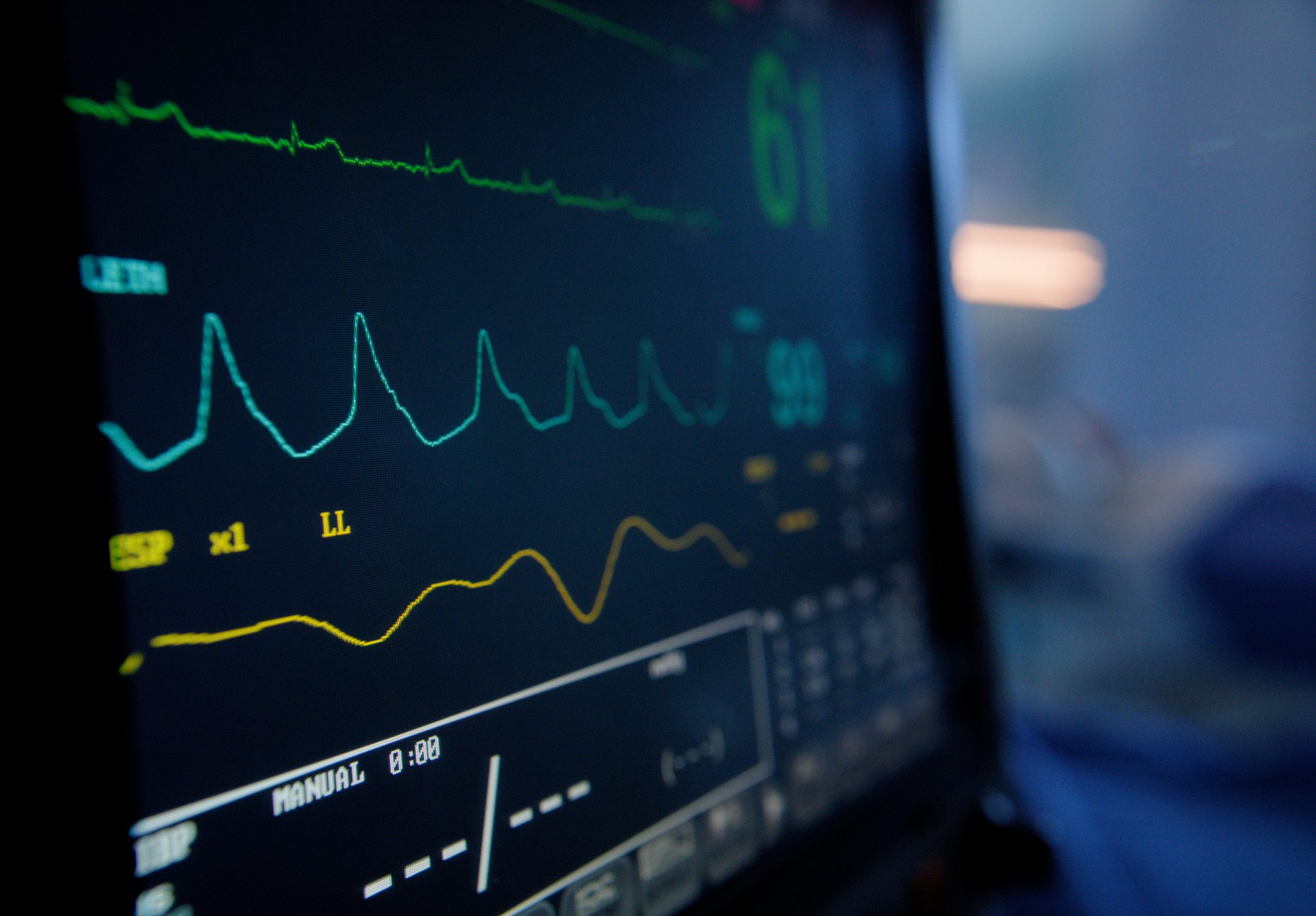
The human heart does not simply beat to the beat of a metronome-like sound, but produces a complex, multi-layered “heart music” that finds its expression in millions of micro-variations. At the center of this melody are the fine control circuits in the sinoatrial (SAN) pacemaker cells, whose coupled “clock systems” – ionic membrane clocks and intracellular calcium clocks – are continuously modulated by the autonomic nervous system. Their interaction creates a heart rhythm symphony that reflects the physiological balance and is adapted to changing requirements in real time. With increasing age, subtle disturbances occur in this system: rhythmic subtleties are lost, the symphony becomes restless and ultimately dissonant, resulting in subclinical rhythm abnormalities and an increased susceptibility to sick sinus syndrome or atrial fibrillation.
You May Also Like
- Alternative to insulin and GLP1
From the β-cell to the center: the versatile role of amylin
- Hormone balance and longevity
Ageing is not a substitution diagnosis
- Cardiovascular risk
Bad news for young men with T2D
- Case Report
6-year-old child with central retinal artery occlusion
- Low grade serous ovarian carcinoma (LGSOC)
Opening up new horizons through combination therapies
- Rare diseases
Yellow nail and Swyer-James syndrome
- Results of a systematic review and meta-analysis
Physical activity as a therapeutic approach for depression and anxiety disorders
- Underestimated risk - findings from a US cohort