Venous thromboembolism (VTE), consisting of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), is the third most common cause of cardiovascular mortality worldwide after myocardial infarction and stroke. Despite continuous progress in anticoagulation, a specific preventive strategy against VTE that goes beyond anticoagulation is still lacking. In recent years, it has been shown that arterial and venous thromboembolism share more common risk factors than previously thought, including dyslipidemia and inflammatory processes.
Autoren
- Tanja Schliebe
Publikation
- CARDIOVASC
Related Topics
You May Also Like
- From biomarkers to gene therapies
Getting to know ataxias
- Evidence-based therapy for psoriasis in difficult locations
IL-23 inhibition in scalp psoriasis: what’s new?
- Obesity in the family practice
Aim for realistic goals and avoid apportioning blame
- Evidence, pathophysiology and management in the light of current data
Heart failure with improved ejection fraction (HFimpEF)
- Early rheumatoid arthritis
C1M has potential as a biomarker
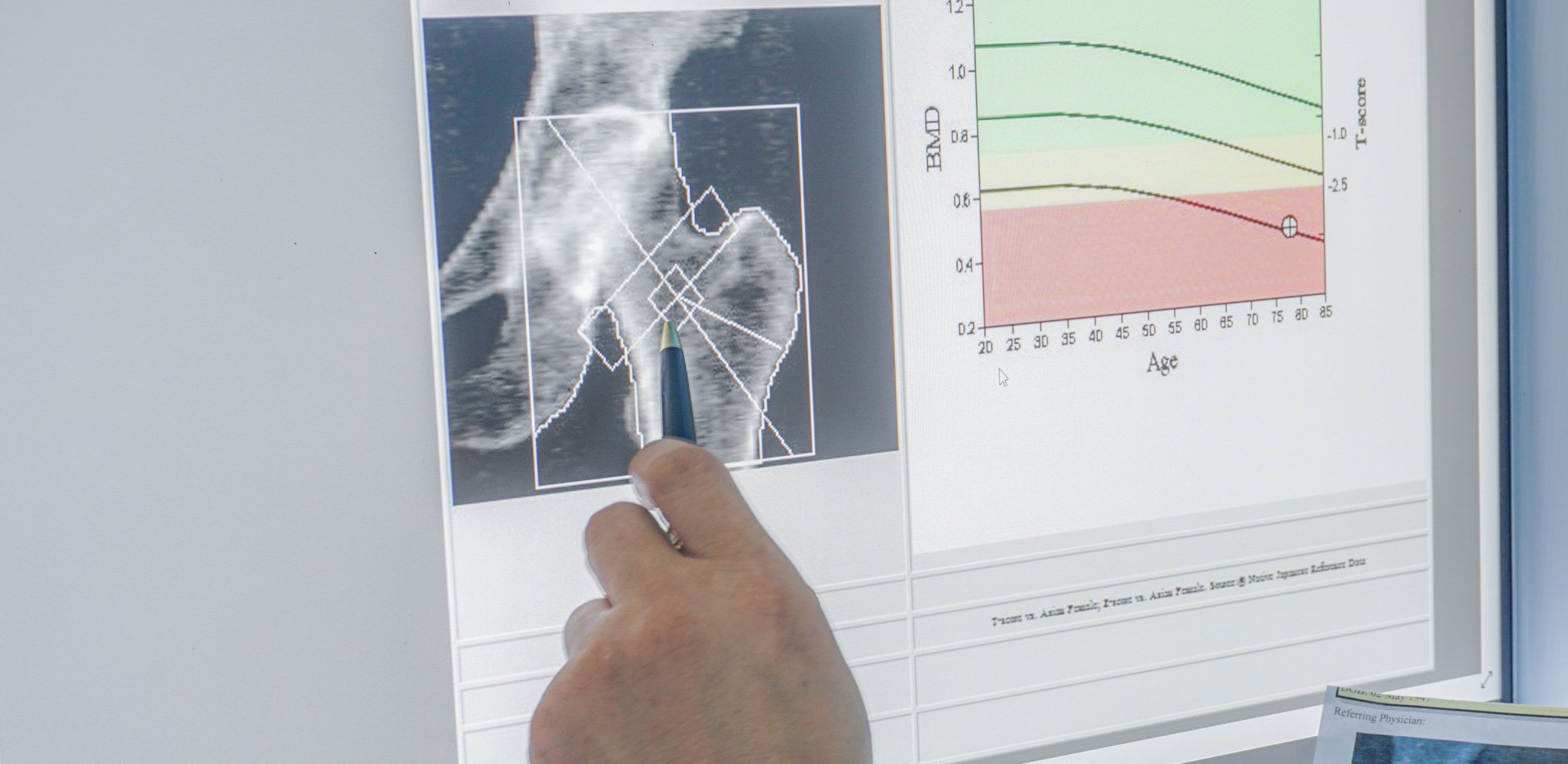
- Osteoporosis
Risk-stratified therapy with osteoanabolic agents improves outcomes
- "Swiss Health Care Atlas"
New indicator: medication for weight regulation
- AI in neurology