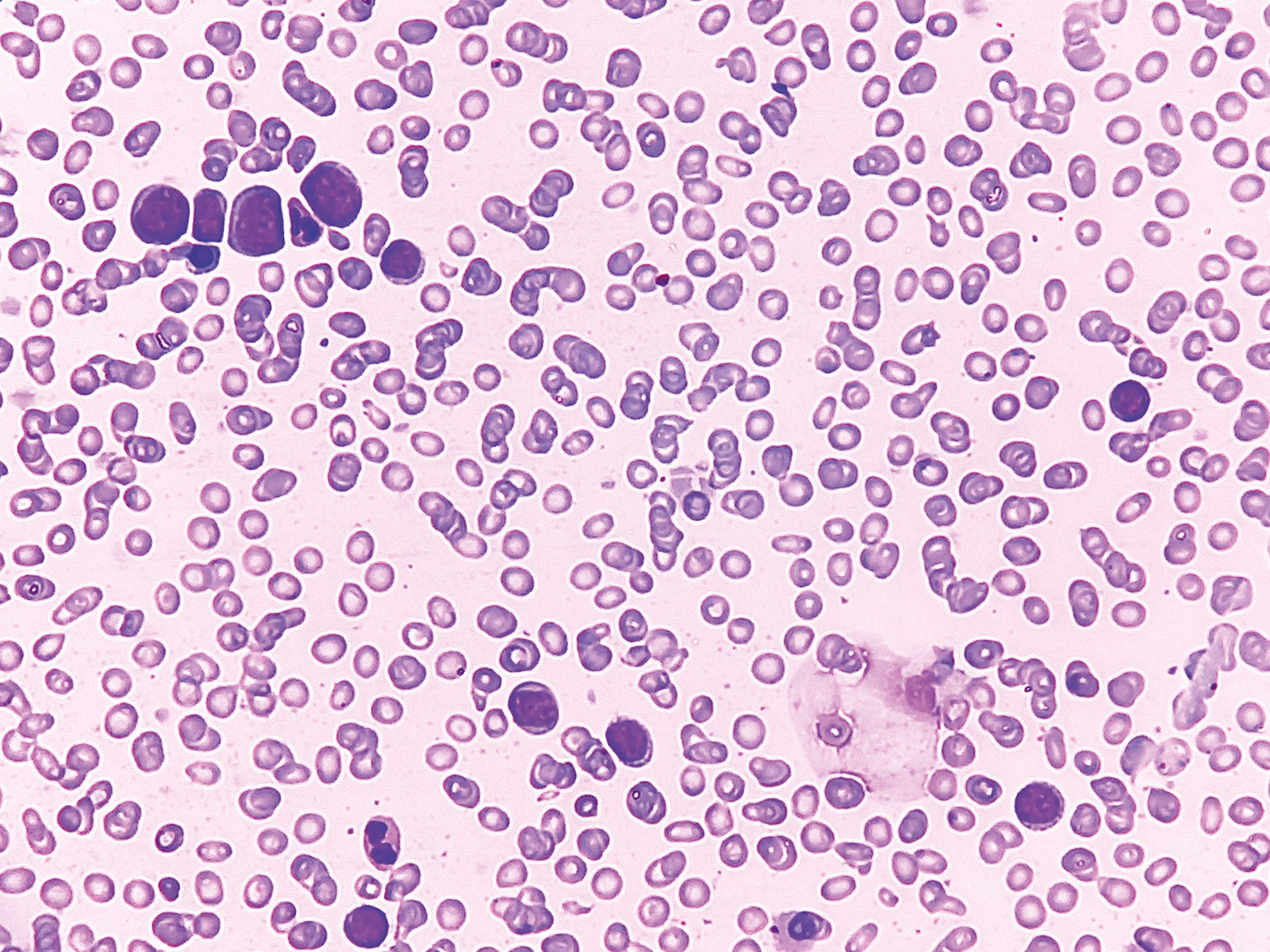
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is often classified as an oncologic emergency leading to rapid evaluation and treatment in the hospital. Previous studies reported that time from diagnosis to treatment (TDT) had no impact on outcomes, but these data were limited to patients already intensively pretreated and/or not living in the US. A new study in adults with newly diagnosed AML, presented at ASH, comes to new conclusions.
Autoren
- Birke Dikken
Publikation
- InFo ONKOLOGIE & HÄMATOLOGIE
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- Study report
Sphingolipid profile in early-stage primary biliary cholangitis
- Angiosarcoma of the heart
A diagnostic and therapeutic “black box”
- Ataxias
Friedreich’s ataxia: when the energy metabolism attacks the nervous system
- Risk of osteoporosis in autoimmune liver diseases
Always determine bone density in PBC, PSC and AIH
- Case report: Complication after type 2 diabetes
Topical corticosteroids lead to ketoacidosis
- NSCLC
Bispecific antibodies for rare EGFR mutations
- Type 2 diabetes - glycemic control and prevention of secondary diseases
Utilizing pleiotropic cardio- and nephroprotective effects of SGLT-2-i and GLP-1-RA
- Subsyndromal anxiety disorders: Family doctor as first point of contact