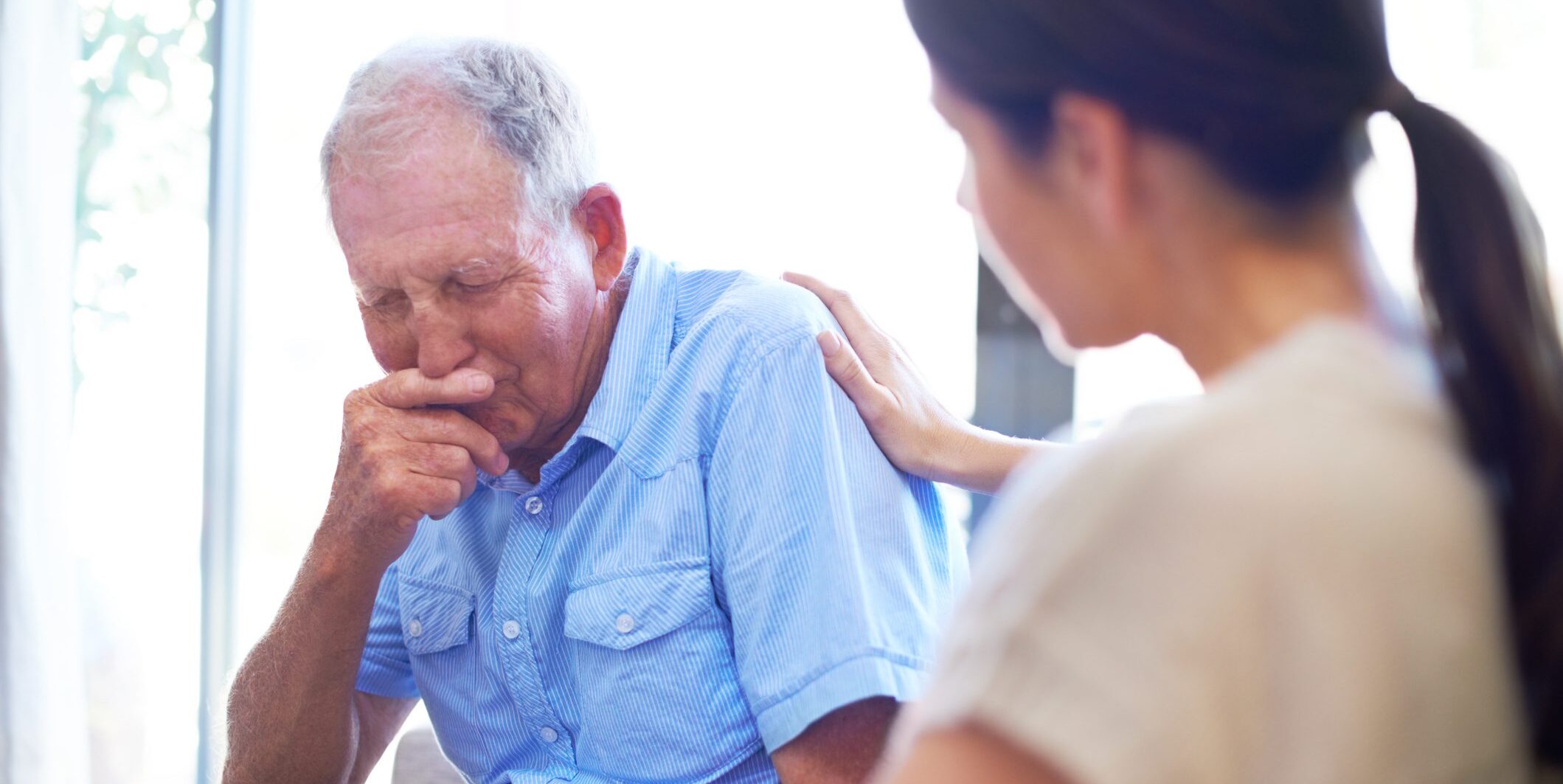
Although dementia is primarily associated with cognitive and functional decline, clinical practice is increasingly showing an increased risk of suicidal thoughts, suicide attempts and suicide death rates. Differences in the distribution of behavioral and psychological symptoms across dementia subtypes suggest that suicide risk is not uniform. The recent systematic review and meta-analysis by Nuzum et al [1] is used as an example to examine how Alzheimer’s dementia, vascular dementia, frontotemporal dementia, Lewy body dementia and mixed forms differ in the occurrence of suicidality and what consequences this has for diagnosis, prevention and treatment.
Autoren
- Tanja Schliebe
Publikation
- InFo NEUROLOGIE & PSYCHIATRIE
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- Contact eczema
Causes and prevention at work
- Pulmonary hypertension
PH and lung diseases
- Respiratory infections: viral bronchitis or bacterial pneumonia?
Old crucial question in the light of current findings
- What biomarkers reveal about "biological youth" - and what not (yet)
Epigenetic ageing
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and nutrition
Calorie optimization in ALS through digital intervention
- "Forgotten axis" between plant substances, gut and systemic health
Microbiome and phytotherapy
- HIV: updated EACS guideline
Individualized approach to sustainable prevention and care
- Evidence-based diagnostics and treatment in the medical setting