The human heart does not simply beat to the beat of a metronome-like sound, but produces a complex, multi-layered “heart music” that finds its expression in millions of micro-variations. At the center of this melody are the fine control circuits in the sinoatrial (SAN) pacemaker cells, whose coupled “clock systems” – ionic membrane clocks and intracellular calcium clocks – are continuously modulated by the autonomic nervous system. Their interaction creates a heart rhythm symphony that reflects the physiological balance and is adapted to changing requirements in real time. With increasing age, subtle disturbances occur in this system: rhythmic subtleties are lost, the symphony becomes restless and ultimately dissonant, resulting in subclinical rhythm abnormalities and an increased susceptibility to sick sinus syndrome or atrial fibrillation.
You May Also Like
- Neuroenhancement
Can you swallow intelligence? Relevant substance classes times for healthy people
- Microbiome, inflammaging and affective/cognitive health
Gut-brain axis in old age
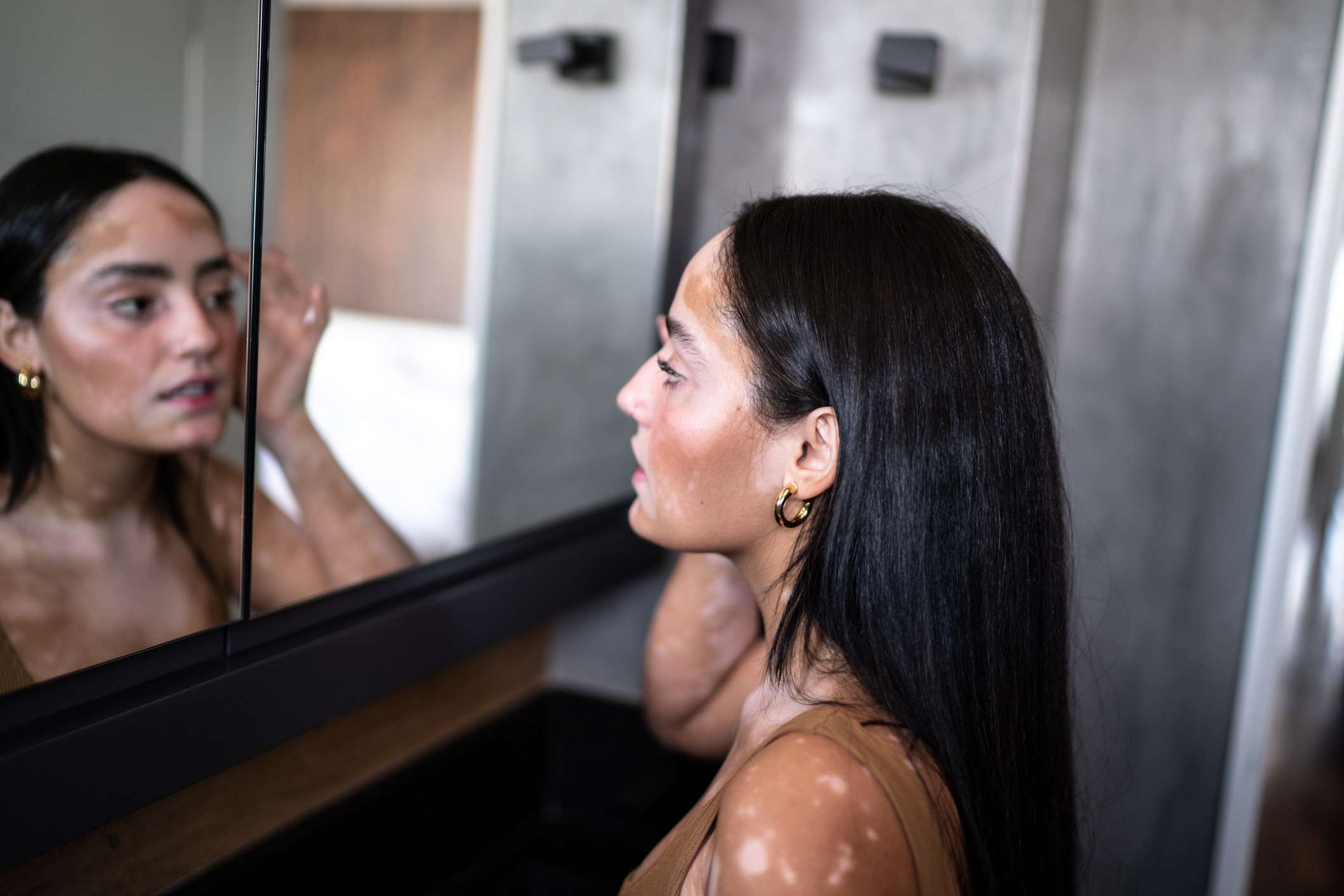
- Vitiligo - the level of suffering should not be underestimated
A lot can be achieved therapeutically nowadays
- Patient-centered rounds in medicine
Aligning care with the patient
- Adrenogenital syndrome
Clinical care from birth to adulthood
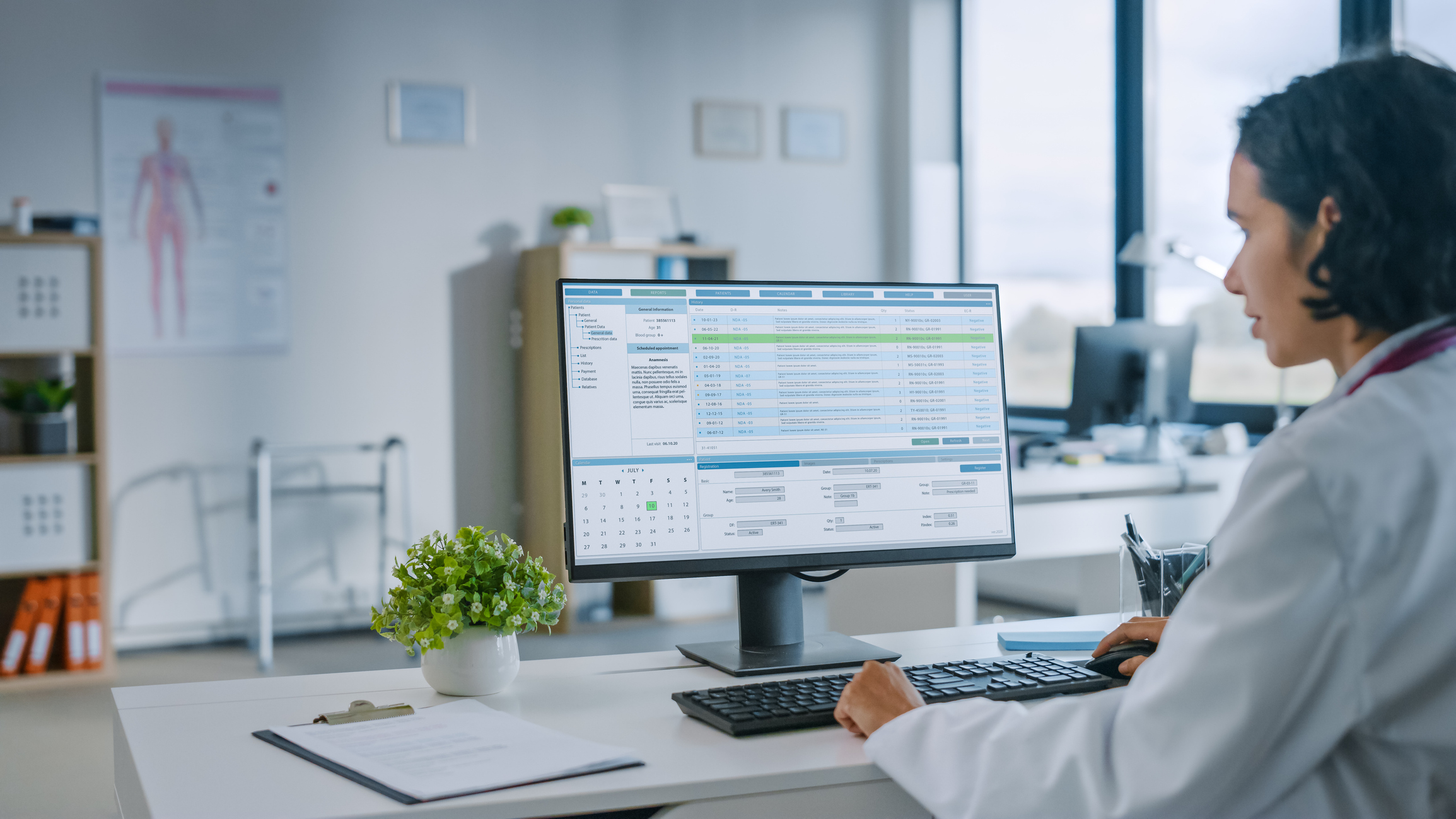
- Communication between hospitals and outpatient care
How does a digital clinical information system prove itself in everyday practice?
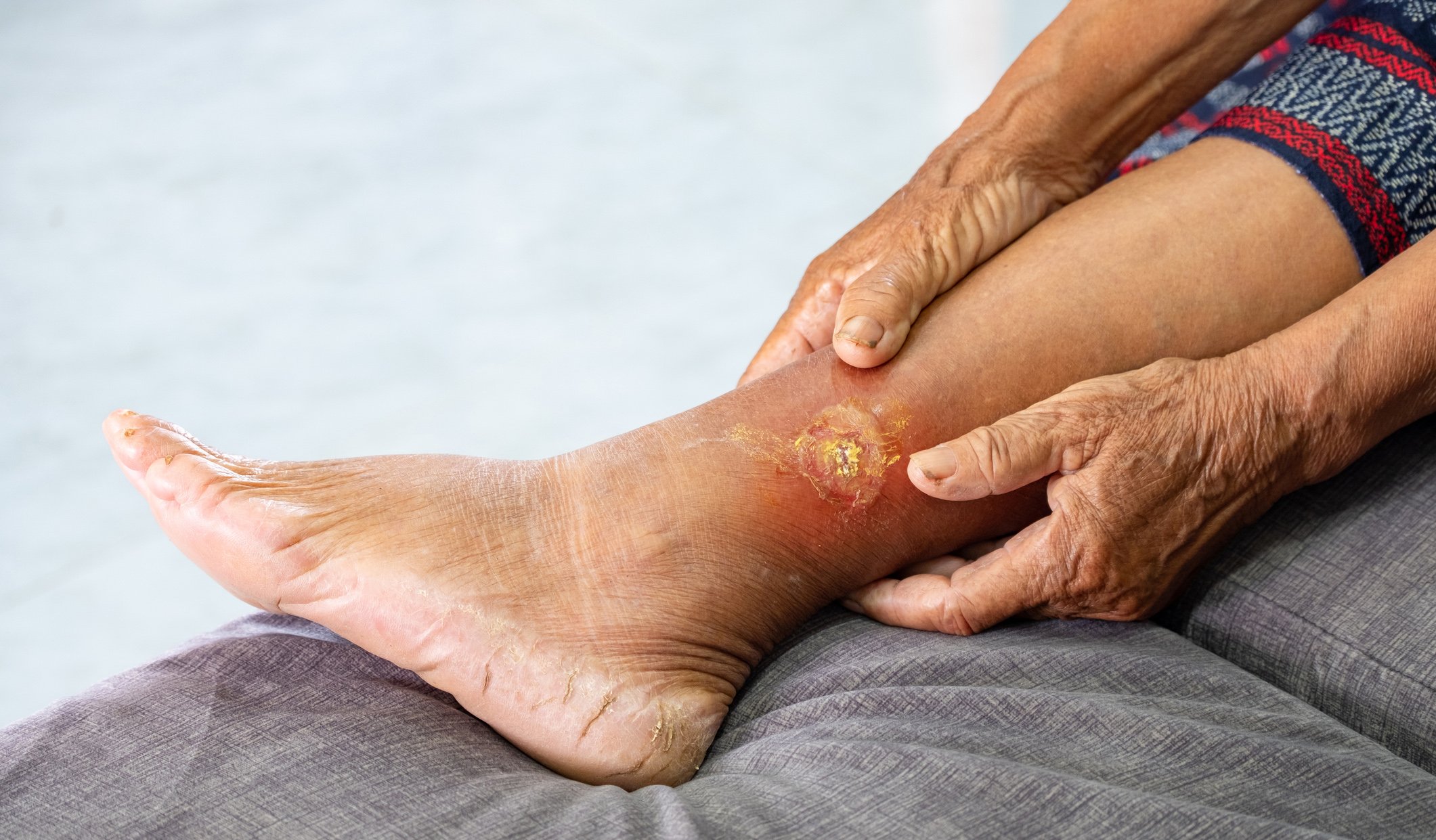
- Chronic and hard-to-heal wounds
Benefit from the advantages of outpatient negative pressure wound therapy
- Acute myeloid leukemia