External stimulation of the trigeminal nerve has already proven effective in migraine prevention. The great advantage is the drug-free treatment, due to which there are practically no side effects. Recent study results have now demonstrated that the neurostimulator is also effective in acute treatment.
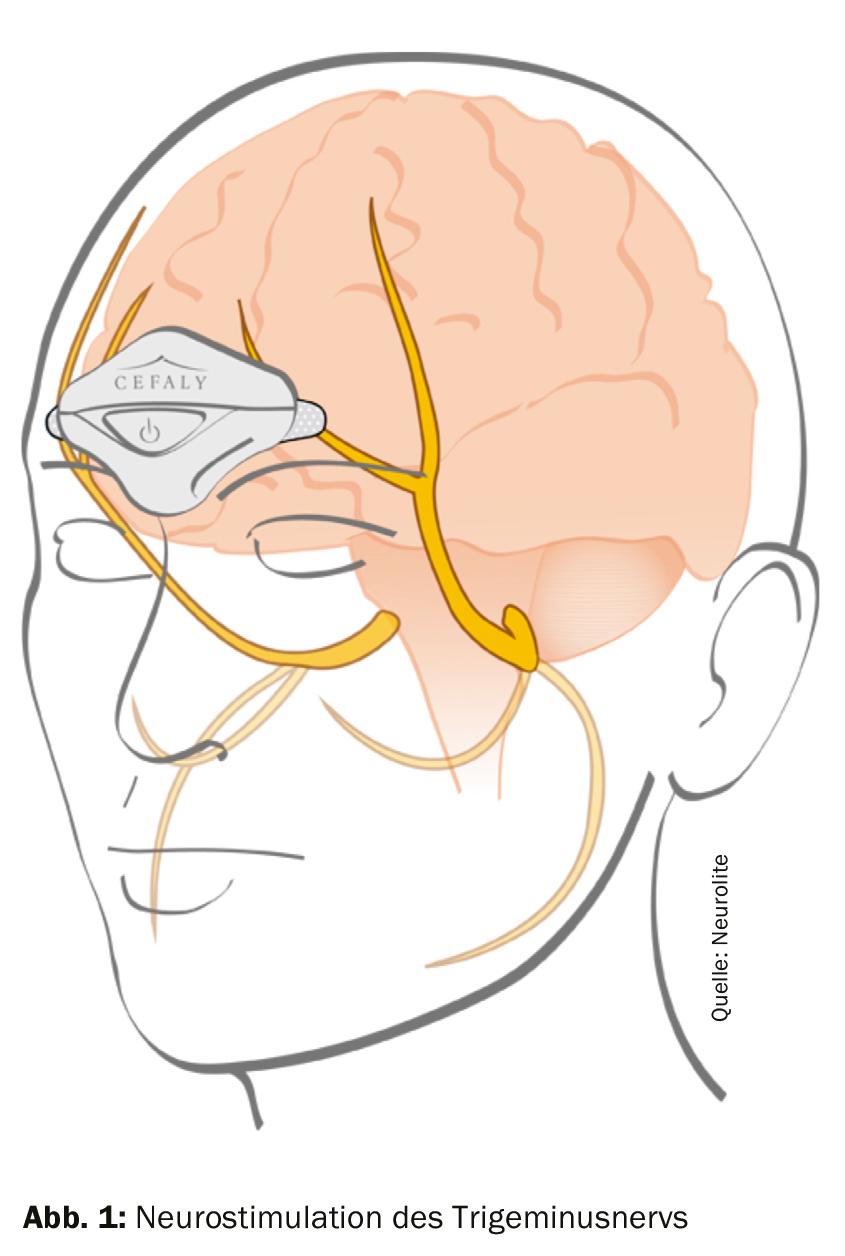
Migraine is a neurobiologically caused dysfunction of the brain, the dura and the corresponding blood vessels. A temporary dysfunction of the balance of pain centers in the brainstem triggers the discomfort. There is an important interconnection between the blood vessels of the brain and the trigeminal nerve. Branches of the nerve are found in the walls of all blood vessels in the brain and its upper branch ends at the exit of the orbit under the frontal skin. Overactivity of nerve cells in the brainstem causes the trigeminal nerve to send pain signals to the brain.
By means of external stimulation of the facial nerve, the patented medical device Cefaly® achieve a significant pain relief up to freedom from pain (Fig. 1). Previously approved in Switzerland for migraine prevention, the external neurostimulator has now demonstrated its good efficacy and tolerability for acute treatment: Significant pain relief was achieved in 85% of patients, and one third of patients were even pain-free after one hour.
Freedom from pain also possible without medication
The ACME (ACute Migraine Therapy with External trigeminal neurostimulation) study was the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial to investigate the effect of trigeminal nerve stimulation for the acute treatment of migraine attacks [1]. It was found that 32% of patients with acute migraine were completely pain-free after one hour of treatment (vs. 6% in the placebo arm). Significant pain reduction was recorded in 85% – almost three times more patients than in the control group. Thus, Cefaly® represents a useful supplement or alternative in the acute and prophylactic treatment of migraine. Results of a pilot study further suggest that the optimal duration of stimulation is approximately two hours and that similar results to triptans can then be achieved [2].
Source: Neurolite
Literature:
- Chou DE, et al: Acute migraine therapy with external trigeminal neurostimulation (ACME): A randomized controlled trial. Cephalalgia 2019; 39(1): 3-14.
- Kuruvilla D, et al: Acute treatment of migraine with external trigeminal nerve stimulation: A pilot trial. Cephalalgia Reports 2019; 2: 1-6.
HAUSARZT PRAXIS 2019; 14(8): 37