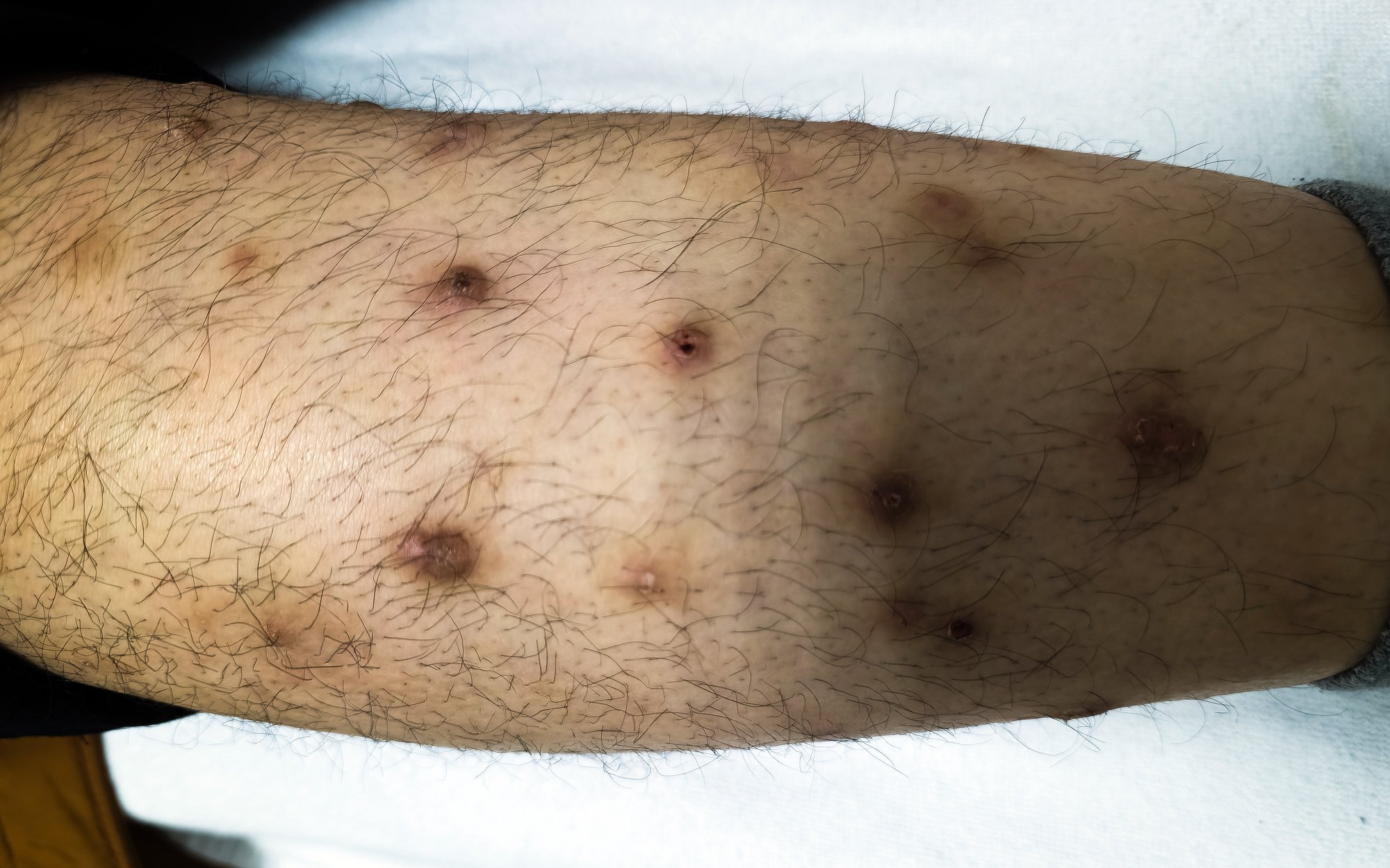
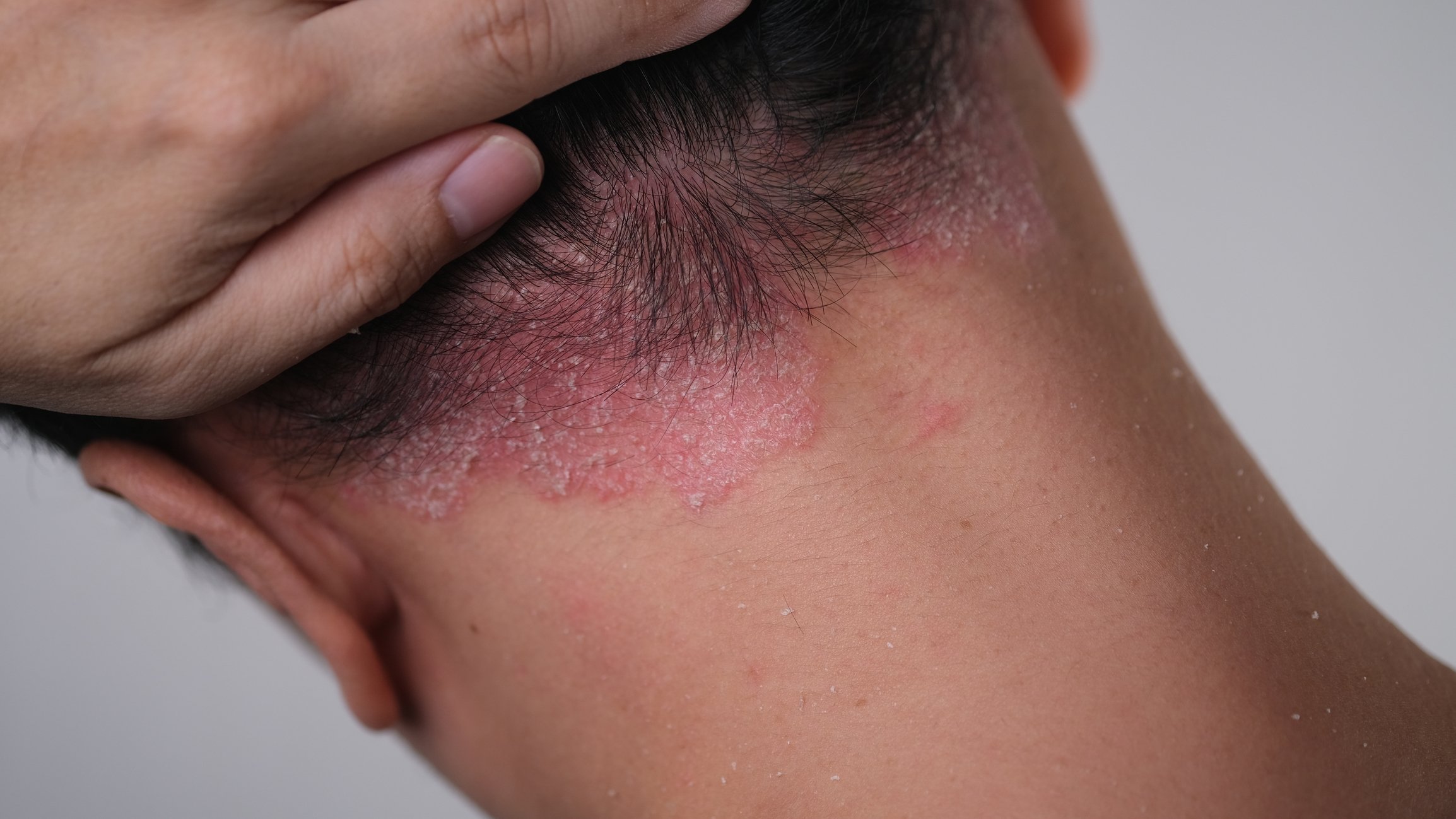
Which mediators are causally involved in peripheral and central itch sensitization in the context of prurigo and prurigo nodularis (PN) and contribute to the maintenance of pruritus is currently being analysed in numerous research projects. With dupilumab and nemolizumab, two therapeutic approaches are now available that combine anti-inflammatory and antipruritic effects and have overcome the approval hurdles for the indication PN. Interesting data from pooled analyses and from the long-term extension phase of the respective approval-relevant studies are now available.
Autoren
- Mirjam Peter, M.Sc.
Publikation
- DERMATOLOGIE PRAXIS
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- From symptom to diagnosis
Abdominal pain – Sprue
- Case Report
76-year-old patient with pustular skin rash
- Sponsored Content: Psoriasis
Dauerhafte Erscheinungsfreiheit auch bei betroffenen speziellen Hautarealen
- Antithymocyte globulin in children with T1D
Old medicine, new hope
- Ginkgo biloba
Database of preclinical and clinical studies is becoming increasingly larger
- Digital biomarkers
Continuous monitoring using digital biomarkers in MS care
- Benefits, limits and safety aspects
Phytotherapy for cardiovascular diseases
- Results of the FOREST HCM study