Allergic reactions following ingestion of food range from mild oral allergy syndrome to anaphylactic shock. Peanuts, hazelnuts, and crustaceans are the most common causes of severe food anaphylaxis. Every affected person should be equipped with an emergency kit. The only effective therapy for food allergies is the elimination diet.
One speaks of food allergies only when the pathological reactions occur after food intake as a result of immunological mechanisms in individuals with a corresponding predisposition. In patients with hay fever, allergic asthma or neurodermatitis (so-called atopics), antibodies of immunoglobulin class E (IgE) against particular protein components, e.g. of food, are involved. These allergen-specific IgE are responsible for allergic reactions in the respiratory tract (rhinitis, asthma), in the skin (allergic urticaria, Quincke’s edema, atopic eczema), in the gastrointestinal tract (itching in the mouth and throat – so-called oral allergy syndrome (OAS), diarrhea, colic), or for an allergic shock. (Fig.1). Symptoms of food allergy can be triggered by even small or moderate amounts of the food in question, disappear after its elimination, and can be convincingly and reproducibly triggered by re-exposure.
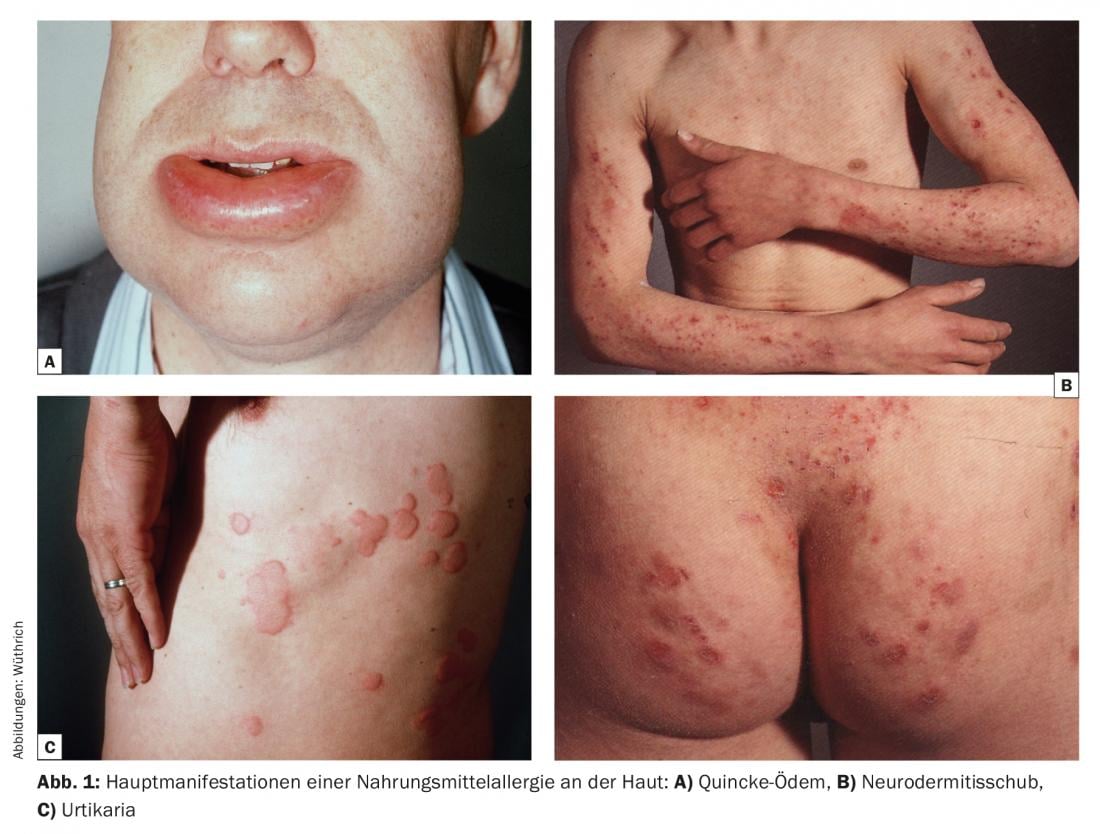
Basically, any food can cause an allergic reaction. Statistics among children and adolescents impressively show that allergy to peanut and hazelnut, which can also be fatal, can become a serious health problem in Switzerland, as it is in the USA and England. In adults, in addition to peanut and nut allergy, celery allergy is prominent.
Fatal food allergy
Headline: “16-year-old girl from Biberstein accidentally ate peanuts to which she was allergic” (Fig. 2) . As seen in the Aargauer Zeitung of 27. June 2009. Lucia died because she bought roasted almonds from a stall on Tower Bridge in London, which were in fact peanuts, to which the girl had a mild allergy, probably oral allergy syndrome. There was swelling of the tongue and throat, vomiting and shortness of breath, and despite the call for an ambulance, the girl died of anaphylactic shock.

“Death from peanut allergy after consumption of a single packaged cereal bar, compliant with the law without declaration of ingredients” was reported from Germany. The 15-year-old schoolgirl had already developed an aversion to pulses (legumes), such as peas, beans, lentils and peanuts, at the age of four. The clarification revealed a clear IgE sensitization to peanuts, so that the child or the parents were advised to consistently avoid peanuts. As an on-demand medication for respiratory distress, the child received salbutamol inhalation spray. There were no incidents until the current event. At a stall in the local schoolyard, the student purchased a single granola bar on each of several consecutive days. Massive respiratory distress and loss of consciousness occurred when a cereal bar was consumed again. After apparently hesitant initiation of first aid measures, the death of the student had to be determined. It is reasonable to conclude that repeated exposure to peanut with pre-existing sensitization resulted in the fatal anaphylactic reaction. The bars came from a larger package with the legally required peanut declaration and warnings for allergy sufferers. However, in accordance with EU law, the individual bars did not contain a separate reference to the ingredients.
Emergency kit – lifesaving!
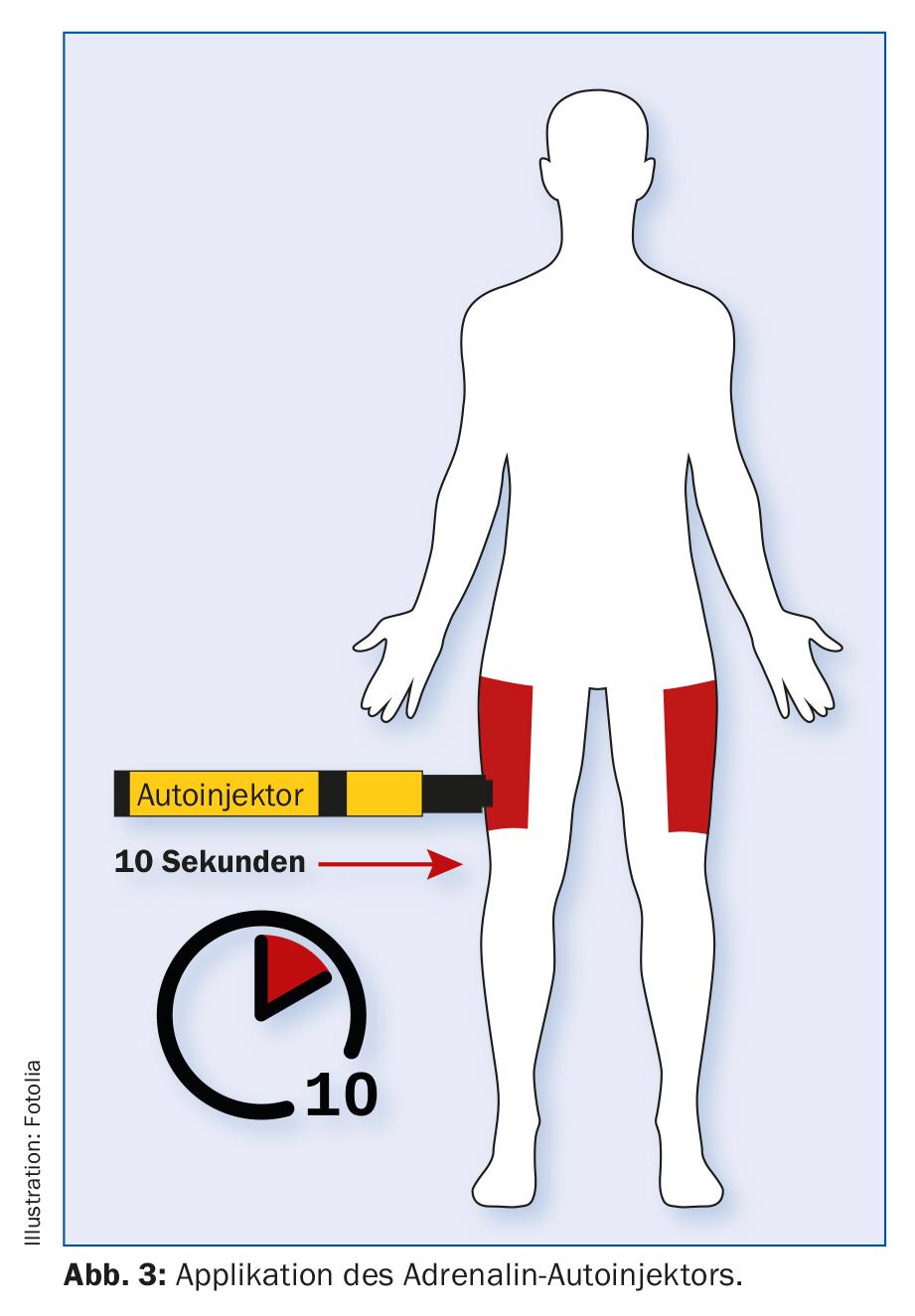
These examples show how important it is for every patient with food allergy to be equipped with an emergency kit. This should include two tablets of an antihistamine (e.g., cetirizine, levocetirizine, or bilastine) and 100 mg of prednisone, and epinephrine if the reaction is severe. EpiPen/EpiPen Junior contains e.g. adrenaline for emergency treatment of allergies and anaphylaxis. The active substance is in the form of a solution for injection, which is filled in a syringe that has all the devices for a single intramuscular self-injection (Fig. 3). Adrenaline – in contrast to antihistamines and steroids – has an immediate and direct effect on the cardiovascular system (by constricting the blood vessels) and on the respiratory organs (by slackening the bronchial muscles). It is crucial for the correct use of the emergency kit that the patient is instructed in its use and that he or she carries it with him or her at every meal out. Parents and school personnel should also be instructed in detail on the procedure to be followed in the event of anaphylactic reactions. After injecting epinephrine, immediately consult a doctor or go to a nearby hospital.
Food allergy therapy
Elimination diet is the only effective therapy for food allergies. A correct allergological diagnosis by a specialist is often necessary to avoid nonsensical diets. Often, unfortunately, the diagnosis of food allergy is made by alternative testing methods, although none is present in a conventional medical examination. It takes good training of the affected person and their family members to implement an elimination diet in cases of true food allergy. Attention should be paid to a balanced diet with vitamins, calcium or protein substitutes. It is advantageous to consult a nutritionist (ecotrophologist). Especially in children, after a longer period of 1-3 years, it is important to clarify allergologically again whether it is necessary to continue the elimination diet.
Literature on request from the author
HAUSARZT PRAXIS 2017; 12(7): 26-28