Studies have shown that altered immune cell transport and pathogenic immune cells are critical factors responsible for mucosal inflammation and tissue destruction in IBD. A defective intestinal barrier and microbial dysbiosis lead to such accumulation and local activation of immune cells, resulting in a pro-inflammatory cytokine loop that overrides anti-inflammatory signals and causes chronic intestinal inflammation.
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) such as Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) are characterized by uncontrolled activation of intestinal immune cells in a genetically susceptible individual. To date, IBD immunopathology cannot be fully explained. However, individual components contributing to the progression of this chronic inflammatory process, including environmental factors, altered immune cell migration processes, as well as genetic, microbial, and immune factors, have been continuously investigated. Following contact of the body with an antigen, activation of antigen-presenting cells (APC) occurs (inflammatory vs. tolerogenic response). APCs can produce mediators such as interleukin 12, leading to activation, proliferation, and imprinting of T cells with an intestinal phenotype by upregulating specific adhesion molecules. A defective intestinal barrier and microbial dysbiosis lead to accumulation and local activation of immune cells, resulting in a pro-inflammatory cytokine loop that overrides anti-inflammatory signals and causes chronic intestinal inflammation. Genetic association studies have identified over 250 susceptibility genes for inflammatory bowel disease, revealing fundamental aspects of the molecular biology of the disease, including the role of autophagy and Th17 cell signaling and development.
In addition to genetic influences, including host genetic polymorphisms in a number of genes involved in microbial recognition and processing, environmental factors such as lifestyle, diet, and medications have also been found to affect the balance, often through their influence on the composition of the gut microbiota. It is now widely accepted that IBD is the result of a “perfect storm” of interactions between a dysbiotic microbiota, an abnormal immune system, and environmental influences in a susceptible host, explains Prof. Dr. Michael Scharl, Stv. Clinic Director Research and Teaching Clinic for Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University Hospital Zurich (Fig. 1) [1,2].
Overview of the structure and function of the gut-associated immune system.
This barrier disruption allows translocation of bacterial antigens in food and in specific regions from the intestinal lumen into the intestinal wall, where they then encounter the human body’s largest collection of immune cells – the musocal immune system, Scharl added. Antigen contact is followed by activation of antigen-presenting cells (APC) (inflammatory vs. tolerogenic response). APCs can produce mediators such as interleukin 12, leading to activation, proliferation, and differentiation of T cells with an intestinal phenotype by upregulating specific adhesion molecules. After recirculation, these T cell subsets can subsequently migrate along chemotactic gradients to the intestine as the target tissue, where they interact with molecules expressed by endothelial cells and initiate the multistep extravasation process of intestinal homing. Once at the site of action, the T cells adapt their surface molecule composition to their environment, resulting in retention in the tissue or, if not activated, recycling to the blood and lymph. If local activation of T cells by antigen presentation takes place in the intestinal tissue, they can cause massive potential damage in the inflamed intestine [1,2].
Deregulated immune responses cause IBD
In addition to an increased number of T cells, which are particularly prevalent in patients with CD, both patients with CD and patients with UC exhibit an increased number of so-called T helper cells type 17 (Th17 cells), which produce the characteristic cytokine (interleukin 17A). Furthermore, in patients with UC, there is an additional increase in type 2 immune cells (Th2 cells), which produce, for example, interleukin 5. Typical cytokines for Th2 cells are IL-4 and IL-13, which are bursts of activated proinflammatory immune cells, and these proinflammatory immune responses are counterregulated by anti-inflammatory immune responses mediated by, for example, regulatory T cells (IL-10 and TGF-beta) or Th1 cells. These cells can also be immunopathogenic and exhibit the following typical cytokines: IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha.
In particular, the imbalance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines that occurs in IBD impedes the resolution of inflammation and instead leads to disease persistence and tissue destruction. Cytokines play a central role in modulating the intestinal immune system. They are produced by lymphocytes (especially T cells of the Th1 and Th2 phenotypes), monocytes, intestinal macrophages, granulocytes, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts. They have proinflammatory functions [interleukin-1 (IL-1), tumor necrosis factor (TNF-alpha), IL-12] or anti-inflammatory functions [interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra), IL-10, transforming growth factor β (TGFβ)]. The mucosal and systemic concentrations of many pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines are increased in IBD. Genome-wide association studies have identified several susceptibility loci for IBD that contain genes encoding cytokines and proteins involved in cytokine signaling. In particular, loss-of-function mutations in genes encoding interleukin-10 (IL-10) and the IL-10 receptor have been shown to be associated with very early-onset IBD [3,4].
Changes in the gut microbiota due to therapeutics.
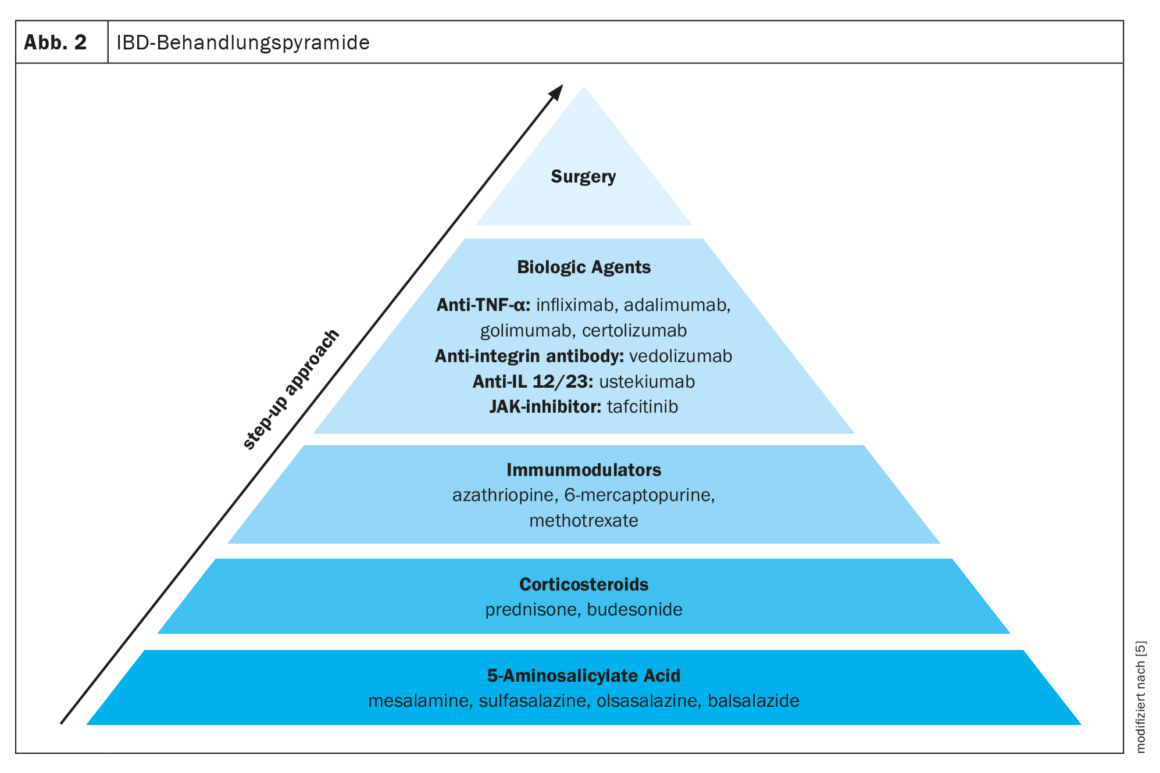
Several medications are available for the treatment of IBD. A staged treatment approach is often used, moving from less specific medications such as 5-aminosalicylic acid, to more potent medications such as corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and biologic agents, depending on the severity of IBD. In addition to drug approaches, the only other option left is surgery (Fig. 2) [5].
A detailed look at the potential mechanisms of action of currently available immunomodulatory therapies reveals that they target multiple potential targets in the mucosal immune system, including immune cells such as B cells, macrophages, and T cells, as well as targets in T cell trafficking and migration. Ustekinumab, for example, blocks differentiation into pro-inflammatory Th1 cells; ozanimod inhibits the migration of pro-inflammatory T cells from the lymph node into the draining lymphatics; Vedolizumab specifically blocks the migration of pro-inflammatory effector T cells from blood vessels into intestinal tissues; and anti-TNFs, anti-IL12/23, and JAK inhibitors block cytokine function or transcription to break the inflammatory cycle [5].
Ustekinumab: differentiation to proinflammatory Th1 effector cells.
A detailed view of T helper cell differentiation in regional lymph nodes shows activation of antigen-presenting cells producing interleukin 12. This meets naive T cells, which undergo further differentiation into so-called Th1 cells. These polarized Th1 cells have homing receptors such as α4β7 that allow them to re-invade the gut microbiota and express the interleukin-12 receptor. Ustekinumab, which targets interleukin 12, can suppress this signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting Th1 cell polarization. The human monoclonal antibody specifically binds to the p40 subunit of IL-12/23, preventing IL-12 and IL-23 from binding to their cell surface receptor complexes, thereby blocking the T helper (Th) 1 (IL-12) and Th17 (IL-23) inflammatory pathways. Ustekinumab is approved in Switzerland for both CD and UC and is administered as an intravenous infusion during induction at an induction dose of 6 mg/kg. After a single infusion, therapy is switched to maintenance therapy with subcutaneous administration, 90 mg, q12w/q8w (review 1) [3,4].
Ozanimod: migration of pro-inflammatory effector T cells from the lymph node to the draining lymphatic vessels.
After priming of T cells, polarized effector cells are generated. These cells leave the regional lymph node to reach the efferent lymphatics and bloodstream. This is an active process that generates a chemotactic gradient mediated, at least in part, by the S1P molecule. S1P binds to the S1P receptor on T cells, this pathway allows the cells to exit the lymph node. Ozanimod, an S1P receptor agonist, interferes with this endpoint of the gradient and prevents the exit of T cells from the regional lymph node. Thus, the highly polarized affected T cells can no longer return to the circulation. The S1P receptor agonist, which was previously studied in patients with multiple sclerosis, is approved in Switzerland for UC. Ozanimod is administered orally in three phases, 0.23 mg day 1-4 qd; 0.46 mg day 5-7 qd; and 0.92 mg qd thereafter (Overview 2) [3,4].
Ozanimod is considered a new option in UC patients. However, as this is a newer biologic agent in IBD treatment, more real-world data beyond clinical trials are needed to assess where the S1P receptor agonist integrates in IBD therapy, explains Prof. Markus Neurath, M.D., clinical director at Erlangen University Hospital. In particular, the real-world cardiovascular side effects and the need for an ECG, highlight the lack of experience in routine clinical practice for this drug to eventually be positioned in UC patients, Neurath added.
Vedolizumab: migration of pro-inflammatory effector T cells from blood vessels to intestinal tissue.
Vedolizumab is a humanized immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) monoclonal antibody. Its gut-selective mechanism of action distinguishes vedolizumab from existing biologics available for the treatment of IBD, which rely on systemic immunosuppression. Immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) antibody specifically blocks α4β7-integrin on the surface of the subpopulation of activated lymphocytes streaming in the bloodstream that are predisposed to homing into the gastrointestinal tract. This blockade disrupts an essential pathophysiological mechanism of IBD that usually allows lymphocyte adhesion to the endothelium of the gastrointestinal tract. Without this adhesion, lymphocytes can no longer migrate from the bloodstream into the inflamed gastrointestine, causing the localized inflammation to subside and setting the stage for long-term disease control. In this context, vedolizumab does not interrupt the homing mechanism of lymphocyte populations to other tissues, such as the central nervous system (CNS), but acts as a drug selectively targeting the intestinal wall via non-systemic immunosuppression. Immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) antibody is approved for CD and UC and is given intravenously (300 mg week 0,2,6; then 300 mg q8w) or subcutaneously (300 mg week 0,2; then 108 mg q2w) (review 3) [3,4,6].
Pleiotropic pro-inflammatory effects of TNF.
TNF is a critical mediator in the control of inflammatory processes in the gut and has been used in routine clinical practice for more than 20 years. TNF and its receptors are critically involved in the pathogenesis of IBD. For example, elevated levels of the soluble form of TNFR1 and TNFR2 were detected in both CD and UC patients, and their expression correlated with disease activity.
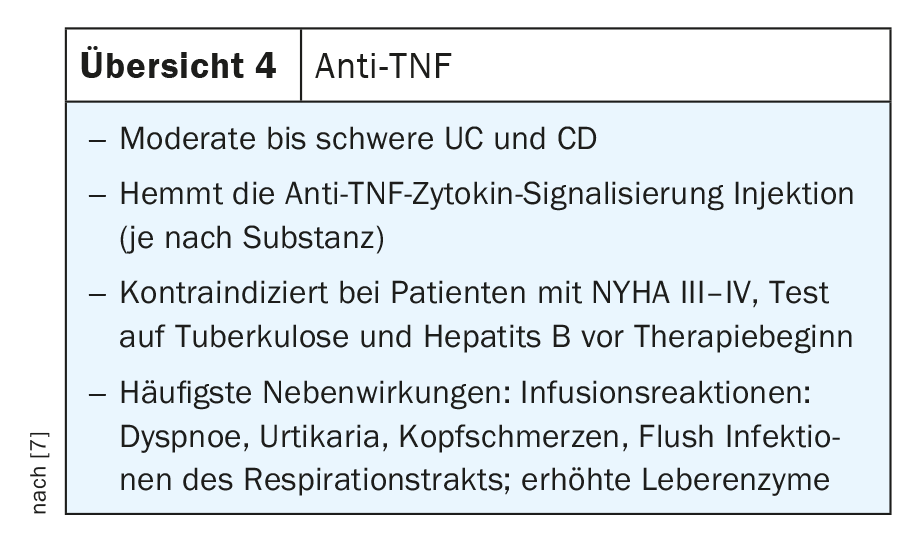
Anti-TNF antibodies block both the transmembrane precursor form (mTNF) and the soluble form (sTNF), thereby reducing the pro-inflammatory milieu in the gut by blocking the interaction between TNF and the TNF receptor, thereby blocking various pro-inflammatory types of immune cells. In addition, TNF causes epithelial cell death. Accordingly, anti-TNF antibodies have multiple mechanisms of action that can be used in clinical practice in IBD patients with both CD and UC. Proven anti-TNF antibodies for routine clinical use include infliximab, adalimumab, golimumab, and certoliizumab pegol, each with different applications. Some of them are available for intravenous therapy, a few are available for both subcutaneous and intravenous therapy, and others are available for subcutaneous administration only (Review 4) [7].
According to Neurath, the various anti-TNF antibodies have proven themselves in clinical practice and are still used selectively today. Whether intravenous or subcutaneous depends somewhat on the clinical setting. If clinical activity is high or if the patient is hospitalized, intravenous administration is certainly a good way to administer anti-TNF antibodies, especially in patients with very high activity who lose a lot of antibodies in the stool. Determining valley level measurements or checking antibody status is not mandatory, Neurath adds. This is usually done only in patients with a lack of response or secondary loss of efficacy, or in patients who fail to achieve the desired clinical primary response. In this case, Neurath added, there are several options: either switch to another agent or add an immunosuppressant such as azathioprine to suppress B-cell responses and anti-drug antibodies. The SONIC trial has already shown that combination therapy, such as azathioprine plus infliximab, is superior to monotherapy with only one of the two. However, combination therapy should depend on clinical activity. Alternatively, the patient may be monitored clinically, for example, with ultrasound scans to protect CRP levels and clinical activities to determine if the patient is in clinical remission. If problems occur, therapy can then either be intensified, e.g. by shortening the infusion interval and increasing the dose of the active agent, or switched to a different class of biologic agents.
Activity of pro-inflammatory Th17 effector cells.
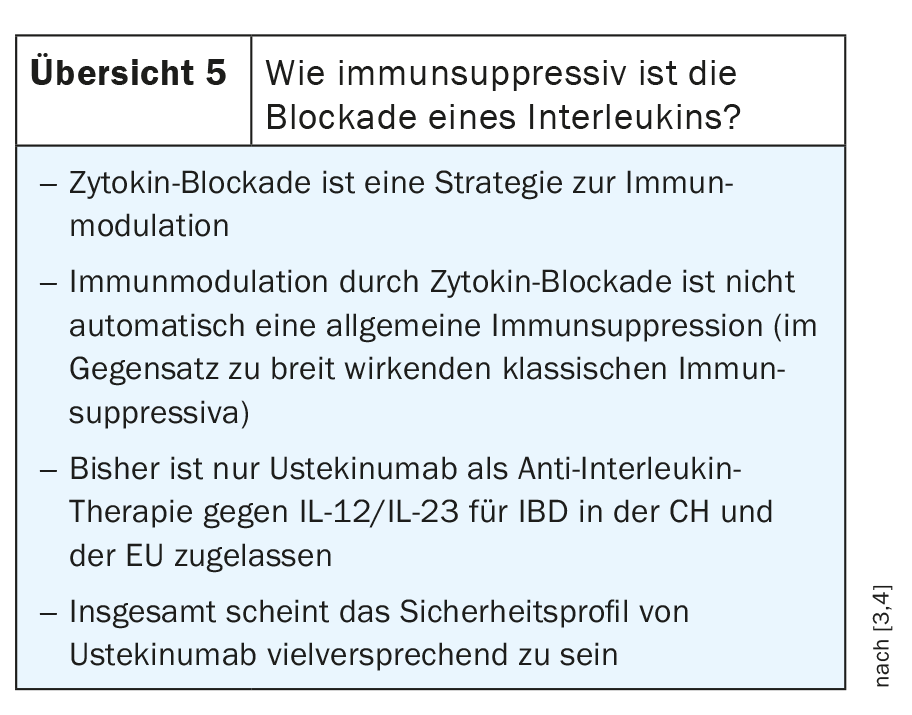
Ustekinumab is an antibody that blocks not only IL 12, but also interleukin 23. IL-23 leads to activation and maintenance of effector functions of proinflammatory Th17 cells in intestinal tissue. Ustekinumab reduces the activity of pro-inflammatory Th17 cells in intestinal tissue by blocking the Il-23/Il-23R interaction. Based on these findings, efforts are underway to develop selective antagonists against interleukin 23. These are not intended to target the P40 subunit, as is the case with ustekinumab, but rather the P19 subunit, which is unique to interleukin 23 and not found in interleukin 12. Some active substances for this purpose are already in clinical trials and will sooner or later be used in clinical practice, for example risankizumab, mirikizumab, guselkumab and brazikumab. In addition, some preliminary data suggest that P19 blockers may also be effective when P40 blockers have not previously worked (review 5) [3,4].
Cytokine signal transduction via JAK/STAT signal transduction pathways.
The Janus kinase signaling pathway and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) plays an important role in the transmission of signals from cell membrane receptors to the nucleus. Many pro-inflammatory cytokines induce transcription of effector genes in the target cell by activating specific JAK/STAT signaling pathways. The human JAK family consists of four JAKs: JAK1, JAK2, JAK3 and TYK2. Tofacitinib, an inhibitor that primarily targets JAK 1 and JAK 3, and to a lesser extent JAK 2, reduces transcription of proinflammatory signaling and effector genes by blocking JAK kinase activity. Tofacitinib is a small molecule that acts on multiple cytokines simultaneously and is available orally. However, the inhibitor has so far only been approved for UC but not for CD (Review 6) [8–10].
Because of its immunomodulatory activity and risk for cardiovascular and thromboembolic events, restrictions on use have been placed on tofacitinib since its approval, making it not a first-line agent, Neurath said. In particular, elderly patients with cardiovascular disease and potentially increased risk of thromboembolic events should be carefully tested before initiating therapy.
In Switzerland, only tofacitinib is currently available for JAK inhibition. However, due to the diverse range of studies, JAK inhibitors are increasingly being approved or are in clinical trials, so that sooner or later a whole range of JAK inhibitors will be available for clinical practice. Here, minute changes in the affinity of the molecules will make a big clinical difference. According to Neurath, there could be relevant differences between the various JAK-1 inhibitors, for example, but this remains to be investigated. The pathogenesis makes it clear that these agents interfere with the activation of immune cells. It will be interesting to compare the efficacy, but more importantly, the safety profile, Neurath added. This is because safety in particular plays a decisive role for clinical routines but also for patients.
Future options and combination therapies in IBD.
According to Neurath, the first data from a combination study with P19 blockers plus anti-TNF antibodies are available and additional studies are ongoing [11]. Essentially, combination therapy was used here to induce remission, so it is not a lifelong combination therapy. However, this could be an option for difficult-to-treat patients. Vedolizimab, in particular, appears to be an attractive partner for combination therapies because it has a very different molecular mechanism of action compared with other agents, so it is easy to at least postulate that there could be synergies, Neurath added. In addition, it is a very safer agent that has a good safety profile, making it an ideal backbone for any combination approach. However, Neurath does not see much potential for combining JAK inhibitors with biological agents.
Take-Home-Messages
- Immunomodulatory therapies target different potential targets in the mucosal immune system.
- Ustekinumab blocks differentiation into Th1 cells (via IL-12), as well as the cytokine IL-23.
- Ozanimod inhibits the emigration of pro-inflammatory T cells from the lymph node into the draining lymphatic vessels.
- Vedolizumab specifically blocks the migration of pro-inflammatory effector T cells from blood vessels into intestinal tissue.
- Anti-TNFs, anti-IL12/23 and JAK inhibitors block cytokine function to stop inflammation.
Literature:
- Neurath MF: Targeting immune cell circuits and trafficking in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Immunol 2019; doi: 10.1038/s41590-019-0415-0.
- de Lange KM, et al.: Genome-wide association study implicates immune activation of multiple integrin genes in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Genet 2017; doi: 10.1038/ng.3760.
- Neurath MF: Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2014; doi: 10.1038/nri3661.
- Neurath MF: Current and emerging therapeutic targets for IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017; doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2016.208.
- Wu N, et al.: Inflammatory bowel disease and the gut microbiota. Proc Nutr Soc 2021; doi: 10.1017/S002966512100197X.
- Denucci CC, et al.: Integrin function in T-cell homing to lymphoid and nonlymphoid sites: getting there and staying there. Crit Rev Immunol 2009; doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v29.i2.10.
- Billmeier U, et al.: Molecular mechanism of action of anti-tumor necrosis factor antibodies in inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2016; doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i42.9300.
- Vetter M, Neurath M: Emerging oral targeted therapies in inflammatory bowel diseases: opportunities and challenges. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 2017; doi: 10.1177/1756283X17727388.
- Seif F, et al.: The role of JAK-STAT signaling pathway and its regulators in the fate of T helper cells. Cell Commun Signal 2017; doi: 10.1186/s12964-017-0177-y.
- Danese S, et al.: JAK selectivity for inflammatory bowel disease treatment: does it clinically matter? Gut 2019; doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318448.
- Feagan BG, et al.: Guselkumab plus golimumab combination therapy versus guselkumab or golimumab monotherapy in patients with ulcerative colitis (VEGA): a randomised, double-blind, controlled, phase 2, proof-of-concept trial. Published :February 01, 2023. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00427-7
HAUSARZT PRAXIS 2023: 18(6): 6–11