The mathematician John Forbes Nash suffered from it, the painter Vincent van Gogh probably also – schizophrenia. One of the most common mental illnesses can catapult sufferers into another world at times. With early treatment, there is the possibility of significantly improving the clinical course of this disease, which manifests itself in many ways.
Schizophrenia affects approximately 1% of the population, making it the third most common mental illness worldwide. In most cases, the first symptoms appear between puberty and the age of 35. In phases, the patient’s thinking, perception, feeling, willing and behavior are massively altered. Their experience may be influenced by delusional thoughts and hallucinations. They react and act unpredictably and uncontrollably during a schizophrenic episode. This is an extreme burden not only for the patients themselves, but also for their relatives.
The causes of the disease are not yet fully understood. However, an inherited predisposition plays a major role. About half of the children of ill parents show mental abnormalities and 12% suffer from schizophrenia themselves. However, increased vulnerability to internal and external stimuli, an imbalance of the neurotransmitters dopamine and glutamate, altered brain structures, and environmental factors can also promote the development of endogenous psychosis. The first warning signs appear months or even years before the first acute episode. Those affected suffer from listlessness, sleep or drive disturbances or a depressed mood. Increased sensitivity to light and sound may also indicate the onset of schizophrenia.
Acute and chronic phases of illness
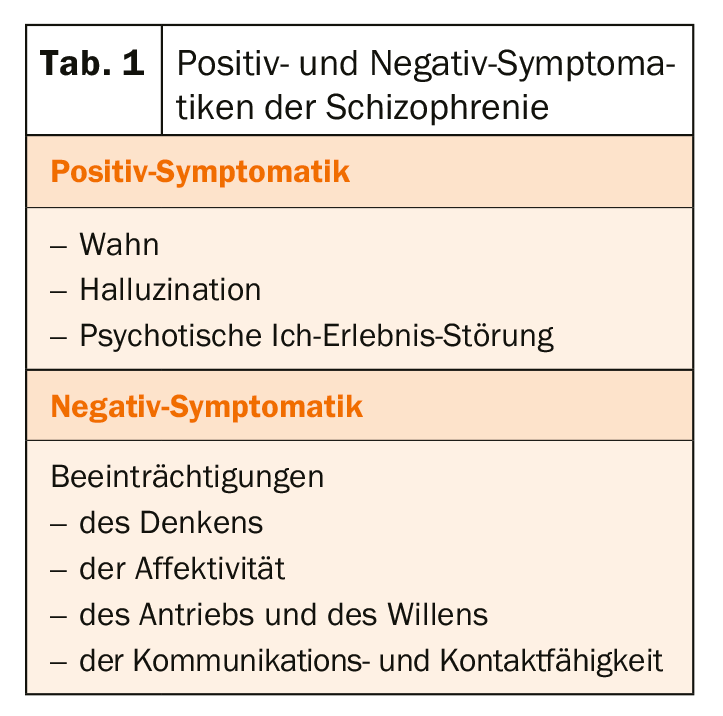
The appearance of the disease is extremely complex and varied. In acute schizophrenia, so-called “positive symptoms” are in the foreground. Patients reject any attribution of being sick at this stage. In the chronic phase, the “negative symptoms” predominate (Table 1) . Schizophrenia is divided into paranoid schizophrenia, hebephrenic schizophrenia and catatonic schizophrenia. However, a clear classification of patients is not always possible. The most common form is paranoid schizophrenia. In the acute phase, delusions and hallucinations are most common. In hebephrenic schizophrenia, thinking, emotions, and drive in particular are severely impaired. In the acute phase, the condition can be confused with bipolar disorder, as the mood can be both euphoric and depressed. For catatonic schizophrenia, mainly psychomotor disorders are typical. However, it rarely occurs nowadays.
Positively influence the course of the disease
Although not curable, schizophrenia is readily treatable today. Therapy management is based on an individually tailored combination of pharmacological measures, psychotherapy and other therapeutic procedures. Especially in the acute phase, the symptoms must be alleviated by means of effective medication. The first effective drugs were antipsychotics. They intervene in the metabolism of neurotransmitters and reduce states of tension and anxiety, delusions and hallucinations. Atypical neuroleptics such as risperidone, clozapine, olanzapine, amisulpride, quetiapine, ziprasidone or aripiprazole are a further development of the classic neuroleptics, have a better effect with fewer side effects. Patients who are depressed at the same time are often prescribed an additional antidepressant. They can positively influence mood, drive and performance. Since many patients suffer from severe anxiety during an acute episode, the short-term use of sedatives may be useful.
Further reading:
- www.neurologen-und-psychiater-im-netz.org/psychiatrie-psychosomatik-psychotherapie/stoerungen-erkrankungen/schizophrenie-und-schizophrene-psychosen/therapie/ (last accessed on 28.03.2020)
- www.gesundheitsinformation.de/schizophrenie.3300.de.html (last accessed on 28.03.2020)
- www.rki.de/DE/Content/Gesundheitsmonitoring/Gesundheitsberichterstattung/GBEDownloadsT/Schizophrenie.pdf?__blob=publicationFile (last accessed on 28.03.2020)
- www.psychosoziale-gesundheit.net/psychiatrie/schizophrenie.html (last accessed on 28.03.2020)
- www.gesundheitsforschung-bmbf.de/de/schizophrenie-wissenschaftler-entratseln-muster-im-gehirn-mit-neuroimaging-erstmals-3058.php (last accessed on 28.03.2020)
InFo NEUROLOGY & PSYCHIATRY 2020; 18(3): 24.