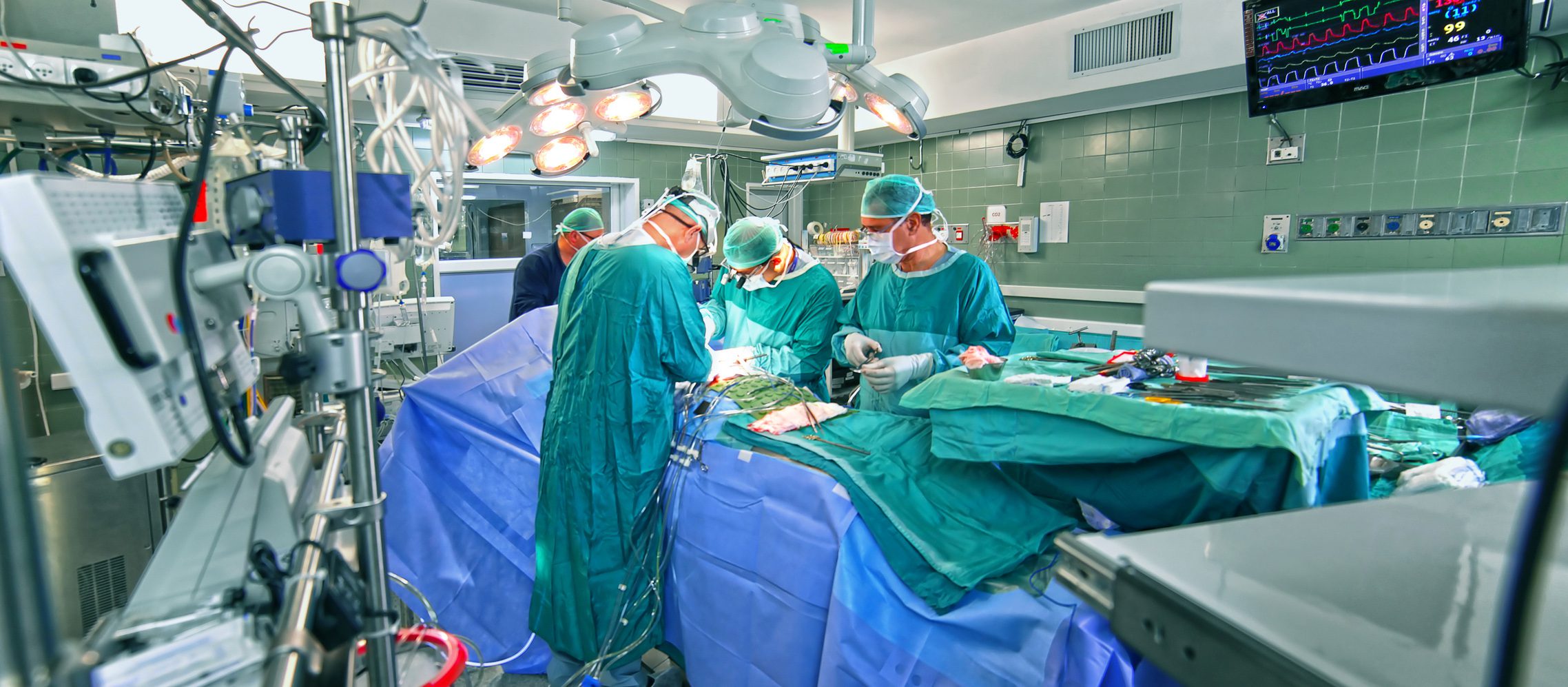
With demographic change and the rising average age of cardiology patients, post-operative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) following heart surgery is becoming increasingly important in clinical terms. If it occurs, patients often suffer from memory loss, concentration problems and slower information processing for months – symptoms that can significantly impair the rehabilitation outcome and quality of life. In their comprehensive review, Tabari et al [1] summarize the current state of research on two key sedatives: Midazolam, a long-established benzodiazepine, and dexmedetomidine (DEX), a newer, highly selective α2-adrenergic agent that shows promising neuroprotective properties.
You May Also Like
- Risk of osteoporosis in autoimmune liver diseases
Always determine bone density in PBC, PSC and AIH
- Case report: Complication after type 2 diabetes
Topical corticosteroids lead to ketoacidosis
- NSCLC
Bispecific antibodies for rare EGFR mutations
- Type 2 diabetes - glycemic control and prevention of secondary diseases
Utilizing pleiotropic cardio- and nephroprotective effects of SGLT-2-i and GLP-1-RA
- Subsyndromal anxiety disorders: Family doctor as first point of contact
Practical recommendations for diagnostics and therapy
- Patient-centered rounds in medicine
Aligning care with the patient
- Restless legs syndrome in children
Relationship between restless legs syndrome and growing pains
- Between hope and evidence gaps