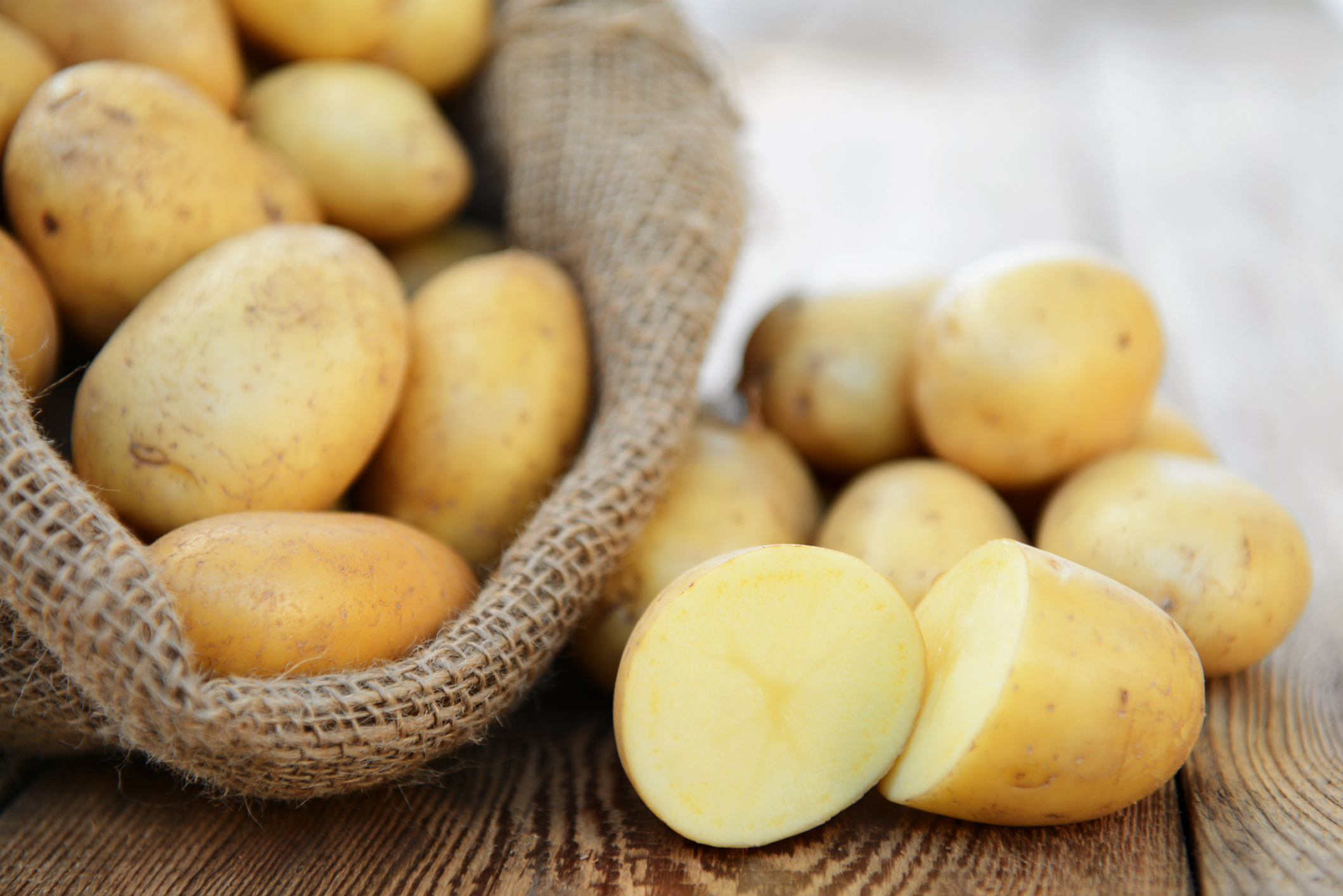
The link between potato consumption and the risk of type 2 diabetes has long been debated. Although potatoes are a staple food worldwide, rich in starch and with a high glycemic index, their role in metabolic health remains unclear. A recent study combining data from three large US cohorts and an updated meta-analysis of prospective studies provide new insights.
Autoren
- Jens Dehn
Publikation
- InFo DIABETOLOGIE & ENDOKRINOLOGIE
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- What biomarkers reveal about "biological youth" - and what not (yet)
Epigenetic ageing
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and nutrition
Calorie optimization in ALS through digital intervention
- "Forgotten axis" between plant substances, gut and systemic health
Microbiome and phytotherapy
- HIV: updated EACS guideline
Individualized approach to sustainable prevention and care
- Evidence-based diagnostics and treatment in the medical setting
Anxiety and depression disorders in adolescence
- Neuroenhancement
Can you swallow intelligence? Relevant substance classes times for healthy people
- Microbiome, inflammaging and affective/cognitive health
Gut-brain axis in old age
- Vitiligo - the level of suffering should not be underestimated